|
Bissau-Guinean
This is a demography of the population of Guinea-Bissau including population density, ethnicity, education level, health of the populace, economic status, religious affiliations and other aspects of the population. Population According to the 2025 revision of the The World Factbook the total population was 2,132,325 in 2024. The proportion of children below the age of 14 in 2020 was 43.17%, 53.75% was between 15 and 65 years of age, while 3.08% was 65 years or older. The proportion of the population below the age of 15 in 2010 was 41.3%, 55.4% were aged between 15 and 65 years of age, while 3.3% were aged 65 years or older. Population Estimates by Sex and Age Group (01.VII.2019) (Data refer to national projections.): Vital statistics Registration of vital events is in Guinea-Bissau not complete. The Population Departement of the United Nations prepared the following estimates. Life expectancy Ethnic groups *Fulani 28.5% * Balanta 22.5% * Mandinga 14.7% * Papel 9.1% ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
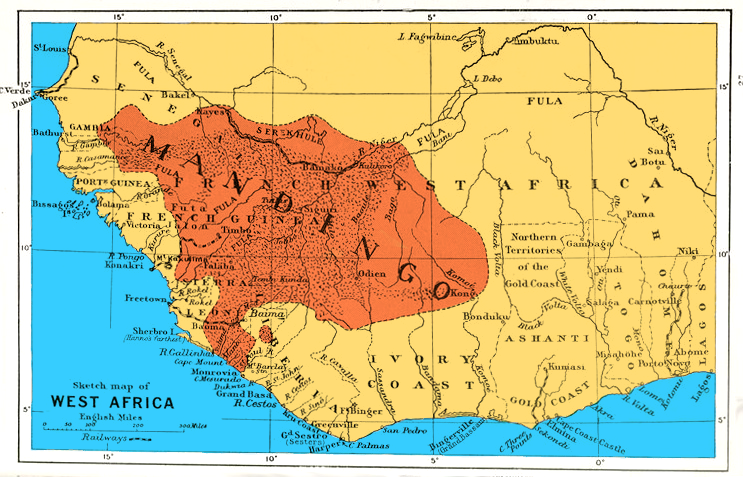
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, The Gambia, southern Senegal and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the List of ethnic groups of Africa, largest ethnolinguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family, which are a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. They are predominantly Subsistence agriculture, subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manjack People
Manjak people or the Manjaco (Manjak language, Manjak: Manjaku; French language, French: Mandjak; Portuguese language, Portuguese: Manjaco; Wolof language, Wolof: Njaago; Jola languages, Jola: Manjago) are a West African ethnic group who primarily reside in Guinea-Bissau with smaller communities in The Gambia, and Senegal. The Manjaco constitute about 14% of the population of Guinea-Bissau. Within Guinea-Bissau, the people primarily live in the Bassarel and Babok areas in the northern coastal Cacheu Region. Language The Manjak language is classified as part of the Bak languages, which is a branch of Niger–Congo. History Pre-colonization Based on early Portuguese records and observations, the Manjaco power structure and society was robust and well established. The people lived in a semi-feudal system where villages were under the subjugation of a leader and that leader reported to the king of the Bassarel and Babok areas, referred to as the King of Bassarel. The king of Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manjak People
Manjak people or the Manjaco ( Manjak: Manjaku; French: Mandjak; Portuguese: Manjaco; Wolof: Njaago; Jola: Manjago) are a West African ethnic group who primarily reside in Guinea-Bissau with smaller communities in The Gambia, and Senegal. The Manjaco constitute about 14% of the population of Guinea-Bissau. Within Guinea-Bissau, the people primarily live in the Bassarel and Babok areas in the northern coastal Cacheu Region. Language The Manjak language is classified as part of the Bak languages, which is a branch of Niger–Congo. History Pre-colonization Based on early Portuguese records and observations, the Manjaco power structure and society was robust and well established. The people lived in a semi-feudal system where villages were under the subjugation of a leader and that leader reported to the king of the Bassarel and Babok areas, referred to as the King of Bassarel. The king of Bassarel presided over a federation of areas some of which were more prosperous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guinea-Bissau Population
Guinea-Bissau, officially the Republic of Guinea-Bissau, is a country in West Africa that covers with an estimated population of 2,026,778. It borders Senegal to Guinea-Bissau–Senegal border, its north and Guinea to Guinea–Guinea-Bissau border, its southeast. Guinea-Bissau was once part of the kingdom of Kaabu, as well as part of the Mali Empire. Parts of this kingdom persisted until the 18th century, while a few others had been under some rule by the Portuguese Empire since the 16th century. In the 19th century, it was colonised as Portuguese Guinea. Portuguese control was restricted and weak until the early 20th century, when its pacification campaigns solidified Portuguese sovereignty in the area. The final Portuguese victory over the last remaining bastion of mainland resistance came in 1915, with the conquest of the Papel people, Papel-ruled Kingdom of Bissau by the Portuguese military officer João Teixeira Pinto, Teixeira Pinto and the Wolof people, Wolof mercenary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Balanta People
The Balanta ( Guinea-Bissau Creole and Portuguese: ''balanta''; ; lit. “those who resist” in Mandinka) are an ethnic group found in Guinea-Bissau, Guinea, Senegal, Cape Verde and The Gambia. They are the second largest ethnic group of Guinea-Bissau, representing around a quarter of the population. Despite their numbers, they have remained outside the colonial and postcolonial state because of their social organisation. The Balanta can be divided into six dialects: Nyacra, Ganja (Mane), Naga, Patch, Sofar and Kentohe. The largest of which are the Balanta Kentohe. The Balantas mainly get their last names from the name that is given to a clan, for example. "Na Sanyang", meaning, "house of Sanyang" – which points to a clan. Normally, in a Balanta society, houses are built based on clans. Normally, the Balantas name their children depending on the circumstances, situations and conditions they are in. For example, a child could be named as "Yabna", which means "rest"; "Alá ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Papel People
Papels, also known as Moium, Oium, Papei, Pepel or Pelels, are an ethnic group primarily located in Guinea-Bissau, though are also found in Casamance (Senegal) and Guinea. Their population in Guinea-Bissau is about 183,000, with 9,000 living outside of the country. They traditionally engaged in hunting and agriculture. History Origins According to oral history, a man named Mecau, the son of a king from the Kingdom of Quinara on the south of the river Geba, arrived at Bissau on one of his hunting trips. He opted to reside there due to its fertile soil and established a kingdom. From Quinara he brought his pregnant sister Punguenhum and his six wives: Intende, Djokom, Mala, Intsoma, Kliker and Intchipolo. Mecau invited other subjects from his father's kingdom to settle the area of Bissau alongside him. From his sister and six wives seven main Papel clans arose. * The N'nssassun (plural, bossassun) clan comes from the line of Punguenhum. This line inherited commandership ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mestizo
( , ; fem. , literally 'mixed person') is a term primarily used to denote people of mixed European and Indigenous ancestry in the former Spanish Empire. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though their ancestors were Indigenous American or Austronesian. The term was used as an ethno-racial exonym for mixed-race that evolved during the Spanish Empire. It was a formal label for individuals in official documents, such as censuses, parish registers, Inquisition trials, and others. Priests and royal officials might have classified persons as mestizos, but individuals also used the term in self-identification. With the Bourbon reforms and the independence of the Americas, the caste system disappeared and terms like "mestizo" fell in popularity. The noun , derived from the adjective , is a term for racial mixing that did not come into usage until the 20th century; it was not a colonial-era term.Rappaport, Joa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Portuguese People
The Portuguese people ( – masculine – or ''Portuguesas'') are a Romance languages, Romance-speaking ethnic group and nation Ethnic groups in Europe, indigenous to Portugal, a country that occupies the west side of the Iberian Peninsula in Southern Europe, south-west Europe, who share Culture of Portugal, culture, ancestry and Portuguese language, language. The Portuguese state began with the founding of the County of Portugal in 868. Following the Battle of São Mamede (1128), Portugal gained international recognition as a Kingdom of Portugal, kingdom through the Treaty of Zamora and the papal bull Manifestis Probatum. This Portuguese state paved the way for the Portuguese people to unite as a nation. The Portuguese Portuguese maritime exploration, explored Hic sunt Dracones, distant lands previously unknown to Europeans—in the Americas, Africa, Asia and Oceania (southwest Pacific Ocean). In 1415, with the conquest of Ceuta, the Portuguese took a significant role in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fula Language
Fula ( ),Laurie Bauer, 2007, ''The Linguistics Student's Handbook'', Edinburgh also known as Fulani ( ) or Fulah (, , ; Adlam script, Adlam: , , ; Ajami script, Ajami: , , ), is a Senegambian languages, Senegambian language spoken by around 36.8 million people as a set of various dialects in a Dialect continuum, continuum that stretches across some 18 countries in West Africa, West and Central Africa. Along with other related languages such as Serer language, Serer and Wolof language, Wolof, it belongs to the Atlantic languages, Atlantic geographic group within Niger–Congo languages, Niger–Congo, and more specifically to the Senegambian languages, Senegambian branch. Unlike most Niger-Congo languages, Fula does not have Tone (linguistics), tones. It is spoken as a first language by the Fula people ("Fulani", ) from the Senegambia, Senegambia region and Guinea to Cameroon, Nigeria, and Sudan and by related groups such as the Toucouleur people in the Senegal River Valley ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Verde
Cape Verde or Cabo Verde, officially the Republic of Cabo Verde, is an island country and archipelagic state of West Africa in the central Atlantic Ocean, consisting of ten volcanic islands with a combined land area of about . These islands lie between west of Cap-Vert, the westernmost point of continental Africa. The List of islands of Cape Verde, Cape Verde islands form part of the Macaronesia ecoregion, along with the Azores, the Canary Islands, Madeira and the Savage Isles. The Cape Verde archipelago was uninhabited until the 15th century, when Portuguese Empire, Portuguese explorers colonized the islands, establishing one of the first Age of Discovery, European settlements in the tropics. Due to its strategic position, Cape Verde became a significant location in the Atlantic slave trade, transatlantic slave trade during the 16th and 17th centuries. The islands experienced economic growth during this period, driven by their role by the rapid emergence of merchants, priva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |