|
Bitegmic
In biology, an integument is the tissue surrounding an organism's body or an organ within, such as skin, a husk, shell, germ or rind. Etymology The term is derived from ''integumentum'', which is Latin for "a covering". In a transferred, or figurative sense, it could mean a cloak or a disguise. In English, "integument" is a fairly modern word, its origin having been traced back to the early seventeenth century; and refers to a material or layer with which anything is enclosed, clothed, or covered in the sense of "clad" or "coated", as with a skin or husk. Botanical usage In botany, the term "integument" may be used as it is in zoology, referring to the covering of an organ. When the context indicates nothing to the contrary, the word commonly refers to an envelope covering the nucellus of the ovule. The integument may consist of one layer (unitegmic) or two layers (bitegmic), each of which consisting of two or more layers of cells. The integument is perforated by a por ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seed
A seed is an embryonic plant enclosed in a protective outer covering, along with a food reserve. The formation of the seed is a part of the process of reproduction in seed plants, the spermatophytes, including the gymnosperm and angiosperm plants. Seeds are the product of the ripened ovule, after the embryo sac is fertilized by sperm from pollen, forming a zygote. The embryo within a seed develops from the zygote, and grows within the mother plant to a certain size before growth is halted. The seed coat arises from the integuments of the ovule. Seeds have been an important development in the reproduction and success of vegetable gymnosperm and angiosperm plants, relative to more primitive plants such as ferns, mosses and liverworts, which do not have seeds and use water-dependent means to propagate themselves. Seed plants now dominate biological niches on land, from forests to grasslands both in hot and cold climates. The term "seed" also has a general meaning t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
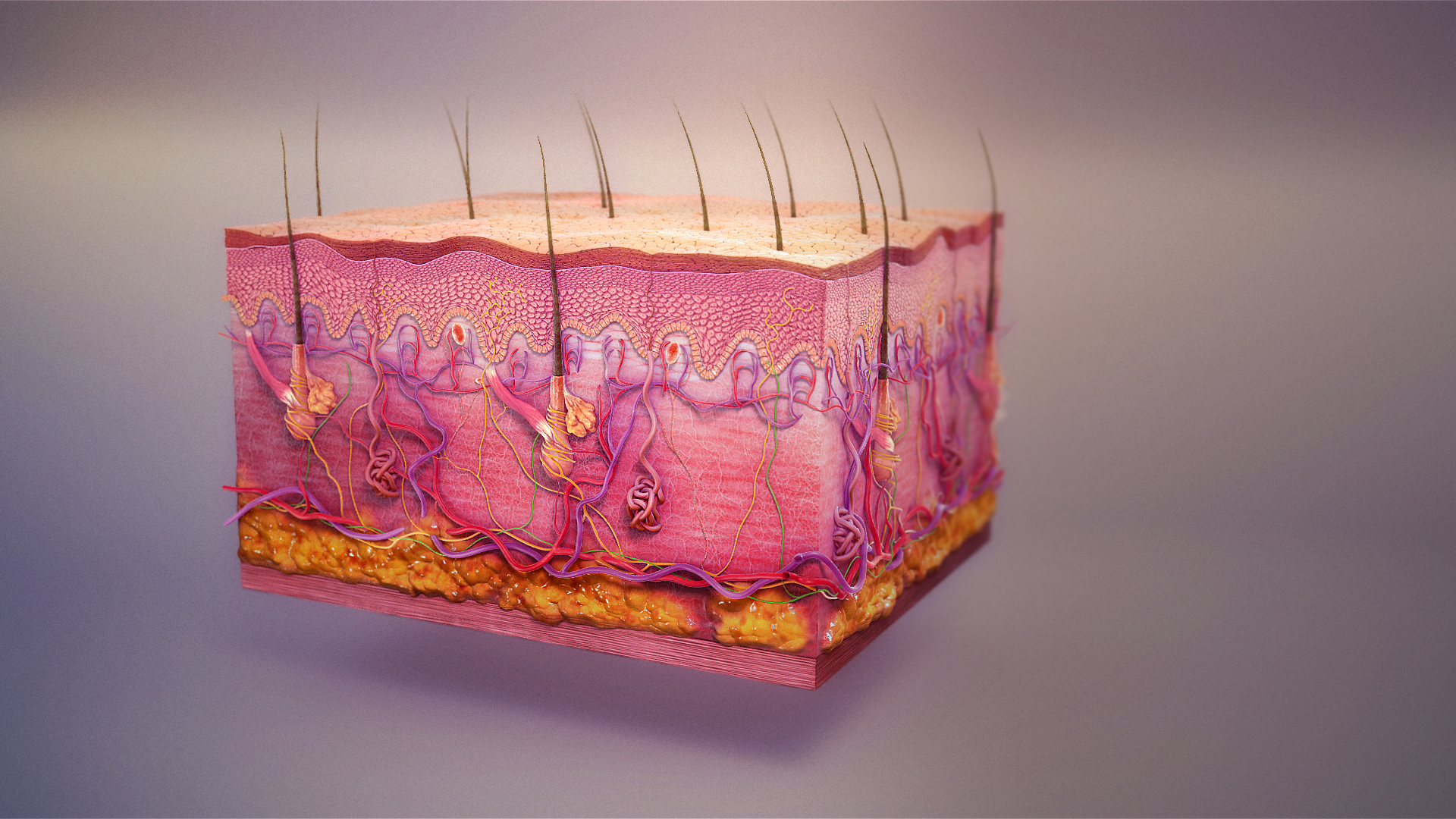
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different cellular differentiation, developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ (anatomy), organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuticle
A cuticle (), or cuticula, is any of a variety of tough but flexible, non-mineral outer coverings of an organism, or parts of an organism, that provide protection. Various types of "cuticle" are non-homologous, differing in their origin, structure, function, and chemical composition. Human anatomy In human anatomy, "cuticle" can refer to several structures, but it is used in general parlance, and even by medical professionals, to refer to the thickened layer of skin surrounding fingernails and toenails (the eponychium), and to refer to the superficial layer of overlapping cells covering the hair shaft ( cuticula pili), consisting of dead cells, that locks the hair into its follicle. It can also be used as a synonym for the epidermis, the outer layer of skin. Cuticle of invertebrates In zoology, the invertebrate cuticle or cuticula is a multi-layered structure outside the epidermis of many invertebrates, notably roundworms and arthropods, in which it forms an exoskelet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its beginnings in prehistoric times. Anatomy is inherently tied to developmental biology, embryology, comparative anatomy, evolutionary biology, and phylogeny, as these are the processes by which anatomy is generated, both over immediate and long-term timescales. Anatomy and physiology, which study the structure and function of organisms and their parts respectively, make a natural pair of related disciplines, and are often studied together. Human anatomy is one of the essential basic sciences that are applied in medicine. The discipline of anatomy is divided into macroscopic and microscopic. Macroscopic anatomy, or gross anatomy, is the examination of an animal's body parts using unaided eyesight. Gross anatomy also includes the branch o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mosasaur
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Ancient Greek, Greek ' meaning 'lizard') comprise a group of extinct, large marine reptiles from the Late Cretaceous. Their first fossil remains were discovered in a limestone quarry at Maastricht on the Meuse in 1764. They belong to the order Squamata, which includes lizards and snakes. Mosasaurs probably evolved from an extinct group of aquatic lizards known as Aigialosauridae, aigialosaurs in the Late Cretaceous, Earliest Late Cretaceous with 42 described genera. During the last 20 million years of the Cretaceous period (Turonian–Maastrichtian ages), with the extinction of the ichthyosaurs and Pliosauridae, pliosaurs, mosasaurs became the dominant marine predators. They themselves became extinct as a result of the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event, K-Pg event at the end of the Cretaceous period, about 66 million years ago. Description Mosasaurs breathed air, were powerful swimmers, and were well-adapted to livi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cat Anatomy
The anatomy of the domestic cat is similar to that of other members of the genus ''Felis''. Mouth Permanent dentition teeth Cats are carnivores that have highly specialized teeth. There are four types of permanent dentition teeth that structure the mouth: twelve ''incisors, four Canine tooth, canines, ten premolars and four Molar (tooth), molars.'' The premolar and first molar are located on each side of the mouth that together are called the carnassial pair. The carnassial pair specialize in cutting food and are parallel to the jaw. The incisors located in the front section of the lower and upper mouth are small, narrow, and have a single root. They are used for grasping and biting food. Deciduous dentition teeth A cat also has a deciduous dentition prior to the formation of the permanent one. This dentition emerges seven days after birth and it is composed of 26 teeth with slight differences. The mouth will have smaller incisors, slender and strongly curved upper canine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integumentary System
The integumentary system is the set of organs forming the outermost layer of an animal's body. It comprises the skin and its appendages, which act as a physical barrier between the external environment and the internal environment that it serves to protect and maintain the body of the animal. Mainly it is the body's outer skin. The integumentary system includes hair, Scale (zoology), scales, feathers, Hoof, hooves, and Nail (anatomy), nails. It has a variety of additional functions: it may serve to maintain water balance, protect the deeper tissues, excrete wastes, and regulate Core temperature, body temperature, and is the attachment site for sensory receptors which detect pain, sensation, pressure, and temperature. Structure Skin The skin is one of the largest organs of the body. In humans, it accounts for about 12 to 15 percent of total body weight and covers 1.5 to 2 m2 of surface area. The skin (integument) is a composite organ, made up of at least two major layers of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Herzog & De Meuron
Herzog & de Meuron Basel Ltd., " Herzog & de Meuron. Retrieved on 11 October 2012. "Herzog & de Meuron Basel Ltd. Rheinschanze 6 4056 Basel, Switzerland" is a Swiss architecture firm with its head office in , Switzerland. The careers of founders Jacques Herzog (born 19 April 1950) and Pierre de Meuron (born 8 May 1950) closely paralleled one another, with both attending the (ETH) in Zurich. They are perhaps best known for their conversion of the giant |
Flesh
Flesh is any aggregation of soft tissues of an organism. Various multicellular organisms have soft tissues that may be called "flesh". In mammals, including humans, ''flesh'' encompasses muscles, fats and other loose connective tissues, but sometimes excluding non-muscular organs (liver, lung, spleen, kidney) and typically discarded parts (hard tendon, brain tissue, intestines, etc.). In a culinary context, consumable animal flesh is called meat, while processed visceral tissues are known as offal. In particular animal groups such as vertebrates, molluscs and arthropods, the flesh is distinguished from tougher body structures such as bone, shell and scute, respectively. In plants, the "flesh" is the juicy, edible structures such as the mesocarp of fruits and melons as well as soft tubers, rhizomes and taproots, as opposed to tougher structures like nuts and stems. In fungi, ''flesh'' refers to trama, the soft, inner portion of a mushroom, or fruit body. A more restrictive u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flensing
Flensing is the removing of the blubber or outer integument of whales, separating it from the animal's meat. Processing the blubber (the subcutaneous fat) into whale oil was the key step that transformed a whale carcass into a stable, transportable commodity. It was an important part of the history of whaling. The whaling that still continues in the 21st century is both industrial and aboriginal. In aboriginal whaling the blubber is rarely rendered into oil, although it may be eaten as '' muktuk''. Terminology English whalemen called it ''flenching'', while American whalemen called it ''cutting-in''. Open-boat Shore and bay whaling In Spitsbergen, in the first half of the 17th century, the processing of whales was primarily done ashore. Where the whale was flensed differed between the English and Dutch. The English brought the whale to the stern of the ship, where men in a boat cut strips of blubber from the whale's back. These were tied together and rowed ashore, where ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dorsal Artery Of The Penis
The dorsal artery of the penis is an artery on the top surface of the penis. It is a branch of the internal pudendal artery. It runs forward on the dorsum of the penis to the glans, where it divides into two branches to the glans penis and the foreskin (prepuce). The dorsal artery of the penis supplies the integument and fibrous sheath of the corpus cavernosum penis, the glans penis, the foreskin, and the skin of the distal shaft. It also branches with circumflex arteries that supply the corpus spongiosum. Its role in erectile function is unknown. The dorsal artery of the penis may be damaged in traumatic amputation of the penis and repairing the dorsal artery surgically prevents skin loss, but it is not essential for sexual and urinary function. Its hemodynamics and blood pressure can be assessed to test for sexual impairment. Structure The dorsal artery of the penis is a branch of the internal pudendal artery. It ascends between the crus penis and the pubic symphys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |