|
Blastophaga Psenes2
''Blastophaga'' is a genus of wasps in the family Agaonidae (fig wasps) which pollinate figs or are otherwise associated with figs, a coevolutional relationship that has been developing for at least 80 million years. Pollinating fig wasps are specific to specific figs. The common fig ''Ficus carica'' is pollinated by ''Blastophaga psenes ''Blastophaga psenes'' is a wasp species in the genus '' Blastophaga''. It pollinates the common fig ''Ficus carica'' and the closely related '' Ficus palmata''. These wasps breed in figs without the need for a colony or nest, and the adults l ...''. The common figs contain no gall flowers for the reception of wasp eggs, and the Blastophaga female moves from flower to flower, incidentally fertilizing them, but is prevented from depositing her eggs. Worn out, the wasp perishes. Any eggs she may have dropped also perish. References * Proctor, M., Yeo, P. & Lack, A. (1996). ''The Natural History of Pollination''. Timber Press, Portland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
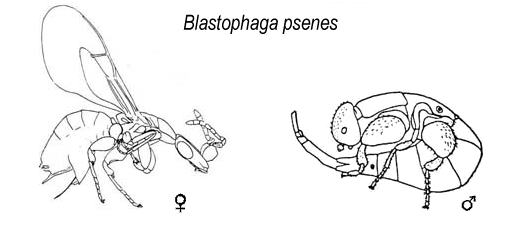
Blastophaga Psenes
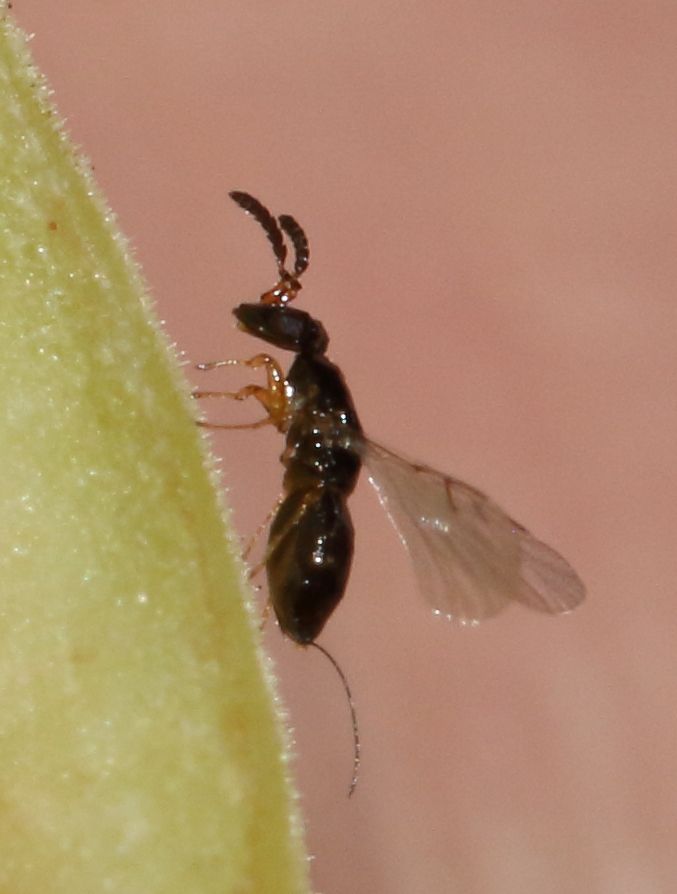
''Blastophaga psenes'' is a wasp species in the genus '' Blastophaga''. It pollinates the common fig ''Ficus carica'' and the closely related '' Ficus palmata''. These wasps breed in figs without the need for a colony or nest, and the adults live for only a few days or weeks. They locate the fig they wish to pollinate primarily using through olfaction. Taxonomy and phylogenetics Mutualism occurs between figs and fig wasps, which creates a need for specific species of figs to be pollinated by specific species of wasps. The origin of mutualism is also the beginning of the fig wasp phylogeny. In the phylogenetic tree, the genus of '' Blastophaga'' and '' Wiebesia'' are very similar. Both of these genera pollinate ''Ficus'' genus of figs. Description and identification ''B. psenes'' are small wasps, approximately only in length. The females are black and shiny, while the males are smaller than the females. The males are wingless, whereas females have wings that are transpar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Ludwig Christian Gravenhorst
Johann Ludwig Christian Carl Gravenhorst (14 November 1777 – 14 January 1857), sometimes Jean Louis Charles or Carl, was a German entomologist, herpetologist, and zoologist. Life Gravenhorst was born in Braunschweig. His early interest in insects was encouraged by two of his professors, both amateur entomologists. He entered the University of Helmstedt to study law in 1797. However, the death of his father two years later left him a great fortune; so he was able to change his direction. He enrolled at the University of Göttingen where he followed the courses of Johann Friedrich Blumenbach. He returned to present his thesis to Helmstädt on a subject of entomology. He went to Paris in 1802 and there met Georges Cuvier, Pierre André Latreille, and Alexandre Brongniart. Parallel to his studies, he assembled, thanks to his financial means, a very important natural history collection. In 1805, he obtained a professorial chair in Göttingen and published the following y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastophaga Psenes
''Blastophaga psenes'' is a wasp species in the genus '' Blastophaga''. It pollinates the common fig ''Ficus carica'' and the closely related '' Ficus palmata''. These wasps breed in figs without the need for a colony or nest, and the adults live for only a few days or weeks. They locate the fig they wish to pollinate primarily using through olfaction. Taxonomy and phylogenetics Mutualism occurs between figs and fig wasps, which creates a need for specific species of figs to be pollinated by specific species of wasps. The origin of mutualism is also the beginning of the fig wasp phylogeny. In the phylogenetic tree, the genus of '' Blastophaga'' and '' Wiebesia'' are very similar. Both of these genera pollinate ''Ficus'' genus of figs. Description and identification ''B. psenes'' are small wasps, approximately only in length. The females are black and shiny, while the males are smaller than the females. The males are wingless, whereas females have wings that are transpar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carl Linnaeus
Carl Linnaeus (23 May 1707 – 10 January 1778), also known after ennoblement in 1761 as Carl von Linné,#Blunt, Blunt (2004), p. 171. was a Swedish biologist and physician who formalised binomial nomenclature, the modern system of naming organisms. He is known as the "father of modern Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy". Many of his writings were in Latin; his name is rendered in Latin as and, after his 1761 ennoblement, as . Linnaeus was the son of a curate and was born in Råshult, in the countryside of Småland, southern Sweden. He received most of his higher education at Uppsala University and began giving lectures in botany there in 1730. He lived abroad between 1735 and 1738, where he studied and also published the first edition of his ' in the Netherlands. He then returned to Sweden where he became professor of medicine and botany at Uppsala. In the 1740s, he was sent on several journeys through Sweden to find and classify plants and animals. In the 1750s and 1760s, he co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blastophaga Auratae
''Blastophaga'' is a genus of wasps in the family Agaonidae (fig wasps) which pollinate figs or are otherwise associated with figs, a coevolutional relationship that has been developing for at least 80 million years. Pollinating fig wasps are specific to specific figs. The common fig ''Ficus carica'' is pollinated by ''Blastophaga psenes ''Blastophaga psenes'' is a wasp species in the genus '' Blastophaga''. It pollinates the common fig ''Ficus carica'' and the closely related '' Ficus palmata''. These wasps breed in figs without the need for a colony or nest, and the adults l ...''. The common figs contain no gall flowers for the reception of wasp eggs, and the Blastophaga female moves from flower to flower, incidentally fertilizing them, but is prevented from depositing her eggs. Worn out, the wasp perishes. Any eggs she may have dropped also perish. References * Proctor, M., Yeo, P. & Lack, A. (1996). ''The Natural History of Pollination''. Timber Press, Portland, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agaonidae
The family Agaonidae is a group of pollinating fig wasps. They spend their larval stage inside the fruits of Ficus, figs. The pollinating wasps (Agaoninae, Kradibiinae, and Tetrapusiinae) are the mutualism (biology), mutualistic partners of the Ficus, fig trees. Extinct forms from the Eocene and Miocene are nearly identical to modern forms, suggesting that the niche has been stable over geologic time. Females emerge from ripe figs and fly to another fig tree with developing Syconium, syconia (which contain the flowers). They enter the syconium via the ostiole, pollinate the flowers, and lay their eggs in some of the ovules. The ovules containing eggs develop into galls that support the growth of the wasp larvae. Prior to the final ripening of the fig, wingless males emerge from the galls they developed in. The males enter the galls of their winged sibling females, mate with them and die within the fruit. The newly hatched females then make their way out of the fruit continuing th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pollination
Pollination is the transfer of pollen from an anther of a plant to the stigma (botany), stigma of a plant, later enabling fertilisation and the production of seeds. Pollinating agents can be animals such as insects, for example bees, beetles or butterflies; birds, and bats; water; wind; and even plants themselves. Pollinating animals travel from plant to plant carrying pollen on their bodies in a vital interaction that allows the transfer of genetic material critical to the reproductive system of most flowering plants. Self-pollination occurs within a closed flower. Pollination often occurs within a species. When pollination occurs between species, it can produce hybrid (biology), hybrid offspring in nature and in plant breeding work. In angiosperms, after the pollen grain (gametophyte) has landed on the stigma (botany), stigma, it germinates and develops a pollen tube which grows down the style (botany), style until it reaches an ovary (botany), ovary. Its two gametes travel down ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus
''Ficus'' ( or ) is a genus of about 850 species of woody trees, shrubs, vines, epiphytes and hemiepiphytes in the family (biology), family Moraceae. Collectively known as fig trees or figs, they are native throughout the tropics with a few species extending into the semi-warm temperate zone. The common fig (''F. carica'') is a temperate species native to southwest Asia and the Mediterranean region (from Afghanistan to Portugal), which has been widely cultivated from ancient times for its fruit, also referred to as figs. The fruit of most other species are also edible though they are usually of only local economic importance or eaten as bushfood. However, they are extremely important food resources for wildlife. Figs are also of considerable cultural importance throughout the tropics, both as objects of worship and for their many practical uses. Description ''Ficus'' is a pantropical genus of trees, shrubs, and vines occupying a wide variety of ecological niches; most a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coevolution
In biology, coevolution occurs when two or more species reciprocally affect each other's evolution through the process of natural selection. The term sometimes is used for two traits in the same species affecting each other's evolution, as well as gene-culture coevolution. Charles Darwin mentioned evolutionary interactions between flowering plants and insects in ''On the Origin of Species'' (1859). Although he did not use the word coevolution, he suggested how plants and insects could evolve through reciprocal evolutionary changes. Naturalists in the late 1800s studied other examples of how interactions among species could result in reciprocal evolutionary change. Beginning in the 1940s, plant pathologists developed breeding programs that were examples of human-induced coevolution. Development of new crop plant varieties that were resistant to some diseases favored rapid evolution in pathogen populations to overcome those plant defenses. That, in turn, required the development of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ficus Carica
The fig is the edible fruit of ''Ficus carica'', a species of tree or shrub in the flowering plant family Moraceae, native to the Mediterranean region, together with western and southern Asia. It has been cultivated since ancient times and is now widely grown throughout the world.''The Fig: its History, Culture, and Curing'', Gustavus A. Eisen, Washington, Govt. print. off., 1901 ''Ficus carica'' is the type species of the genus ''Ficus'', which comprises over 800 tropical and subtropical plant species. A fig plant is a deciduous tree or large shrub, growing up to tall, with smooth white bark. Its large leaves have three to five deep lobes. Its fruit (referred to as syconium, a type of is tear-shaped, long, with a green fruit that may ripen toward purple or brown, and sweet soft reddish flesh containing numerous crunchy seeds. The milky sap of the green parts is an irritant to human skin. In the Northern hemisphere, fresh figs are in season from late August to early Octobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hymenoptera Genera
Hymenoptera is a large order of insects, comprising the sawflies, wasps, bees, and ants. Over 150,000 living species of Hymenoptera have been described, in addition to over 2,000 extinct ones. Many of the species are parasitic. Females typically have a special ovipositor for inserting eggs into hosts or places that are otherwise inaccessible. This ovipositor is often modified into a stinger. The young develop through holometabolism (complete metamorphosis)—that is, they have a wormlike larval stage and an inactive pupal stage before they reach adulthood. Etymology The name Hymenoptera refers to the wings of the insects, but the original derivation is ambiguous. All references agree that the derivation involves the Ancient Greek πτερόν (''pteron'') for wing. The Ancient Greek ὑμήν (''hymen'') for membrane provides a plausible etymology for the term because species in this order have membranous wings. However, a key characteristic of this order is that the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |