|
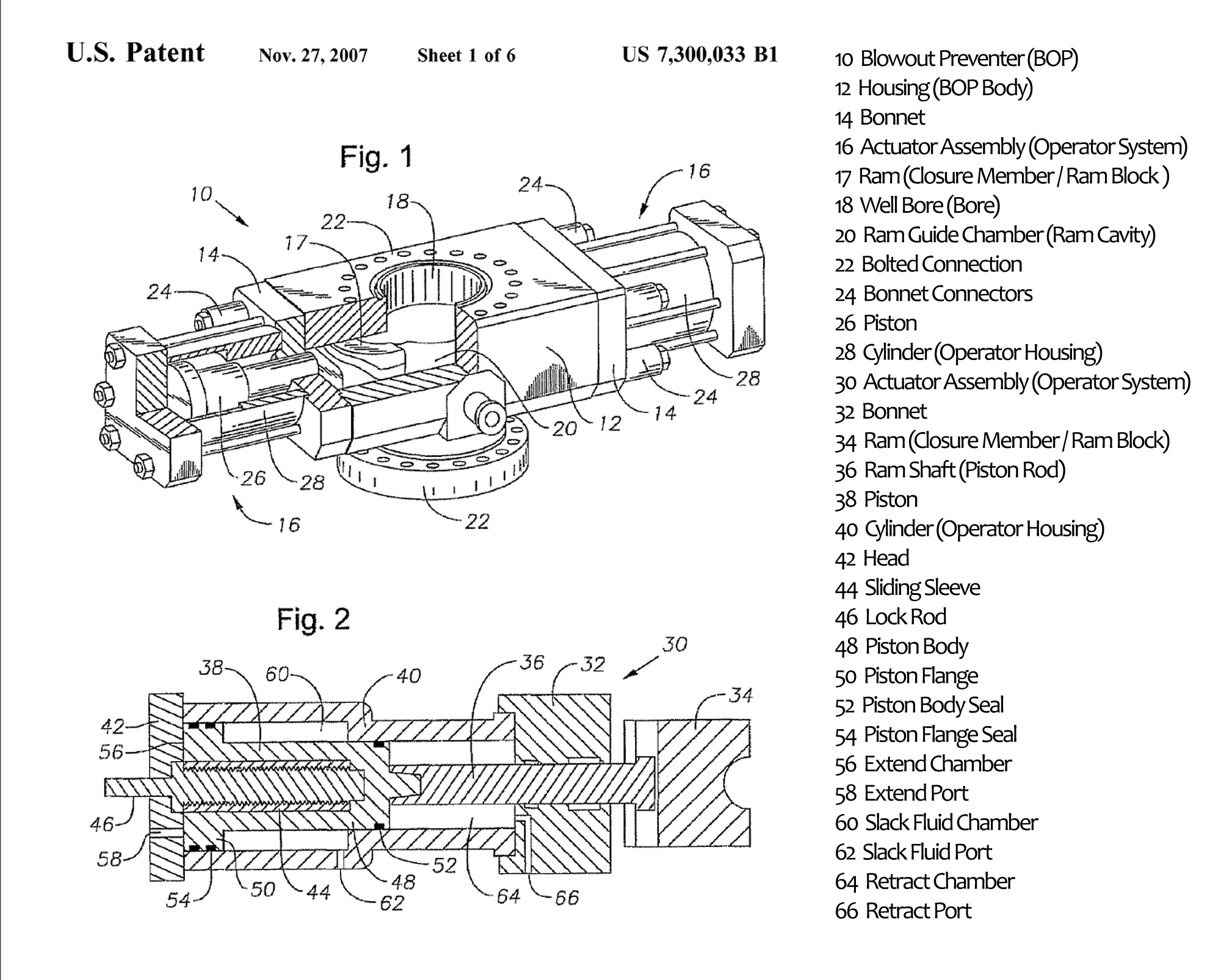
Blow Out Preventer
A blowout preventer (BOP) (pronounced B-O-P) is a specialized valve or similar mechanical device, used to seal, control and monitor oil well, oil and gas wells to prevent Blowout (well drilling), blowouts, the uncontrolled release of crude oil or natural gas from a well. They are usually installed in stacks of other valves. The earliest blowout preventers; Regan Type K Annulars were used, beginning in the 1930s to cope with extreme erratic pressures and uncontrolled flow (Blowout (well drilling)#Formation kick, formation kick) emanating from a Petroleum reservoir, well reservoir during drilling. Kicks can lead to a potentially catastrophic event known as a blowout. In addition to controlling the downhole (occurring in the drilled hole) pressure and the flow of oil and gas, blowout preventers are intended to prevent tubing (e.g. drill pipe and Casing (borehole), well casing), tools, and drilling fluid from being blown out of the wellbore (also known as bore hole, the hole lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucas Gusher
Lucas or LUCAS may refer to: People * Lucas (surname) * Lucas (given name) Arts and entertainment * Luca Family Singers, or the Lucas, a 19th-century African-American singing group * Lucas, a 1960s Swedish pop group formed by Janne Lucas Persson * ''Lucas'' (album) (2007), an album by Skeletons and the Kings of All Cities * ''Lucas'' (1986 film), an American romantic-comedy teen film * ''Lucas'' (2021 film), a Spanish thriller drama film * ''Lucas'' (novel) (2003), by Kevin Brooks Organisations * Lucas Industries, a former British manufacturer of motor industry and aerospace industry components * Lucasfilm, an American film and television production company * LucasVarity, a defunct British automotive parts manufacturer, successor to Lucas Industries Places Australia * Lucas, Victoria Mexico * Cabo San Lucas, Baja California United States * Lucas, Illinois * Lucas, Iowa * Lucas County, Iowa * Lucas, Kansas * Lucas, Kentucky * Lucas, Michigan * Lucas, Missouri * Lu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blowout Preventer
A blowout preventer (BOP) (pronounced B-O-P) is a specialized valve or similar mechanical device, used to seal, control and monitor oil well, oil and gas wells to prevent Blowout (well drilling), blowouts, the uncontrolled release of crude oil or natural gas from a well. They are usually installed in stacks of other valves. The earliest blowout preventers; Regan Type K Annulars were used, beginning in the 1930s to cope with extreme erratic pressures and uncontrolled flow (Blowout (well drilling)#Formation kick, formation kick) emanating from a Petroleum reservoir, well reservoir during drilling. Kicks can lead to a potentially catastrophic event known as a blowout. In addition to controlling the downhole (occurring in the drilled hole) pressure and the flow of oil and gas, blowout preventers are intended to prevent tubing (e.g. drill pipe and Casing (borehole), well casing), tools, and drilling fluid from being blown out of the wellbore (also known as bore hole, the hole lead ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cameron Ram-type Blowout Preventer (1922)
The Cameron ram-type blowout preventer was the first successful blowout preventer (BOP) for oil wells. It was developed by James S. Abercrombie and Harry S. Cameron in 1922. The device was issued on January 12, 1926. The blowout preventer was designated as a Mechanical Engineering Landmark in 2003. History While drilling an oil or gas well, the top of the wellbore is lined with a casing. The drill string runs through the casing. The annular (ring-shaped) region between the casing and the drill stem is filled with drilling mud which provides hydrostatic pressure to keep the formation fluid from coming up the wellbore. If the pressure of the formation fluid exceeds the hydrostatic pressure of the drilling mud, the oil or gas can blow out of the wellbore. This has caused spills of large quantities of oil and fires on drilling rigs. The blowout of the Lucas well at the Spindletop field in 1901 lasted for over nine days and spilled over of oil. James Smither Abercrombie (1891–1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drilling Rig (petroleum)
This article lists the main components of a petroleum onshore drilling rig. Offshore drilling rigs have similar elements, but are configured with a number of different drilling systems to suit drilling in the marine environment. The equipment associated with a rig is to some extent dependent on the type of rig but typically includes at least some of the items listed below. {{clear List of items # Mud tank #Shale shakers # Suction line (mud pump) #Mud pump #Motor or power source #Hose #Drawworks # Standpipe # Kelly hose # Goose-neck # Traveling block # Drill line # Crown block #Derrick # Racking Board (Sometimes referred to as the Monkey Board) #Stand (of drill pipe) # Setback (floor) #Swivel (On newer rigs this may be replaced by a top drive) #Kelly drive #Rotary table # Drill floor # Bell nipple #Blowout preventer (BOP) Annular type #Blowout preventer (BOP) Pipe ram & blind ram #Drill string #Drill bit # Casing head or Wellhead # Flow line Explanation * Bell nipple (#22) i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well Integrity
An oil well is a drillhole boring (earth), boring in Earth that is designed to bring petroleum oil hydrocarbons to the surface. Usually some natural gas is released as associated petroleum gas along with the oil. A well that is designed to produce only gas may be termed a gas well. Wells are created by drilling down into an Petroleum reservoir, oil or gas reserve and if necessary equipped with extraction devices such as pumpjacks. Creating the wells can be an expensive process, costing at least hundreds of thousands of dollars, and costing much more when in difficult-to-access locations, e.g., oil platform, offshore. The process of modern drilling for wells first started in the 19th century but was made more efficient with advances to oil drilling rigs and technology during the 20th century. Wells are frequently sold or exchanged between different oil and gas companies as an asset – in large part because during falls in the price of oil and gas, a well may be unproductive, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrostatics
Hydrostatics is the branch of fluid mechanics that studies fluids at hydrostatic equilibrium and "the pressure in a fluid or exerted by a fluid on an immersed body". The word "hydrostatics" is sometimes used to refer specifically to water and other liquids, but more often it includes both gases and liquids, whether compressible or incompressible. It encompasses the study of the conditions under which fluids are at rest in stable equilibrium. It is opposed to ''fluid dynamics'', the study of fluids in motion. Hydrostatics is fundamental to ''hydraulics'', the engineering of equipment for storing, transporting and using fluids. It is also relevant to geophysics and astrophysics (for example, in understanding plate tectonics and the anomalies of the Earth's gravitational field), to meteorology, to medicine (in the context of blood pressure), and many other fields. Hydrostatics offers physical explanations for many phenomena of everyday life, such as why atmospheric pressur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drilling Fluid
In geotechnical engineering, drilling fluid, also known as drilling mud, is used to aid the drilling of boreholes into the earth. Used while drilling oil and natural gas wells and on exploration drilling rigs, drilling fluids are also used for much simpler boreholes, such as water wells. The two main categories of drilling fluids are water-based muds (WBs), which can be dispersed and non-dispersed, and non-aqueous muds, usually called oil-based muds (OBs). Along with their formatives, these are used along with appropriate polymer and clay additives for drilling various oil and gas formations. Gaseous drilling fluids, typically utilizing air or natural gas, sometimes with the addition of foaming agents, can be used when downhole conditions permit. The main functions of liquid drilling fluids are to exert hydrostatic pressure to prevent formation fluids from entering into the well bore, and carrying out drill cuttings as well as suspending the drill cuttings while drill ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drill Pipe
Drill pipe, is hollow, thin-walled, steel or aluminium alloy pipe (material), piping that is used on drilling rig (petroleum), drilling rigs. It is hollow to allow drilling fluid to be pumped down the hole through the bit and back up the annulus (oil well), annulus. It comes in a variety of sizes, strengths, and wall thicknesses, but is typically 27 to 32 feet in length (Range 2). Longer lengths, up to 45 feet, exist (Range 3). Background Drill stems must be designed to transfer drilling torque for combined lengths that often exceed several miles down into the Earth's crust, and also must be able to resist pressure differentials between inside and outside (or vice versa), and have sufficient strength to suspend the total weight of deeper components. For deep wells this requires tempered steel tubes that are expensive, and owners spend considerable efforts to reuse them after finishing a well. A used drill stem is inspected on site, or off location. Ultrasonic testing and modifie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wellhead
A wellhead is the component at the surface of an oil or gas well that provides the structural and pressure-containing interface for the drilling and production equipment. The primary purpose of a wellhead is to provide the suspension point and pressure seals for the casing strings that run from the bottom of the hole sections to the surface pressure control equipment. While drilling the oil well, surface pressure control is provided by a blowout preventer (BOP). If the pressure is not contained during drilling operations by the column of drilling fluid, casings, wellhead, and BOP, a well blowout could occur. When the well has been drilled, it is completed to provide an interface with the reservoir rock and a tubular conduit for the well fluids. The surface pressure control is provided by a Christmas tree, which is installed on top of the wellhead, with isolation valves and choke equipment to control the flow of well fluids during production. Wellheads are typically welded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Formation Fluid
Formation fluid refers to the naturally occurring liquids and gases contained in geologic formations. Fluids introduced during the drilling process are called drilling fluids. Fluids in an oil or gas reservoir are called reservoir fluids. The fluids flowing from the wellhead of an oil or gas well are called production fluid Production fluid, or well fluid, is the fluid mixture of oil, gas and water in formation fluid that flows to the surface of an oil well from a reservoir. Its consistency and composition varies. Fluids may be described by a multitude of characte ...s. References Oilfield terminology {{geology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Well Kill
A well kill is the operation of placing a column of special fluids of the required density into a well bore in order to prevent the flow of reservoir fluids without the need for pressure control equipment at the surface. It works on the principle that the hydrostatic head of the "kill fluid" or "kill mud" will be enough to suppress the pressure of the formation fluids. Well kills may be planned in the case of advanced interventions such as workovers, or be contingency operations. The situation calling for a well kill will dictate the method taken. Not all well kills are deliberate. On occasion, the unintended accumulation of fluids, either from injection of chemicals like methanol from the surface, or from liquids produced from the reservoir, can be enough to kill the well, particularly gas wells, which are notoriously easy to kill. Well control in general is an extremely expensive and dangerous operation. Extensive training, testing, proof of competence, and experience are p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |