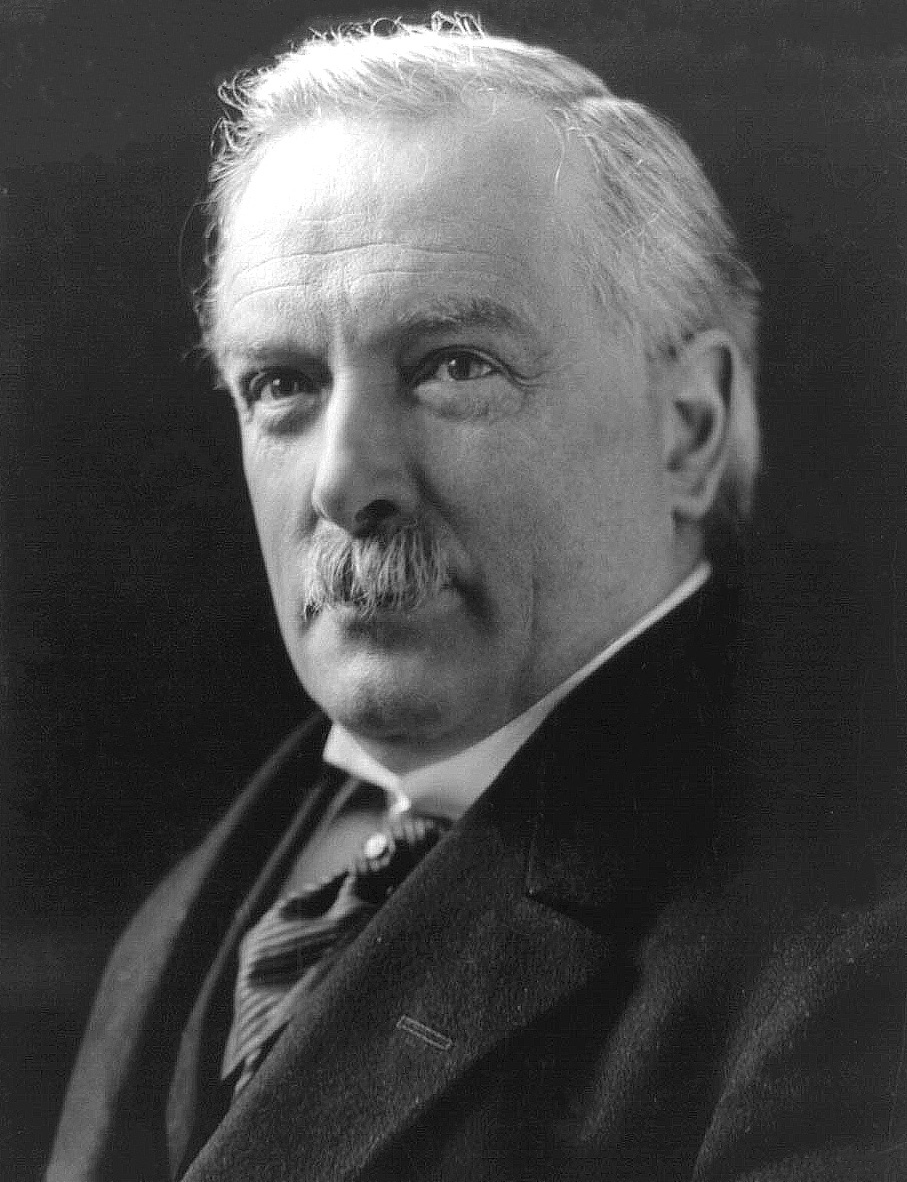|
Blind Persons Act 1920
The Blind Persons Act 1920 ( 10 & 11 Geo. 5. c. 49) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom, since repealed. It provided a pension allowance for blind persons aged between 50 and 70 (after which they became eligible for the old age pension), directed local authorities to make provision for the welfare of blind people and regulated charities in the sector. The act was passed in response to pressure from the National League of the Blind (NLB) who claimed many of their members were living in poverty. The NLB carried out a series of strikes and protests including the 5–25 April 1920 blind march. The Blind Persons Act was first debated on 26 April and received royal assent on 16 August. The pensions provisions were superseded and repealed by the Old Age Pensions Act 1936 and the remainder of the act by the National Assistance Act 1948 ( 11 & 12 Geo. 6. c. 29), it remains in force in Ireland. The act was the first disability-specific legislation to be passed anywh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10 & 11 Geo
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, Numeral (linguistics), numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest Positive number, positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit (measurement), unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In Digital electronics, digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In math ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ben Purse
Benjamin Ormond Purse (29 August 187431 March 1950) was a British trade unionist and campaigner for the rights of blind people. Purse, who was completely blind by the age of 13, was a piano tuner. He became a founder-member of the National League of the Blind (NLB) in 1894 and was elected as its first general secretary in 1897. Purse held the position for two years, during which he founded its journal the ''Blind Advocate''. Purse became president of the NLB in 1905 and held the position until 1916. He was regarded as particularly energetic in this role, successfully negotiating concessionary travel for blind people with 37 municipal authorities, attending an international conference and giving evidence to the 1907 Royal Commission on the Poor Laws. The early NLB had been a combative organisation, confronting charities that it claimed exploited blind workers, but Purse put it on more conciliatory footing, that won it support from key political figures. Purse campaigned for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equality Act 2010
The Equality Act 2010 (c. 15) is an act of Parliament of the United Kingdom passed during the Brown ministry with the primary purpose of consolidating, updating and supplementing the numerous prior Acts and Regulations, that formed the basis of anti-discrimination law in mostly England, Scotland and Wales; some sections also apply to Northern Ireland. These consisted, primarily, of the Equal Pay Act 1970, the Sex Discrimination Act 1975, the Race Relations Act 1976, the Disability Discrimination Act 1995 and three major statutory instruments protecting against discrimination in employment on grounds of sexual orientation, age, and religion or belief. The act protects people against discrimination, harassment or victimisation in employment, and as users of private and public services based on these protected characteristics: age, disability, sex, sexual orientation, marriage and civil partnership, gender reassignment, pregnancy and maternity, race, and religion or belief. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disability Discrimination Act 2005
The Disability Discrimination Act 2005 (c. 13) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. History The Disability Discrimination Act 1995 had been amended before. Service providers such as libraries, banks, shops and restaurants didn't have to adjust their policies, for example by offering documents in accessible formats, until 1999. Provisions The Act applied the Disability Discrimination Act 1995 to housing, police, local authorities. The Act puts a positive "Disability Equality Duty" in place. This legal duty requires public sector organisations (which include schools and colleges, NHS trusts, libraries, police forces, central and local government) to promote equality positively and proactively by involving people with disabilities, drawing on evidence to create action plans to achieve equality and promoting positive attitudes. All such organisations are required to develop policies and working practices which actively promote the equality of disabled people as em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disability Discrimination Act 1995
The Disability Discrimination Act 1995 (c. 50) (informally, and hereafter, the DDA) is an Act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom which has now been repealed and replaced by the Equality Act 2010, except in Northern Ireland where the Act still applies. Formerly, it made it unlawful to discriminate against people in respect of their disabilities in relation to employment, the provision of goods and services, education and transport. The DDA is a civil rights law. Other countries use constitutional, social rights or criminal law to make similar provisions. The Equality and Human Rights Commission combats discrimination. Equivalent legislation exists in Northern Ireland, which is enforced by the Northern Ireland Equality Commission. History The Act was the culmination of a public campaign, and at least 100,000 people in demonstrations, to force the government to end state and business discrimination against disabled people. While the Race Relations Act 1976 and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Free State
The Irish Free State (6 December 192229 December 1937), also known by its Irish-language, Irish name ( , ), was a State (polity), state established in December 1922 under the Anglo-Irish Treaty of December 1921. The treaty ended the three-year Irish War of Independence between the forces of the Irish Republic – the Irish Republican Army (1919–1922), Irish Republican Army (IRA) – and The Crown, British Crown forces. The Free State was established as a dominion of the British Empire. It comprised 26 of the 32 counties of Ireland. Northern Ireland, which was made up of the remaining six counties, exercised its right under the Treaty to opt out of the new state. The Irish Free State government consisted of the Governor-General of the Irish Free State, governor-general – the viceregal representative of the King – and the Executive Council of the Irish Free State, Executive Council (cabinet), which replaced both the revolutionary Government of the 2nd Dáil, Dáil Governm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poor Law
In English and British history, poor relief refers to government and ecclesiastical action to relieve poverty. Over the centuries, various authorities have needed to decide whose poverty deserves relief and also who should bear the cost of helping the poor. Alongside ever-changing attitudes towards poverty, many methods have been attempted to answer these questions. Since the early 16th century legislation on poverty enacted by the Parliament of England, poor relief has developed from being little more than a systematic means of punishment into a complex system of government-funded support and protection, especially following the creation in the 1940s of the welfare state. Tudor era In the late 15th century, Parliament took action on the growing problem of poverty, focusing on punishing people for being " vagabonds" and for begging. In 1495, during the reign of King Henry VII, Parliament enacted the Vagabonds and Beggars Act 1494. This provided for officers of the law to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal London Society For Blind People
The Royal London Society for Blind People (RLSB) was a UK charity that existed for 175 years to help blind and partially sighted young people in London and the South East through a blend of sports, education, and creative and developmental services. On 1 January 2017, the Royal Society for Blind Children (RSBC) and Royal London Society for Blind People (RLSB) joined to create a charity in England & Wales under the name of the Royal Society for Blind Children. History On 12 January 1838, Thomas Lucas established The London Society for Teaching the Blind to Read in the city of London, where he introduced his Lucas Type, an early form of embossed text. Funds for the school were raised largely through the efforts of the Ladies' Committee under the secretaryship of Mrs Lydia Johnson. Her husband, Percival Norton Johnson, founder of what is now Johnson Matthey plc, also took a prominent role in the affairs of the Society for many years. Over the years the school slowly expanded, mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the Bicameralism, bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. The leader of the majority party in the House of Commons by convention becomes the prime minister. Other parliaments have also had a lower house called the "House of Commons". History and naming The House of Commons of England, House of Commons of the Kingdom of England evolved from an undivided parliament to serve as the voice of the tax-paying subjects of the Ceremonial counties of England, counties and the borough constituency, boroughs. Knight of the shire, Knights of the shire, elected from each county, were usually landowners, while the borough members were often from the merchant classes. These members represented subjects of the Crown who were not Lords Temporal or Spiritual, who themselves sat in the House of Lords. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
David Lloyd George
David Lloyd George, 1st Earl Lloyd-George of Dwyfor (17 January 1863 – 26 March 1945) was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1916 to 1922. A Liberal Party (United Kingdom), Liberal Party politician from Wales, he was known for leading the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom during the First World War, for social-reform policies, for his role in the Paris Peace Conference (1919–1920), Paris Peace Conference, and for negotiating the establishment of the Irish Free State. Born in Chorlton-on-Medlock, Manchester, and raised in Llanystumdwy, Lloyd George gained a reputation as an orator and proponent of a Welsh blend of radical Liberal ideas that included support for Welsh devolution, the Disestablishment of the Church in Wales, disestablishment of the Church of England in Wales, equality for labourers and tenant farmers, and reform of land ownership. He won 1890 Caernarvon Boroughs by-election, an 1890 by-election to become the Member of Parliam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Assistance Act 1948
The National Assistance Act 1948 ( 11 & 12 Geo. 6. c. 29) is an act of Parliament passed in the United Kingdom by the Labour government of Clement Attlee. It formally abolished the Poor Law system that had existed since the reign of Elizabeth I, and established a social safety net for those who did not pay national insurance contributions (such as the homeless, the physically disabled, and unmarried mothers) and were therefore left uncovered by the National Insurance Act 1946 and the National Insurance (Industrial Injuries) Act 1946. It also provided help to elderly people who required supplementary benefits to make a subsistence living, and obliged local authorities to provide suitable accommodation for those who through infirmity, age, or any other reason were "in need of care and attention not otherwise available to them". The legislation also empowered local authorities to grant financial aid to organizations of volunteers concerned with the provision of recreational facilit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
11 & 12 Geo
Eleven or 11 may refer to: *11 (number) * One of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011 Literature * ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn *''Eleven'', a 1970 collection of short stories by Patricia Highsmith *''Eleven'', a 2004 children's novel in The Winnie Years by Lauren Myracle *''Eleven'', a 2008 children's novel by Patricia Reilly Giff *''Eleven'', a short story by Sandra Cisneros Music * Eleven (band), an American rock band * Eleven: A Music Company, an Australian record label *Up to eleven, an idiom from popular culture, coined in the movie ''This Is Spinal Tap'' Albums * ''11'' (The Smithereens album), 1989 * ''11'' (Ua album), 1996 * ''11'' (Bryan Adams album), 2008 * ''11'' (Sault album), 2022 * ''Eleven'' (Harry Connick, Jr. album), 1992 * ''Eleven'' (22-Pistepirkko album), 1998 * ''Eleven'' (Sugarcult album), 1999 * ''Eleven'' (B'z album), 2000 * ''Eleven'' (Reamonn album), 2010 * ''Eleven'' (Martina McBride album), 2011 * ''Eleven'' (Mr F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |