|
Blera
Blera is a small town and ''comune'' in the northern Lazio region of Italy. It was known during the Middle Ages In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the 5th to the late 15th centuries, similarly to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and ... as Bieda, an evolved form of its ancient name, which was restored in the twentieth century. It is the birthplace of Pope Sabinian; Pope Paschal II was also originally thought to be from here. It is situated on a long, narrow tongue of rock at the junction of two deep glens. This cites History In ancient times, Blera was an Etruscan town on the Via Clodia. It was of little importance, and is known to be mentioned only by geographers and in inscriptions. In 772, it was destroyed by the Lombards of King Desiderius. In the thirteenth-fifteenth centuries, it belonged to the Di Vico family. In 1247 the army of Frederi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
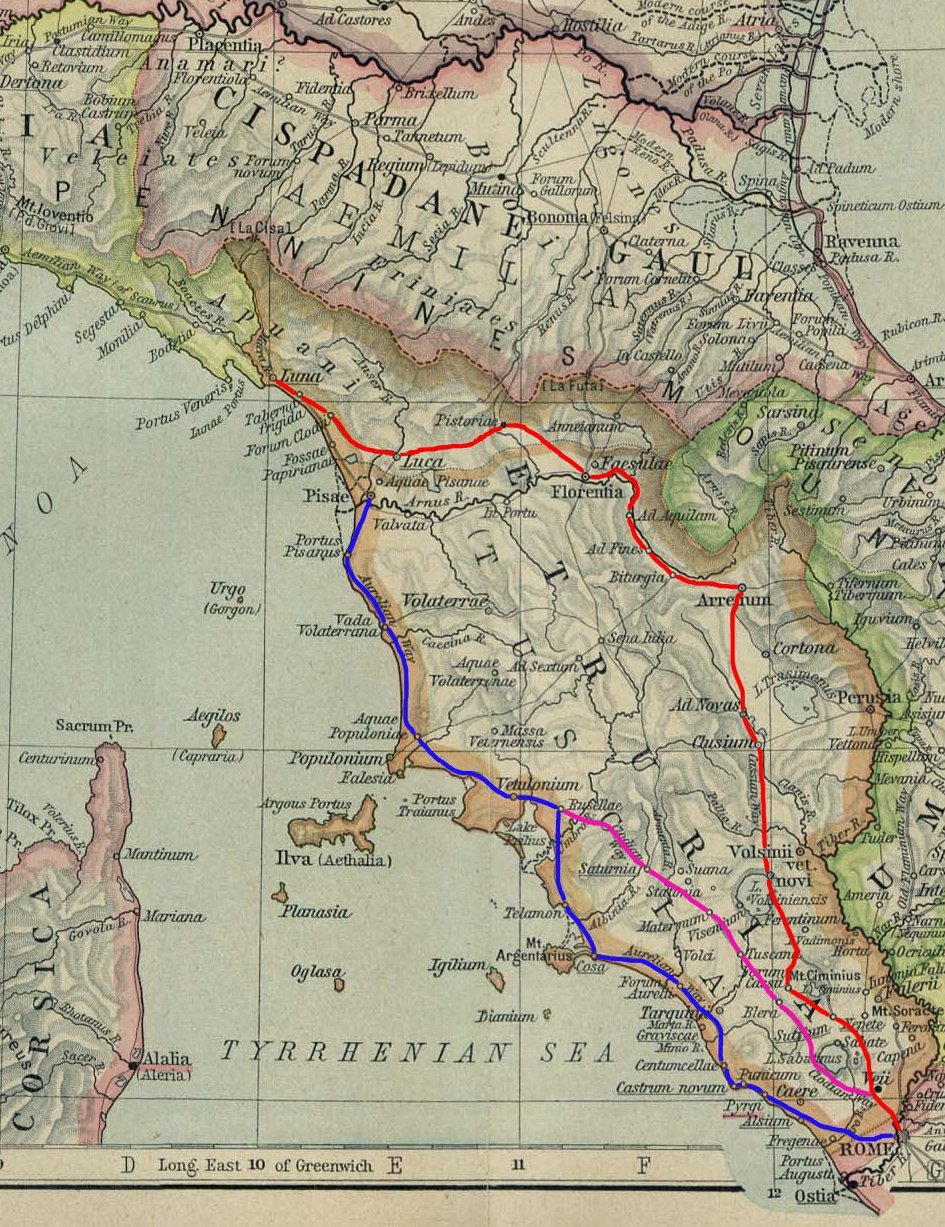
Via Clodia
The Via Clodia was an ancient high road of Italy. Situated between the Via Cassia and the Via Aurelia, it is different from them notably in that the latter was designed primarily for military long-haul, irrespective of settlements they met, but the Via Clodia was of short-range, intended for commercial traffic with the colonies in Etruscan lands. Its origin is uncertain, but most scholars agree that it was built by the Romans on an existing Etruscan route (between Pitigliano, Sorano and Sovana) on the path of the existing Etruscan "Via Cava"). However we can speak of the Via Clodia from the end of the 3rd century BC, and that from 225 BC it was paved. The existing road was probably used as a way of penetration and conquest of Etruria by the Roman army begun in 310 BC. The road never seems to have had heavy traffic, only connecting Rome with Etruria inner north-western cities. The stretch between Bracciano and Oriolo Romano continues a straight line whose paving stones are found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pope Sabinian
Pope Sabinian () was the bishop of Rome from 13 September 604 to his death on 22 February 606. His pontificate occurred during the Eastern Roman domination of the papacy. He was the fourth former ''apocrisiarius'' to Constantinople to be elected pope. Apocrisiariat Sabinian was born at Blera (Bieda) near Viterbo. He had been sent by Pope Gregory I, who had a high opinion of him, as ''apocrisiarius'' to the imperial court in Constantinople. In 595, Gregory was angered by Sabinian's lack of resolution in discussion with Emperor Maurice about the disputed assumption of the title "ecumenical patriarch" by John IV of Constantinople. Sabinian was then recalled and sent on a mission to Gaul the same year. He returned to Rome in 597. Pontificate Sabinian was elected to succeed Gregory probably in March 604, but had to wait for imperial ratification before being consecrated in September. During his pontificate, Sabinian was seen as a counterfoil to Gregory I. The ''Liber pontificali ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Institute In Rome
The Swedish Institute in Rome (, ) is a research institution that serves as the base for archaeological excavations and other scientific research in Italy. It also pursues academic instruction in archaeology and art sciences as well as arranging conferences with themes of interest to the institute. The institute has at its disposal a building in central Rome, designed by Ivar Tengbom, with a relatively well-supplied library, archaeological laboratory and around twenty rooms and smaller apartments for the use of visiting researchers and holders of scholarships. The institute was founded in 1925 by, among others, King Gustaf VI Adolf, then Crown Prince of Sweden. Excavations The institute has conducted several major excavations. Before World War II, excavations were carried out on the Forum Romanum among other places, but since then most of them have taken place in southern Etruria. * Acquarossa, 1966–1978 * San Giovenale, 1956–1965 * Luni sul Mignone, 1960–1963 * Selvase ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rock-cut Tombs
A rock-cut tomb is a burial chamber that is cut into an existing, naturally occurring rock formation, so a type of rock-cut architecture. They are usually cut into a cliff or sloping rock face, but may go downward in fairly flat ground. It was a common form of burial for the wealthy in ancient times in several parts of the world. Important examples are found in Egypt, most notably in the town of Deir el-Medina (Seet Maat), located between the Valley of the Kings and the Valley of the Queens. Other notable clusters include numerous Rock-cut tombs in ancient Israel (modern Israel and the Palestinian territories), at Naghsh-e Rostam necropolis in Iran, at Myra in Lycia (today in Turkey), Nabataean tombs in Petra (modern Jordan) and Mada'in Saleh (Saudi Arabia), Sicily ( Pantalica) and Larnaca. Indian rock-cut architecture is very extensive, but does not feature tombs. Chronology * Egyptian rock-cut tombs (1450 BCE, Thebes, Egypt). * Phrygian rock-cut tombs such as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lazio
Lazio ( , ; ) or Latium ( , ; from Latium, the original Latin name, ) is one of the 20 Regions of Italy, administrative regions of Italy. Situated in the Central Italy, central peninsular section of the country, it has 5,714,882 inhabitants and a GDP of more than €212 billion per year, making it the country's second most populated region and second largest regional economy after Lombardy. The capital of Lazio is Rome, which is the capital city of Italy. Lazio was the home of the Etruscan civilization, then stood at the center of the Roman Republic, of the Roman Empire, of the Papal States, of the Kingdom of Italy and of the Italian Republic. Lazio boasts a rich cultural heritage. Great artists and historical figures lived and worked in Rome, particularly during the Italian Renaissance period. In remote antiquity, Lazio (''Latium'') included only a limited part of the current region, between the lower course of the Tiber, the Tyrrhenian Sea, the Monti Sabini and the Pontine M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor
Frederick II (, , , ; 26 December 1194 – 13 December 1250) was King of Sicily from 1198, King of Germany from 1212, King of Italy and Holy Roman Emperor from 1220 and King of Jerusalem from 1225. He was the son of Emperor Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry VI of the Hohenstaufen dynasty (the second son of Emperor Frederick Barbarossa) and Queen Constance I of Sicily of the Hauteville dynasty. Frederick was one of the most powerful figures of the Middle Ages and ruled a vast area, beginning with Sicily and stretching through Italy all the way north to Germany. Viewing himself as a direct successor to the Roman emperors of antiquity, he was Holy Roman Emperor, Emperor of the Romans from his papal coronation in 1220 until his death; he was also a claimant to the title of King of the Romans from 1212 and unopposed holder of that monarchy from 1215. As such, he was King of Germany, King of Italy, of Italy, and King of Burgundy, of Burgundy. At the age of three, he was crowned King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opus Caementicium
Roman concrete, also called , was used in construction in ancient Rome. Like its modern equivalent, Roman concrete was based on a hydraulic-setting cement added to an aggregate. Many buildings and structures still standing today, such as bridges, reservoirs and aqueducts, were built with this material, which attests to both its versatility and its durability. Its strength was sometimes enhanced by the incorporation of pozzolanic ash where available (particularly in the Bay of Naples). The addition of ash prevented cracks from spreading. Recent research has shown that the incorporation of mixtures of different types of lime, forming conglomerate "clasts" allowed the concrete to self-repair cracks. Roman concrete was in widespread use from about 150 BC; some scholars believe it was developed a century before that. It was often used in combination with facings and other supports, and interiors were further decorated by stucco, fresco paintings, or coloured marble. Further inn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papal States
The Papal States ( ; ; ), officially the State of the Church, were a conglomeration of territories on the Italian peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope from 756 to 1870. They were among the major states of Italy from the 8th century until the unification of Italy, which took place between 1859 and 1870, culminated in their demise. The state was legally established in the 8th century when Pepin the Short, king of the Franks, gave Pope Stephen II, as a temporal sovereign, lands formerly held by Arian Christian Lombards, adding them to lands and other real estate formerly acquired and held by the bishops of Rome as landlords from the time of Constantine onward. This donation came about as part of a process whereby the popes began to turn away from the Byzantine emperors as their foremost temporal guardians for reasons such as increased imperial taxes, disagreement with respect to iconoclasm, and failure of the emperors, or their exarchs in Italy, to pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
House Of Anguillara
Anguillara were a baronial family of Latium, especially powerful in Rome and in the current province of Viterbo during the Middle Ages and the early Renaissance. The Anguillara were of Norman descent. They most likely took, or gave, their name from the city of Anguillara Sabazia, on the Lake Bracciano. The name itself could refer to the Italian word '':wiktionary:anguilla, anguilla'' (eel), or, as claimed by some, to a Roman villa (''villa angularia'') on a corner (Latin: ''angulum'') of the Lake. A first Count Ramone Anguillara is recorded as a probably legendary enemy of the Popes. In 1090 is known a Gherardo, lord of Anguillara, who was allied with the Prefetti di Vico against the commune of Rome. His successors were John, who took Santa Severa, and Niccolò, who conquered Tolfa in 1146. In 1186 Pandolfo I Anguillara, Pandolfo I started a long struggle with the Vicos for the control of northern Latium and met the Henry VI, Holy Roman Emperor, Henry VI at Orvieto, also hosting h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boniface IX
Pope Boniface IX (; ; c. 1350 – 1 October 1404, born Pietro Tomacelli) was head of the Catholic Church from 2 November 1389 to his death, in October 1404. He was the second Roman pope during the Western Schism.Richard P. McBrien, ''Lives of the Popes'', (HarperCollins, 2000), 249. In this time, the Avignon claimants, Clement VII and Benedict XIII, maintained the Roman Curia in Avignon, under the protection of the French monarchy. He is the last pope to date to take on the pontifical name "Boniface". Early life Born c. 1350 in Naples, Pietro (also Piero or Perino) Cybo Tomacelli was son of Baron Giacomo Tomacelli and Verdella Caracciolo, feudataries of Casarano and nearby Casaranello, from noble neapolitan families, and a descendant of Tamaso Cybo, who belonged to an influential noble family from Genoa and settled in Casarano in the Kingdom of Naples. He was baptized in the paleochristian church of Santa Maria della Croce (the church of Casaranello). An unsympathetic German c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desiderius
Desiderius, also known as Daufer or Dauferius (born – died ), was king of the Lombards in northern Italy, ruling from 756 to 774. The Frankish king of renown, Charlemagne, married Desiderius's daughter and subsequently conquered his realm. Desiderius is remembered for this connection to Charlemagne and for being the last Lombard ruler to exercise regional kingship. Rise to power Born in Brescia, Desiderius was originally a royal officer, the ''dux'' of Tuscia and he became king after the death of Aistulf in 756. At that time, Aistulf's predecessor, Ratchis, left his monastic retreat of Montecassino and tried to seize the kingdom, but Desiderius put his revolt down quickly with the support of Pope Stephen II. At his coronation, Desiderius promised to restore many lost papal towns to the Holy See and even enlarge the Papal State. By 757, Desiderius began securing his power, taking what historian Walter Goffart terms, "vigorous steps to suppress resistance to himself in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Di Vico
Di or DI may refer to: Arts and media Music * Di, a tone in the solfège ascending chromatic scale existing between Do and Re * dizi (instrument) or di, a Chinese transverse flute * ''D.I.'' (band), a punk band from Southern California ** ''D.I.'' (EP), a 1983 EP by the same band above Other media * '' The D.I.'', 1957 military film by Jack Webb * '' Dagens Industri'', a Swedish financial newspaper * DI.FM, an internet radio service Businesses and organisations * Defence Intelligence, a UK military intelligence agency * Defensa Interior, an anti-Franco militant anarchist group in 1960s Spain * Deseret Industries, an LDS thrift store * Desert Inn, a former casino in Las Vegas * Direction Italy, a liberal-conservative political party in Italy * Dirgantara Indonesia, an Indonesian aircraft company * Discovery Institute, an intelligent design advocacy group * Marabu (airline) (IATA code: DI), an Estonian leisure airline * Norwegian Air UK (former IATA code: DI), a former UK a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |