|
Bleb (medicine)
In medicine, a bleb is a blister-like protrusion (often hemispherical) filled with serous fluid. Blebs can form in a number of tissues by different pathologies, including frostbite and can "appear and disappear within a short time interval". In pathology pulmonary blebs are small subpleural thin-walled air-containing spaces, not larger than 1-2 cm in diameter. Their walls are less than 1 mm thick. If they rupture, they allow air to escape into pleural space, resulting in a spontaneous pneumothorax. In ophthalmology, blebs may be formed intentionally in the treatment of glaucoma. In such treatments, functional blebs facilitate the circulation of aqueous humor, the blockage of which will lead to increase in eye pressure. Use of collagen matrix wound modulation device such as ologen during glaucoma surgery is known to produce vascular and functional blebs, which are positively correlated with treatment success rate. In the lungs, a bleb is a collection of air within the layers of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRBNS
Blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome is a rare disorder that consists mainly of abnormal blood vessels affecting the skin or internal organs – usually the gastrointestinal tract. The disease is characterized by the presence of fluid-filled blisters ( blebs) as visible, circumscribed, chronic lesions (nevi). BRBNS is caused by somatic mutations in the TEK (TIE2) gene. It was described by William Bennett Bean in 1958. Presentation BRBNS is a venous malformation, formerly, though incorrectly, thought to be related to the hemangioma. It sometimes causes serious bleeding. Lesions are most commonly found on the skin and in the small intestine and distal large bowel. The lesions can also be found in the central nervous system, liver, and muscles. It usually presents soon after birth or during early infancy. Causes The cause of blue rubber bleb nevus syndrome is currently unknown. The syndrome is considered sporadic. A patient who is diagnosed with BRBNS likely has a family history o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medicine
Medicine is the science and Praxis (process), practice of caring for a patient, managing the diagnosis, prognosis, Preventive medicine, prevention, therapy, treatment, Palliative care, palliation of their injury or disease, and Health promotion, promoting their health. Medicine encompasses a variety of health care practices evolved to maintain and restore health by the prevention (medical), prevention and therapy, treatment of illness. Contemporary medicine applies biomedical sciences, biomedical research, medical genetics, genetics, and medical technology to diagnosis (medical), diagnose, treat, and prevent injury and disease, typically through pharmaceuticals or surgery, but also through therapies as diverse as psychotherapy, splint (medicine), external splints and traction, medical devices, biologic medical product, biologics, and Radiation (medicine), ionizing radiation, amongst others. Medicine has been practiced since Prehistoric medicine, prehistoric times, and for most o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blister
A blister is a small pocket of body fluid ( lymph, serum, plasma, blood, or pus) within the upper layers of the skin, usually caused by forceful rubbing (friction), burning, freezing, chemical exposure or infection. Most blisters are filled with a clear fluid, either serum or plasma. However, blisters can be filled with blood (known as " blood blisters") or with pus (for instance, if they become infected). The word "blister" entered English in the 14th century. It came from the Middle Dutch and was a modification of the Old French , which meant a leprous nodule—a rise in the skin due to leprosy. In dermatology today, the words ''vesicle'' and ''bulla'' refer to blisters of smaller or greater size, respectively. To heal properly, a blister should not be popped unless medically necessary. If popped, the bacteria can spread. The excess skin should not be removed because the skin underneath needs the top layer to heal properly. Causes A blister may form when the skin ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serous Fluid
In physiology, serous fluid or serosal fluid (originating from the Medieval Latin word ''serosus'', from Latin ''serum'') is any of various body fluids resembling serum, that are typically pale yellow or transparent and of a benign nature. The fluid fills the inside of body cavities. Serous fluid originates from serous glands, with secretions enriched with proteins and water. Serous fluid may also originate from mixed glands, which contain both mucous and serous cells. A common trait of serous fluids is their role in assisting digestion, excretion, and respiration. In medical fields, especially cytopathology, serous fluid is a synonym for effusion fluids from various body cavities. Examples of effusion fluid are pleural effusion and pericardial effusion. There are many causes of effusions which include involvement of the cavity by cancer. Cancer in a serous cavity is called a serous carcinoma. Cytopathology evaluation is recommended to evaluate the causes of effusions in these cav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frostbite
Frostbite is a skin injury that occurs when exposed to extreme low temperatures, causing the freezing of the skin or other tissues, commonly affecting the fingers, toes, nose, ears, cheeks and chin areas. Most often, frostbite occurs in the hands and feet. The initial symptoms are typically a feeling of cold and tingling or numbing. This may be followed by clumsiness with a white or bluish color to the skin. Swelling or blistering may occur following treatment. Complications may include hypothermia or compartment syndrome. People who are exposed to low temperatures for prolonged periods, such as winter sports enthusiasts, military personnel, and homeless individuals, are at greatest risk. Other risk factors include drinking alcohol, smoking, mental health problems, certain medications, and prior injuries due to cold. The underlying mechanism involves injury from ice crystals and blood clots in small blood vessels following thawing. Diagnosis is based on symptoms. Severity ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Lung Pneumatosis
A focal lung pneumatosis, is an enclosed pocket of air or gas in the lung and includes blebs, bullae, pulmonary cysts, and lung cavities. Blebs and bullae can be classified by their wall thickness. * A bleb has a wall thickness of less than 1 mm. By radiology definition, it is up to 1 cm in total size. By pathology definition, it originates in the pleurae (rather than in the lung parenchyma). *A bulla has a wall thickness of less than 1 mm. By radiology definition, it has a total size of greater than 1 cm. By pathology definition, it originates in the lung parenchyma (rather than in the pleurae). * A lung cyst has a wall thickness of up to 4 mm. A minimum wall thickness of 1 mm has been suggested, but thin-walled pockets may be included in the definition as well. * A cavity has a wall thickness of more than 4 mm. The terms above, when referring to sites other than the lungs, often imply fluid content. Lung cysts are seen in about 8% of the general population, with an increased ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pneumothorax
A pneumothorax is an abnormal collection of air in the pleural space between the lung and the chest wall. Symptoms typically include sudden onset of sharp, one-sided chest pain and shortness of breath. In a minority of cases, a one-way valve is formed by an area of damaged tissue, and the amount of air in the space between chest wall and lungs increases; this is called a tension pneumothorax. This can cause a steadily worsening oxygen shortage and low blood pressure. This leads to a type of shock called obstructive shock, which can be fatal unless reversed. Very rarely, both lungs may be affected by a pneumothorax. It is often called a "collapsed lung", although that term may also refer to atelectasis. A primary spontaneous pneumothorax is one that occurs without an apparent cause and in the absence of significant lung disease. A secondary spontaneous pneumothorax occurs in the presence of existing lung disease. Smoking increases the risk of primary spontaneous pneumot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology ( ) is a surgical subspecialty within medicine that deals with the diagnosis and treatment of eye disorders. An ophthalmologist is a physician who undergoes subspecialty training in medical and surgical eye care. Following a medical degree, a doctor specialising in ophthalmology must pursue additional postgraduate residency training specific to that field. This may include a one-year integrated internship that involves more general medical training in other fields such as internal medicine or general surgery. Following residency, additional specialty training (or fellowship) may be sought in a particular aspect of eye pathology. Ophthalmologists prescribe medications to treat eye diseases, implement laser therapy, and perform surgery when needed. Ophthalmologists provide both primary and specialty eye care - medical and surgical. Most ophthalmologists participate in academic research on eye diseases at some point in their training and many include research as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is a group of eye diseases that result in damage to the optic nerve (or retina) and cause vision loss. The most common type is open-angle (wide angle, chronic simple) glaucoma, in which the drainage angle for fluid within the eye remains open, with less common types including closed-angle (narrow angle, acute congestive) glaucoma and normal-tension glaucoma. Open-angle glaucoma develops slowly over time and there is no pain. Peripheral vision may begin to decrease, followed by central vision, resulting in blindness if not treated. Closed-angle glaucoma can present gradually or suddenly. The sudden presentation may involve severe eye pain, blurred vision, mid-dilated pupil, redness of the eye, and nausea. Vision loss from glaucoma, once it has occurred, is permanent. Eyes affected by glaucoma are referred to as being glaucomatous. Risk factors for glaucoma include increasing age, high pressure in the eye, a family history of glaucoma, and use of steroid medicatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aqueous Humour
The aqueous humour is a transparent water-like fluid similar to plasma, but containing low protein concentrations. It is secreted from the ciliary body, a structure supporting the lens of the eyeball. It fills both the anterior and the posterior chambers of the eye, and is not to be confused with the vitreous humour, which is located in the space between the lens and the retina, also known as the posterior cavity or vitreous chamber. Blood cannot normally enter the eyeball. Structure Composition * Amino acids: transported by ciliary muscles *98% water * Electrolytes ( pH = 7.4 -one source gives 7.1) **Sodium = 142.09 **Potassium = 2.2 - 4.0 **Calcium = 1.8 **Magnesium = 1.1 **Chloride = 131.6 **HCO3- = 20.15 **Phosphate = 0.62 ** Osm = 304 *Ascorbic acid *Glutathione * Immunoglobulins Function *Maintains the intraocular pressure and inflates the globe of the eye. It is this hydrostatic pressure that keeps the eyeball in a roughly spherical shape and keeps the walls of the eye ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visceral Pleura
The pulmonary pleurae (''sing.'' pleura) are the two opposing layers of serous membrane overlying the lungs and the inside of the surrounding chest walls. The inner pleura, called the visceral pleura, covers the surface of each lung and dips between the lobes of the lung as ''fissures'', and is formed by the invagination of lung buds into each thoracic sac during embryonic development. The outer layer, called the parietal pleura, lines the inner surfaces of the thoracic cavity on each side of the mediastinum, and can be subdivided into ''mediastinal'' (covering the side surfaces of the fibrous pericardium, oesophagus and thoracic aorta), ''diaphragmatic'' (covering the upper surface of the diaphragm), ''costal'' (covering the inside of rib cage) and cervical (covering the underside of the suprapleural membrane) pleurae. The visceral and the mediastinal parietal pleurae are connected at the root of the lung ("hilum") through a smooth fold known as ''pleural reflections'', a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
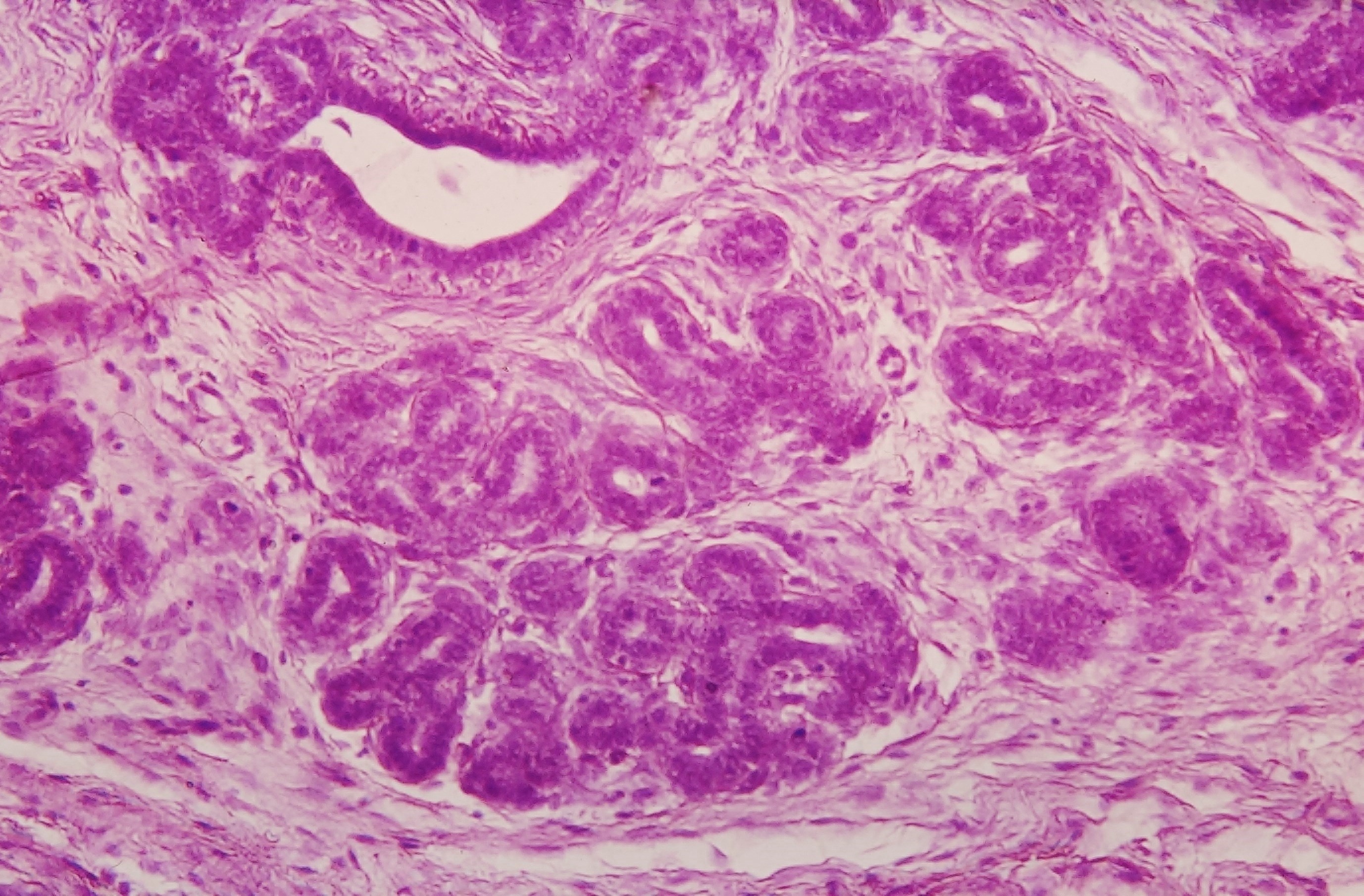
Mammary Gland
A mammary gland is an exocrine gland in humans and other mammals that produces milk to feed young offspring. Mammals get their name from the Latin word ''mamma'', "breast". The mammary glands are arranged in organs such as the breasts in primates (for example, humans and chimpanzees), the udder in ruminants (for example, cows, goats, sheep, and deer), and the dugs of other animals (for example, dogs and cats). Lactorrhea, the occasional production of milk by the glands, can occur in any mammal, but in most mammals, lactation, the production of enough milk for nursing, occurs only in phenotypic females who have gestated in recent months or years. It is directed by hormonal guidance from sex steroids. In a few mammalian species, male lactation can occur. With humans, male lactation can occur only under specific circumstances. Mammals are divided into 3 groups: prototherians, metatherians, and eutherians. In the case of prototherians, both males and females have functional ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |