|
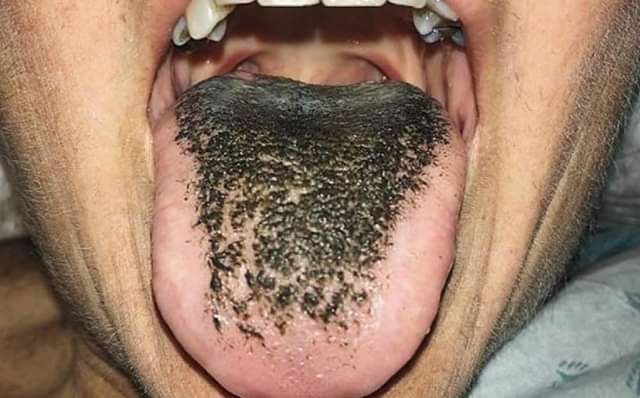
Black Hairy Tongue
Black hairy tongue syndrome (BHT) is a condition of the tongue in which the small bumps on the tongue elongate with black or brown discoloration, giving a black and hairy appearance. The appearance may be alarming, but it is a harmless condition. Predisposing factors include smoking, xerostomia (dry mouth), soft diet, poor oral hygiene and certain medications. Management is facilitated by improving oral hygiene, especially scraping or brushing the tongue. Signs and symptoms Hairy tongue largely occurs in the central part of the dorsal tongue, just anterior (in front) of the circumvallate papillae, although sometimes the entire dorsal surface may be involved. Discoloration usually accompanies hairy tongue, and may be yellow, brown or black. Apart from the appearance, the condition is typically asymptomatic, but sometimes people may experience a gagging sensation or a bad taste. There may also be associated oral malodor (intra-oral halitosis). The term "melanoglossia' is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Lancet
''The Lancet'' is a weekly peer-reviewed general medical journal, founded in England in 1823. It is one of the world's highest-impact academic journals and also one of the oldest medical journals still in publication. The journal publishes original research articles, review articles ("seminars" and "reviews"), editorials, book reviews, correspondence, as well as news features and case reports. ''The Lancet'' has been owned by Elsevier since 1991, and its editor-in-chief since 1995 has been Richard Horton. The journal has editorial offices in London, New York City, and Beijing. History ''The Lancet'' was founded in 1823 by Thomas Wakley, an English surgeon who named it after the surgical instrument called a lancet (scalpel). According to BBC, the journal was initially considered to be radical following its founding. Members of the Wakley family retained editorship of the journal until 1908. In 1921, ''The Lancet'' was acquired by Hodder & Stoughton. Elsevier acquire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiotherapy
Radiation therapy or radiotherapy (RT, RTx, or XRT) is a treatment using ionizing radiation, generally provided as part of cancer therapy to either kill or control the growth of malignant cells. It is normally delivered by a linear particle accelerator. Radiation therapy may be curative in a number of types of cancer if they are localized to one area of the body, and have not spread to other parts. It may also be used as part of adjuvant therapy, to prevent tumor recurrence after surgery to remove a primary malignant tumor (for example, early stages of breast cancer). Radiation therapy is synergistic with chemotherapy, and has been used before, during, and after chemotherapy in susceptible cancers. The subspecialty of oncology concerned with radiotherapy is called radiation oncology. A physician who practices in this subspecialty is a radiation oncologist. Radiation therapy is commonly applied to the cancerous tumor because of its ability to control cell growth. Ionizin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opportunistic Infection
An opportunistic infection is an infection that occurs most commonly in individuals with an immunodeficiency disorder and acts more severe on those with a weakened immune system. These types of infections are considered serious and can be caused by a variety of pathogens including viruses, bacteria, fungi, and parasites. Under normal conditions, such as in humans with uncompromised immune systems, an opportunistic infection would be less likely to cause significant harm and would typically result in a mild infection or no effect at all. These opportunistic infections can stem from a variety of sources, such as a weakened immune system (caused by human immunodeficiency virus and acquired immunodeficiency syndrome), when being treated with immunosuppressive drugs (as in cancer treatment), when a microbiome is altered (such as a disruption in gut microbiota), or when integumentary barriers are breached (as in penetrating trauma). Opportunistic infections can contribute to antimic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairy Leukoplakia
Hairy leukoplakia is a white patch on the side of the tongue with a corrugated or hairy appearance. It is caused by Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) and occurs usually in persons who are immunocompromised, especially those with human immunodeficiency virus infection/ acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (HIV/AIDS). The white lesion, which cannot be scraped off, is benign and does not require any treatment, although its appearance may have diagnostic and prognostic implications for the underlying condition. Depending upon what definition of leukoplakia is used, hairy leukoplakia is sometimes considered a subtype of leukoplakia, or a distinct diagnosis. Signs and symptoms There are no symptoms associated with the lesion itself, although many and varied symptoms and signs may be associated with the underlying cause of immunosuppression. The lesion is a white patch, which almost exclusively occurs on the lateral surfaces of the tongue, although rarely it may occur on the buccal mucosa, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parakeratosis
Parakeratosis is a mode of keratinization characterized by the retention of nuclei in the stratum corneum. In mucous membranes, parakeratosis is normal.Kumar, Vinay; Fausto, Nelson; Abbas, Abul (2010) ''Robbins & Cotran Pathologic Basis of Disease'' (8th ed.). Saunders. Page 1170. . In the skin, this process leads to the abnormal replacement of annular squames with nucleated cells. Parakeratosis is associated with the thinning or loss of the granular layer and is usually seen in diseases of increased cell turnover, whether inflammatory or neoplastic. Parakeratosis is seen in the plaques of psoriasis and in dandruff. Granular parakeratosis (originally termed axillary granular parakeratosis) is an idiopathic, benign, nondisabling cutaneous disease that manifests with intertriginous erythematous, brown or red, scaly or keratotic papules and plaques. It presents in all age groups and has no established clinical associations. File:Histopathology of reactive hyperkeratosis.jpg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histology
Histology, also known as microscopic anatomy or microanatomy, is the branch of biology that studies the microscopic anatomy of biological tissue (biology), tissues. Histology is the microscopic counterpart to gross anatomy, which looks at larger structures visible without a microscope. Although one may divide microscopic anatomy into ''organology'', the study of organs, ''histology'', the study of tissues, and ''cytology'', the study of cell (biology), cells, modern usage places all of these topics under the field of histology. In medicine, histopathology is the branch of histology that includes the microscopic identification and study of diseased tissue. In the field of paleontology, the term paleohistology refers to the histology of fossil organisms. Biological tissues Animal tissue classification There are four basic types of animal tissues: muscle tissue, nervous tissue, connective tissue, and epithelial tissue. All animal tissues are considered to be subtypes of these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biopsy
A biopsy is a medical test commonly performed by a surgeon, interventional radiologist, an interventional radiologist, or an interventional cardiology, interventional cardiologist. The process involves the extraction of sampling (medicine), sample Cell (biology), cells or Biological tissue, tissues for examination to determine the presence or extent of a disease. The tissue is then Histopathology, fixed, dehydrated, embedded, sectioned, stained and mounted before it is generally examined under a microscope by a pathologist; it may also be analyzed chemically. When an entire lump or suspicious area is removed, the procedure is called an excisional biopsy. An incisional biopsy or core biopsy samples a portion of the abnormal tissue without attempting to remove the entire lesion or tumor. When a sample of tissue or fluid is removed with a needle in such a way that cells are removed without preserving the histological architecture of the tissue cells, the procedure is called a needle as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bismuth Subsalicylate
Bismuth subsalicylate, sold generically as pink bismuth and under brand names including Pepto-Bismol, Pepti-Calm, and BisBacter, is a medication used to treat temporary discomfort of the stomach and gastrointestinal tract. This includes an upset stomach, heartburn, or other similar symptoms. Bismuth subsalicylate has the empirical chemical formula C7H5BiO4, and is a colloidal substance obtained by hydrolysis of bismuth salicylate (Bi(C6H4(OH)CO2)3). Medical uses As a derivative of salicylic acid, bismuth subsalicylate displays anti-inflammatory and bactericidal action. It also acts as an antacid. Mechanism of action Bismuth subsalicylate is used as an antacid and antidiarrheal, and to treat some other gastrointestinal symptoms, such as nausea. The means by which this occurs is still not well documented. It is thought to be some combination of the following: [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chlorhexidine
Chlorhexidine is a disinfectant and antiseptic which is used for skin disinfection before surgery and to disinfect surgical instruments. It is also used for cleaning wounds, preventing dental plaque, treating yeast infections of the mouth, and to keep urinary catheters from blocking. It is used as a liquid or a powder. It is commonly used in Ionic compound, salt form, either the gluconate or the acetate. Side effects may include skin irritation, Human tooth, tooth discoloration, and allergic reactions, although, apart from discoloration, the risk appears to be the same as that for povidone-iodine. Chlorhexidine rinse is also known to have a bitter metallic aftertaste. Rinsing with water is not recommended as it is known to increase the bitterness. It may cause eye problems if direct contact occurs. Use in pregnancy appears to be safe. Chlorhexidine may come mixed in ethanol, alcohol, water, or surfactant solution. It is effective against a range of microorganisms, but does not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liquorice
Liquorice ( Commonwealth English) or licorice (American English; see spelling differences; ) is the common name of ''Glycyrrhiza glabra'', a flowering plant of the bean family Fabaceae, from the root of which a sweet, aromatic flavouring is extracted. The liquorice plant is an herbaceous perennial legume native to West Asia, North Africa, and Southern Europe. Liquorice is used as a flavouring in confectionery, tobacco, beverages, and pharmaceuticals, and is marketed as a dietary supplement. Liquorice extracts have been used in herbalism and traditional medicine. Excessive consumption of liquorice (more than per day of pure glycyrrhizinic acid, a key component of liquorice) can lead to undesirable consequences. Clinically, it is suspected that overindulgence in liquorice may manifest as unexplained hypertension, low blood potassium levels ( hypokalemia), and muscle weakness in individuals. Consuming liquorice should be avoided during pregnancy. Etymology The word '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betel-chewing
Betel nut chewing, also called betel quid chewing or areca nut chewing, is a practice in which areca nuts (also called "betel nuts") are chewed together with slaked lime and betel leaves for their stimulant and narcotic effects, the primary psychoactive compound being arecoline. The practice is widespread in Southeast Asia, Micronesia, Island Melanesia, and South Asia. It is also found among both Han Chinese immigrants and indigenous peoples of Taiwan, Madagascar, and parts of southern China. It was introduced to the Caribbean in colonial times. The preparation combining the areca nut, slaked lime, and betel (Piper betle) leaves is known as a betel quid (also called ''paan'' or ''pan'' in South Asia), but the exact composition of the mixture varies geographically. It can sometimes include other substances for flavoring and to freshen the breath, like coconut, Date palm, dates, sugar, menthol, saffron, cloves, aniseed, cardamom, and many others. The areca nut can be replaced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niacin (nutrient)
Vitamin B3, colloquially referred to as niacin, is a vitamin family that includes three forms, or vitamers: nicotinic acid (niacin), nicotinamide (niacinamide), and nicotinamide riboside. All three forms of vitamin B3 are converted within the body to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD). NAD is required for human life and people are unable to make it within their bodies without either vitamin B3 or tryptophan. Nicotinamide riboside was identified as a form of vitamin B3 in 2004. Niacin (the nutrient) can be manufactured by plants and animals from the amino acid tryptophan. Niacin is obtained in the diet from a variety of whole and processed foods, with highest contents in fortified packaged foods, meat, poultry, red fish such as tuna and salmon, lesser amounts in nuts, legumes and seeds. Niacin as a dietary supplement is used to treat pellagra, a disease caused by niacin deficiency. Signs and symptoms of pellagra include skin and mouth lesions, anemia, headaches, and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |