|
Boko Alphabet
Boko (or bookoo) is a Latin-script alphabet used to write the Hausa language. The first boko alphabet was devised by Europeans in the early 19th century, and developed in the early 20th century by the British and French colonial authorities. It was made the official Hausa alphabet in 1930. Since the 1950s boko has been the main alphabet for Hausa. Arabic script (''Hausa language#Ajami (Arabic), ajami'') is now only used in Islamic schools and for Islamic literature. Since the 1980s, Nigerian boko has been based on the Pan-Nigerian alphabet. The word ''boko'' also refers to non-Islamic (usually western) education ('yan boko = "modern school") or secularism. The word is often described as being a borrowing from English ''book''. However, in 2013, leading Hausa expert Paul Newman (linguist), Paul Newman published "The Etymology of Hausa Boko", in which he presents the view that boko is in fact a native word meaning "sham, fraud", a reference to "Western learning and writing" being see ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin-script Alphabet
A Latin-script alphabet (Latin alphabet or Roman alphabet) is an alphabet that uses Letter (alphabet), letters of the Latin script. The 21-letter archaic Latin alphabet and the 23-letter classical Latin alphabet belong to the oldest of this group. The 26-letter modern Latin alphabet is the newest of this group. Encoding The 26-letter ISO basic Latin alphabet (adopted from the earlier ASCII) contains the 26 letters of the English alphabet. To handle the many other alphabets also derived from the classical Latin one, ISO and other telecommunications groups "extended" the ISO basic Latin multiple times in the late 20th century. More recent international standards (e.g. Unicode) include those that achieved ISO adoption. Key types of differences Apart from alphabets for modern spoken languages, there exist phonetic alphabets and spelling alphabets in use derived from Latin script letters. Historical languages may also have used (or are now studied using) alphabets that are deri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
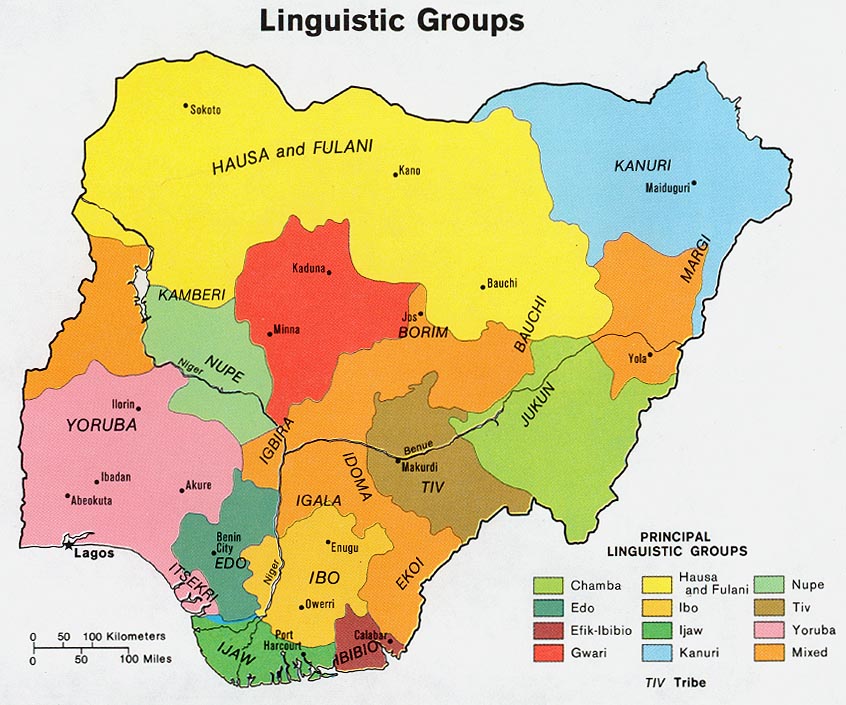
Hausa Language
Hausa (; / ; Hausa Ajami, Ajami: ) is a Chadic language spoken primarily by the Hausa people in the northern parts of Nigeria, Ghana, Cameroon, Benin and Togo, and the southern parts of Niger, and Chad, with significant minorities in Ivory Coast. A small number of speakers also exist in Sudan. Hausa is a member of the Afroasiatic language family and is the most widely spoken language within the Chadic branch of that family. Despite originating from a non-tonal language family, Hausa utilizes differences in pitch to distinguish words and grammar. ''Ethnologue'' estimated that it was spoken as a first language by some 58 million people and as a second language by another 36 million, bringing the total number of Hausa speakers to an estimated 94 million. In Nigeria, the Hausa film industry is known as Kannywood. Classification Hausa belongs to the West Chadic languages subgroup of the Chadic languages group, which in turn is part of the Afroasiatic languages, Afro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pan-Nigerian Alphabet
The Pan-Nigerian alphabet is a set of 33 Latin letters standardised by the National Language Centre of Nigeria in the 1980s. It is intended to be sufficient to write all the languages of Nigeria without using digraphs. History Several hundred different languages are spoken in Nigeria. The different Latin alphabets made it impractical to create Nigerian typewriters. In the 1980s the National Language Centre (NLC) undertook to develop a single alphabet suitable for writing all the languages of the country, and replacing use of Arabic script, taking as its starting point a model proposed by linguist Kay Williamson in 1981. A typeface was developed in 1985–1986 by Edward Oguejofor and Victor Manfredi, in co-operation with the NLC, with technical assistance from Hermann Zapf. Characters The acute ( ´ ), grave ( ` ) and circumflex ( ˆ ) accents are also used to mark High, Low, and Falling tone respectively. Mid tone (in languages which contrast High, Mid, and Low) is left ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secularism
Secularism is the principle of seeking to conduct human affairs based on naturalistic considerations, uninvolved with religion. It is most commonly thought of as the separation of religion from civil affairs and the state and may be broadened to a similar position seeking to remove or to minimize the role of religion in any public sphere. Secularism may encapsulate anti-clericalism, atheism, naturalism, non-sectarianism, neutrality on topics of religion, or antireligion. Secularism is not necessarily antithetical to religion, but may be compatible with it. As a philosophy, secularism seeks to interpret life based on principles derived solely from the material world, without recourse to religion. It shifts the focus from religion towards "temporal" and material concerns. There are distinct traditions of secularism like the French, Turkish, American and Indian models. These differ greatly, from the American emphasis on avoiding an established religion and the freedom of bel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Christian Science Monitor
''The Christian Science Monitor'' (''CSM''), commonly known as ''The Monitor'', is a nonprofit news organization that publishes daily articles both in Electronic publishing, electronic format and a weekly print edition. It was founded in 1908 as a daily newspaper by Mary Baker Eddy, founder of the new religious movement Christian Science, Church of Christ, Scientist. Since its founding, the newspaper has been based in Boston. Over its existence, seven ''Monitor'' journalists have been awarded the Pulitzer Prize, including Edmund Stevens (1950), John Hughes (editor), John Hughes (1968), Howard James (1968), Robert Cahn (1969), Richard Strout (1978), David S. Rohde (1996), and Clay Bennett (cartoonist), Clay Bennett (2002)."Pulitzer Prizes" at ''The Christian Science Monitor'' official website H ...
|
Paul Newman (linguist)
Paul Newman (born 1937) is an American linguist active in the study of African languages. He writes on the Hausa language of Nigeria and on the Chadic language family. He wrote the ''Modern Hausa–English Dictionary'' (1977), co-authored with his wife, Roxana Ma Newman, and ''The Hausa Language: An Encyclopedic Reference Grammar'' (2000). He is the founder of the ''Journal of African Languages and Linguistics'', a journal in the field of African-language studies. He has taught at Yale University, the University of Leiden, and the Centre for the Study of Nigerian Languages at Bayero University in Kano, Nigeria. He is currently Distinguished Professor in the Department of Linguistics at Indiana University after serving two terms as chairman of the department. Newman is a strong advocate of the theories of his mentor, Joseph Greenberg, and has published a work in defense of Greenberg's classification of African languages entitled ''On Being Right''. Newman is also interested in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Learning
Western education is the form of education that mainly originated in or is characteristic of the Western world. History Ancient era Medieval era Modern era Pre-contemporary history outside of the West The introduction of Western education into the rest of the world occurred to a large degree through imperialism. This affected the way that Western education was absorbed and influenced by the world. Africa Asia East Asia In China, as reformers sought to grapple with the foreign domination of the late 19th century, they came to a conclusion of re-ordering Chinese society through a process of self-strengthening, which included taking ideas from the West. Even before the Edo period, Japan had established significant contact with Western knowledge through Rangaku (Dutch Learning). While maintaining its isolationist sakoku policy, Japan permitted limited trade with the Dutch East India Company at Dejima, Nagasaki. This unique arrangement allowed Japanese sch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quranic
The Quran, also Romanization, romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a Waḥy, revelation directly from God in Islam, God (''Allah, Allāh''). It is organized in 114 chapters (, ) which consist of individual verses ('). Besides its religious significance, it is widely regarded as the finest work in Arabic literature, and has significantly influenced the Arabic, Arabic language. It is the object of a modern field of academic research known as Quranic studies. Muslims believe the Quran was orally revealed by God to the final Islamic Prophets and messengers in Islam, prophet Muhammad in Islam, Muhammad through the Angel#Islam, angel Gabriel#Islam, Gabriel incrementally over a period of some 23 years, beginning on the Night of Power, Laylat al-Qadr, when Muhammad was 40, and concluding in 632, the year of his death. Muslims regard the Quran as Muhammad's most important Islamic view of miracles, miracle, a proof of his prophet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sh (digraph)
The digraph/letter Sh is a digraph (orthography), digraph of the Latin alphabet, which is written as a combination of S and H. European languages Albanian In Albanian language, Albanian, sh represents . It is considered a distinct letter, named shë, and placed between S and T in the Albanian alphabet. Breton In Breton language, Breton, sh represents . It is not considered a distinct letter and it is a variety of zh (e. g. ("older"). It is not considered as a digraph in compound words, such as ''kroashent'' ("roundabout": ''kroaz'' ("cross") + ''hent'' ("way", "ford"). English In English language, English, usually represents . The main exception is in compound words, where the and are not a digraph, but pronounced separately, e.g. ''hogshead'' is ''hogs-head'' , not ''*hog-shead'' . ''Sh'' is not considered a distinct letter for collation purposes. American Literary braille includes a single-cell contraction for the digraph with the dot pattern (1 4 6). In isol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ts (digraph)
This is a list of digraphs used in various Latin alphabets. In the list, letters with diacritics are arranged in alphabetical order according to their base, e.g. is alphabetised with , not at the end of the alphabet, as it would be in Danish, Norwegian and Swedish. Substantially-modified letters, such as (a variant of ) and (based on ), are placed at the end. Capitalisation only involves the first letter ( becomes ) unless otherwise stated ( becomes in Dutch, and digraphs marking eclipsis in Irish, are capitalised on the second letter, i.e. becomes ). Apostrophe Source: (capital ) is used in Bari for . (capital ) is used in Bari for . is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark or ''yin'' tone . It is also often written as . is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark . is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark . is used in the Wu MiniDict Romanisation for dark . (capital ) is used in Bari and Hausa (in Nigeria) for , but in Nige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apostrophe
The apostrophe (, ) is a punctuation mark, and sometimes a diacritical mark, in languages that use the Latin alphabet and some other alphabets. In English, the apostrophe is used for two basic purposes: * The marking of the omission of one or more letters, e.g. the contraction (grammar), contraction of "do not" to "don't" * The marking of Possessive, possessive case of nouns (as in "the eagle's feathers", "in one month's time", "the twins' coats") It is also used in a few exceptional cases for the #Use in forming some plurals, marking of plurals, e.g. "p's and q's" or Oakland A's. The same mark is used as a single quotation mark. It is also substituted informally for other marks for example instead of the prime symbol to indicate the units of foot (unit), foot or minutes of arc. The word ''apostrophe'' comes from the Ancient Greek language, Greek (hē apóstrophos [prosōidía], '[the accent of] turning away or elision'), through Latin language, Latin and French language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niger
Niger, officially the Republic of the Niger, is a landlocked country in West Africa. It is a unitary state Geography of Niger#Political geography, bordered by Libya to the Libya–Niger border, north-east, Chad to the Chad–Niger border, east, Nigeria to the Niger–Nigeria border, south, Benin and Burkina Faso to the Benin-Niger border, south-west, Mali to the Mali–Niger border, west, and Algeria to the Algeria–Niger border, north-west. It covers a land area of almost , making it the largest landlocked country in West Africa and the second-largest landlocked nation in Africa behind Chad. Over 80% of its land area lies in the Sahara. Its Islam in Niger, predominantly Muslim population of about million lives mostly in clusters in the south and west of the country. The capital Niamey is located in Niger's south-west corner along the namesake Niger River. Following the spread of Islam to the region, Niger was on the fringes of some states, including the Kanem–Bornu Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |