|
Black Patch Park
Black Patch Park is a park in Smethwick, West Midlands, England. It is bounded by Foundry Lane, Woodburn Road, Perrott Street and Kitchener Street, at . The park, covering over , was part of a sparsely populated landscape of commons and woodland (known as The Black Patch), dotted with farms and cottages which has been transformed from heath to farmland then to a carefully laid out municipal park surrounded by engineering companies employing thousands of people; Tangyes, Nettlefolds, (later GKN plc), the Birmingham Railway Carriage and Wagon Company, Birmingham Aluminium Castings, ironworks, glassmaking and brewing. These factories, including the Soho Foundry, started by James Watt and Matthew Boulton are, but for foundations and frontages, almost all gone. Much of what is known about Black Patch Chaplin Park appears in a book by Ted Rudge, developed from an Open University degree thesis, and published by Birmingham City Council in 2003. Rudge's research records how, from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Smethwick
Smethwick () is an industrial town in the Sandwell district, in the county of the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. It lies west of Birmingham city centre. Historically it was in Staffordshire and then Worcestershire before being placed into West Midlands county. In 2019, the ward of Smethwick had an estimated population of 15,246, while the wider built-up area subdivision has a population of 53,653. History It was suggested that the name Smethwick meant "smiths' place of work", but a more recent interpretation has suggested the name means "the settlement on the smooth land". Smethwick was recorded in the Domesday Book as ''Smedeuuich'', the ''d'' in this spelling being the Anglo-Saxon letter eth. Until the end of the 18th century it was an outlying hamlet of the south Staffordshire village of Harborne. Harborne became part of the county borough of Birmingham and thus transferred from Staffordshire to Warwickshire in 1891, leaving Smethwick in the County of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham Canal Navigations
Birmingham Canal Navigations (BCN) is a network of canals connecting Birmingham, Wolverhampton, and the eastern part of the Black Country. The BCN is connected to the rest of the English canal system at several junctions. It was owned and operated by the Birmingham Canal Navigation Company from 1767 to 1948. At its working peak, the BCN contained about 160 miles (257 km) of canals; today just over 100 miles (160 km) are navigable, and the majority of traffic is from tourist and residential narrowboats. History The earliest mention of the Birmingham Canal Navigation appears in ''Aris's Birmingham Gazette'' on 11 April 1768. Here it was reported that on 25 March 1768, the first general assembly of the Company of Proprietors of the Birmingham Canal Navigation was held at the Swann Inn, Birmingham, to raise funds to submit for an act of Parliament. The first canal to be built in the area was the Birmingham Canal, authorized by the (8 Geo. 3. c. 38) and built from 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Telford
Thomas Telford (9 August 1757 – 2 September 1834) was a Scottish civil engineer. After establishing himself as an engineer of road and canal projects in Shropshire, he designed numerous infrastructure projects in his native Scotland, as well as harbours and tunnels. Such was his reputation as a prolific designer of highways and related bridges, he was dubbed the 'Colossus of Roads' (a pun on the Colossus of Rhodes), and, reflecting his command of all types of civil engineering in the early 19th century, he was elected as the first president of the Institution of Civil Engineers, a post he held for 14 years until his death. The town of Telford in Shropshire was named after him. Early career Telford was born on 9 August 1757, at Glendinning, a hill farm east of Eskdalemuir Kirk, in the rural List of Church of Scotland parishes, parish of Westerkirk, in Eskdale, Dumfries and Galloway, Eskdale, Dumfriesshire. His father John Telford, a shepherd, died soon after Thomas was born. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Black Country
The Black Country is an area of England's West Midlands. It is mainly urban, covering most of the Dudley and Sandwell metropolitan boroughs, with the Metropolitan Borough of Walsall and the City of Wolverhampton. The road between Wolverhampton and Birmingham was described as "one continuous town" in 1785. The area was one of the Industrial Revolution's birthplaces. Its name was first recorded in the 1840s, and derives either from the thick coal seam close to the surface or the production of coal, coke, iron, glass, bricks and steel which produced high levels of soot and air pollution. Extent The Black Country has no single set of defined boundaries. Some traditionalists define it as "the area where the coal seam comes to the surface – so West Bromwich, Coseley, Oldbury, Blackheath, Cradley Heath, Old Hill, Bilston, Dudley, Tipton, Wednesbury, and parts of Halesowen, Walsall and Smethwick or what used to be known as Warley." There are records from the 18th century ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Brindley
James Brindley (1716 – 27 September 1772) was an English engineer. He was born in Tunstead, Derbyshire, and lived much of his life in Leek, Staffordshire, becoming one of the most notable engineers of the 18th Century. Born in the Peak District, which in those days was extremely isolated, Brindley received little formal education, but was educated at home by his mother. At age 17, encouraged by his mother, he was apprenticed to a millwright in exceptional skill and ability. Having completed his apprenticeship he set up business for himself as a wheelwright in Leek, Staffordshire. In 1750 he expanded his business by renting a millwright's shop in Burslem from the Wedgwoods who became his lifelong friends. He soon established a reputation for ingenuity and skill at repairing many different kinds of machinery. In 1752 he designed and built an engine for draining a coal mine, the Wet Earth Colliery at Clifton, formerly in Lancashire, now in Greater Manchester. Three years l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handsworth Booth Street Tram Stop
Handsworth Booth Street tram stop is a tram stop in Handsworth, Birmingham, England. It was opened on 31 May 1999 and is situated on West Midlands Metro Line 1. It is situated on the site of the old Handsworth and Smethwick railway station, which closed in 1972. The Birmingham to Worcester railway line runs alongside, but the stop is served only by trams, as there are no railway platforms. Immediately south of the tram stop the West Midlands Metro passes over a modern bridge which takes the line over a siding for an adjacent scrap metal works. This bridge was constructed under instruction from Network Rail. Services On Mondays to Fridays, West Midlands Metro The West Midlands Metro is a light-rail/tram system in the county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. The network has List of West Midlands Metro tram stops, 33 stops with a total of of track; it currently consists of a single r ... services in each direction between Edgbaston Village and Wolverhampt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winson Green Outer Circle Tram Stop
Winson Green Outer Circle tram stop is a tram stop in Winson Green, Birmingham, England. It was opened on 31 May 1999 and is situated on West Midlands Metro Line 1. Its name is derived from its connection with the Outer Circle bus route. The pedestrian approach to the stop is decorated by Tim Tolkien's '' James Watt's Mad Machine''. It is one of only a few West Midlands Metro stops to have an island platform, rather than two side platforms. This is due to a lack of space at the site. The Birmingham to Worcester railway line runs alongside, but the stop is served only by trams, as there are no railway platforms. In addition the railway line between the Stour Valley Line and former Grand Junction Line crosses over the lines just south of the tram stop. Services On Mondays to Fridays, West Midlands Metro The West Midlands Metro is a light-rail/tram system in the county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. The network has List of West Midlands Metro tram stops, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Midlands Metro
The West Midlands Metro is a light-rail/tram system in the county of West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. The network has List of West Midlands Metro tram stops, 33 stops with a total of of track; it currently consists of a single route, Line 1, which operates between the cities of Birmingham and Wolverhampton via the towns of Bilston, West Bromwich and Wednesbury, on a mixture of Abandoned railway, former railway lines and urban on-street running. The system is owned by the public body Transport for West Midlands, and operated by Midland Metro Limited, a company wholly owned by the West Midlands Combined Authority. During August 1995, a 25-year contract for the design, construction, operation and maintenance of Line 1 was awarded to the #Operator, Altram consortium; construction commenced three months later. It was launched on 30 May 1999 as Midland Metro, partly using the disused Birmingham Snow Hill to Wolverhampton Low Level Line. During 2006, Gio. Ansaldo & C., ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sustrans
Sustrans ( ) is a United Kingdom-based walking, wheeling and cycling charity, and the custodian of the National Cycle Network. Its flagship project is the National Cycle Network, which has created of signed cycle routes throughout the United Kingdom, including of traffic-free paths. The rest of the network is on previously existing and mostly minor roads, in which motor traffic will be encountered. In Scotland, Sustrans has established partnership teams, embedding officers in local councils as well as NHS Scotland, the Scottish Environment Protection Agency, NatureScot, Scottish Natural Heritage, and Transport for Edinburgh. History Sustrans was formed in Bristol in July 1977 as Cyclebag by a group of cyclists and environmentalism, environmentalists, as a result of doubts about the desirability of dependence on the private car, following the 1973 oil crisis, and the almost total lack of specific provision for cyclists in most British cities, in contrast to some other Europ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Handsworth, West Midlands
Handsworth () is an inner-city area of Birmingham in the county of the West Midlands (county), West Midlands, England. Historically in Staffordshire, Handsworth lies just outside Birmingham City Centre and near the town of Smethwick. In 2021 the ward had a population of 11,820. History The name ''Handsworth'' originates from its Anglo-Saxons, Saxon owner Hondes and the Old English language, Old English word ''weorthing'', meaning farm or estate. It was recorded in the Domesday Book, Domesday Survey of 1086, as a holding of William Fitz-Ansculf, the Lord of Dudley, although at that time it would only have been a very small village surrounded by farmland and extensive woodland. One of the oldest buildings in Handsworth is the Old Town Hall, Handsworth, Old Town Hall which dates from 1460. Historically in the county of Staffordshire, it remained a small village from the 13th century to the 18th century. Accommodation was built for factory workers, the village quickly grew, and in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
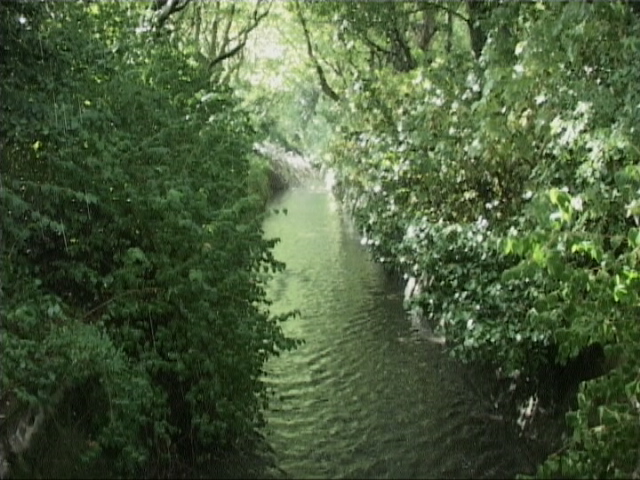
Hockley Brook
Hockley Brook is a brook, or stream, in north Birmingham, England. It rises just outside the city, in Smethwick, and runs through Black Patch Park and then through the city's Soho, Hockley and Aston districts, to its confluence with the River Tame, beneath Gravelly Hill Interchange. From there, its waters flow, via the Trent, to the Humber Estuary and the North Sea. At the eastern end, it is known as Aston Brook, giving its name to Aston Brook Street. It previously marked the boundary between Birmingham (then Warwickshire) and Smethwick (then Staffordshire); between the then Staffordshire country villages of Handsworth and Smethwick;Ted Rudge ''Brumroamin: Birmingham and Midland Romany Gypsy and Traveller Culture''. Birmingham City Council Department of Leisure & Community Services (2003) and between Birmingham and Aston, before the city absorbed the latter district. The brook once fed several mills and provided water for Matthew Boulton's Soho Manufactory. In post-World War ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |