|
Biskupija
Biskupija ( sr-Cyrl, Бискупија) is a village and municipality in Šibenik-Knin County, Croatia. The seat of the municipality is the village of Orlić. Etymology The word ''Biskupija'' in Croatian means diocese, referring to the former estate and seat of Croatian bishops in this area. The place was also known as ''Kosovo'' from 11th til 18th century, after the Kosovo field. ''Kosovo'' is still used as name for the train station located in the municipality. Geography The municipality covers a karst field called Kosovo field (, ) located between the mountains of Promina and Veliki Kozjak. The village of Biskupija itself is located in the north of the municipality, just south of Knin. The D33 and D1 state roads and the Zagreb-Split railway pass through the municipality. Languages Along with Croatian, which is the official language in the whole country, Serbian language and Serbian Cyrillic alphabet are co-official on the territory of the municipality. As of 2023, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knin
Knin () is a city in the Šibenik-Knin County of Croatia, located in the Dalmatian hinterland near the source of the river Krka (Croatia), Krka, an important traffic junction on the rail and road routes between Zagreb and Split, Croatia, Split. Knin rose to prominence twice in history, as the capital of both the Kingdom of Croatia (925–1102), medieval Kingdom of Croatia and briefly of the self-proclaimed Republic of Serbian Krajina within the newly independent Croatia, Republic of Croatia for the duration of the Croatian War of Independence from 1991 to 1995. Etymology The name is likely derived from the Illyrian language, Illyrian ''Ninia''. According to an alternative explanation, offered by Franz Miklosich and Petar Skok, the name - derived from a Slavic root ''*tьn-'' ("to cut", "to chop") - means "cleared forest". The medieval names of Knin include ; ; . The Latin name is still used as a titular see, titular episcopal see, the Diocese of Tinum. History Ancient The are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bishop Of Knin
The Diocese of Knin (, also ''Tinum'') was founded in 1050 and is today a titular see of the Latin Church of the Catholic Church. Its ''cathedra'' was located in Knin,''Annuario Pontificio 2013'' (Libreria Editrice Vaticana 2013 ), p. 991 Croatia. History The history of the diocese of Knin can be traced from the mid-11th century when a court bishop was established by the Kings of Croatia under the title "Bishop of the Croats" (''episcopus Chroatorum''). Its see was originally located in the Romanesque church of Saint Mary in the royal village of Biskupija near Knin. Following the 1185 ecclesial council in Split, the bishop was transferred to Knin, and renamed "Bishop of Knin". The construction of a new cathedral was initiated in 1203, on the basis of a previous 10th-century royal monastery in Kapitul, and was consecrated during the tenure of Bishop Nicholas (1270-1272). A history of the successive bishops, from Mark in 1050 to Joseph in 1755, is given in Daniele Farlati's ''Illy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Demetrius Zvonimir Of Croatia
Demetrius Zvonimir (, ; Old Church Slavic: ⰸⱏⰲⱏⱀⰻⰿⰻⱃⱏ; died 1089) was a King of Croatia and Dalmatia from 1075 or 1076 until his death in 1089. Prior to that, Zvonimir also served as Ban of Croatia (1064/1070–1074). His native name was Zvonimir, but adopted the forename Demetrius at his coronation. He first served as ban in the service of King Peter Krešimir IV. Afterwards, Peter Krešimir IV appointed him duke and declared him as his heir. In 1075 or 1076, Demetrius Zvonimir succeeded to the Croatian throne through papal diplomacy. His reign is characterized as relatively peaceful, with no extensive war campaigns, focused instead on Croatia's economic and cultural development. He inherited the Croatian state at its height and ruled from the city of Knin. Medieval legends allege his assassination, but his death and succession are subjects of controversy in historiography. His reign was followed by a period of anarchy, which ended with the ascension of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
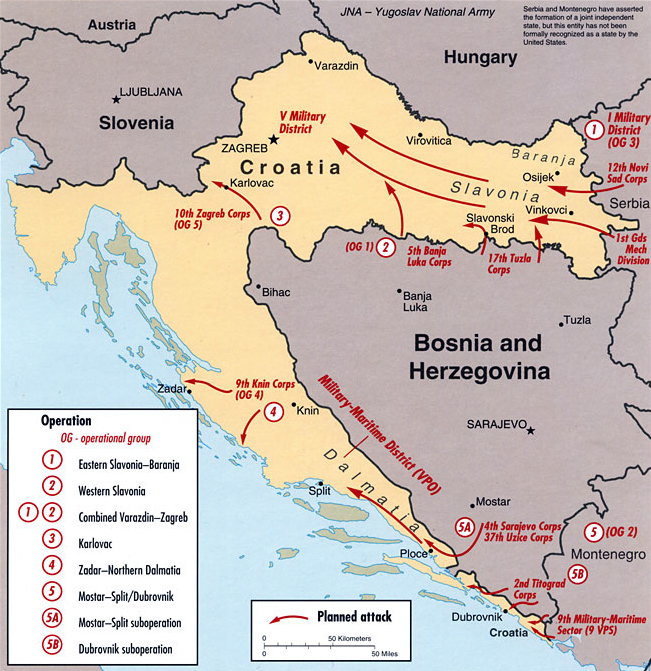
Croatian War Of Independence
The Croatian War of Independence) and (rarely) "War in Krajina" ( sr-Cyrl-Latn, Рат у Крајини, Rat u Krajini) are used. was an armed conflict fought in Croatia from 1991 to 1995 between Croats, Croat forces loyal to the Government of Croatia—which had declared Independence of Croatia, independence from the Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia (SFRY)—and the Serbs, Serb-controlled Yugoslav People's Army (JNA) and Serbs of Croatia, local Serb forces, with the JNA ending its combat operations by 1992. A majority of Croats supported Croatia's independence from Yugoslavia, while many ethnic Serbs living in Croatia, supported by Republic of Serbia (1992–2006), Serbia, opposed the secession and advocated Serb-claimed lands to be in a common state with Serbia. Most Serbs sought a new Serb state within a Yugoslav federation, including areas of Croatia and Bosnia and Herzegovina with ethnic Serb majorities or significant minorities, and attempted to conquer as muc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D33 Road (Croatia)
D33 connects Šibenik to Drniš and Knin. Furthermore, the road has junctions to major state roads, namely D8 in Šibenik, connecting to Biograd na Moru and Trogir, and D1 in Knin, which in turn connects to Sinj to the south and to Gračac to the north. The southern terminus of the road is found in Vidici interchange near Šibenik. The road is also connected to A1 motorway in Šibenik interchange. The road is long. The northern terminus of the road is at Strmica border crossing to Bosnia and Herzegovina, where the road proceeds to Drvar. Part of the road between Lozovac and Vidici interchange in Šibenik is executed as a single-carriageway, two-lane expressway with a speed limit of and, until 2012, used to be designated as D533 road. The road, as well as all other state roads in Croatia, is managed and maintained by Hrvatske ceste, a state-owned company. Traffic volume Traffic is regularly counted and reported by Hrvatske ceste, operator of the road. Substantial va ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
D1 Road (Croatia)
The state road D1 () is a national highway in Croatia. It is a one-lane highway that spans from Macelj border crossing in the north via Krapina, Zagreb, Karlovac, Slunj, Gračac, Knin, Sinj, ending in Split (city), Split. It is long overall. Before the A1 (Croatia), A1 and A2 (Croatia), A2 dual carriage motorways were completed in 2005 and 2007, respectively, the D1 was probably the busiest road during the summer in Croatia as it connected the northern border as well as the city of Zagreb with the tourist resorts on the Adriatic Sea. Since then, the traffic has waned significantly, but the D1 remains relevant as an alternative to the tolled highways. Route description North of Zagreb the D1 is mostly parallel to the A2 (Croatia), A2 motorway up to the Krapina interchange, connecting to a number of the A2 interchanges directly or via connector roads. It also runs parallel with railway tracks in some sections running through hilly terrain. A part of the D1 state r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Šibenik-Knin County
Šibenik-Knin County (; ) is a county in southern Croatia, located in the north-central part of Dalmatia. The biggest city in the county is Šibenik, which also serves as county seat. Other notable towns in the county are Knin, Vodice, Drniš and Skradin. The county covers 2984 km2. It includes 242 islands and national parks, Krka and Kornati. Administrative division Šibenik-Knin county is administratively subdivided into: * City of Šibenik (county seat) * City of Knin * Town of Drniš * Town of Skradin * Town of Vodice * Municipality of Biskupija * Municipality of Civljane * Municipality of Ervenik * Municipality of Kijevo * Municipality of Kistanje * Municipality of Murter-Kornati — Murter, the capital of the municipality * Municipality of Pirovac * Municipality of Primošten * Municipality of Promina — Oklaj, the capital of the municipality * Municipality of Rogoznica * Municipality of Ružić — Gradac, the capital of the municipality * Munici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of Croatia
Municipalities in Croatia (; plural: ''općine'') are the second-lowest administrative unit of government in the country, and along with List of cities in Croatia, cities and towns (''grad'', plural: ''gradovi'') they form the second level of administrative subdisivion, after Counties of Croatia, counties. Each municipality consists of one or more settlements (''naselja'') , which are the third-level spatial units of Croatia. Though equal in powers and administrative bodies, municipalities and towns differ in that municipalities are usually more likely to consist of a collection of villages in rural or suburban areas, whereas towns are more likely to cover urbanised areas. Law of Croatia, Croatian law defines municipalities as local self-government units which are established, in an area where several inhabited settlements represent a natural, economic and social entity, related to one other by the common interests of the area's population. As of 2023, the 21 counties of Croatia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dalmatian Hinterland
The Dalmatian Hinterland () is the southern inland hinterland in the historical Croatian region of Dalmatia. The name means 'beyond (the) hills', which is a reference to the fact that it is the part of Dalmatia that is not coastal and the existence of the concordant coastline where hills run parallel to the coast. Geography Dalmatian Zagora, in the strict sense, spans from the hinterland east of Šibenik to the border with Bosnia and Herzegovina and continues south to Vrgorac, just north of the Neum corridor. Its borders are present in two counties: Split-Dalmatia and Šibenik-Knin. The terrain in Zagora is fairly rugged: in the region immediately bordering the coastline, it is mostly flat but dry, mainly covered with ''makija'' (maquis, macchia). More inland, greener pastures can be seen, as the climate and elevations change. Karst topography dominates the landscape. The land is interspersed with river canyons, of Krka, Čikola, Cetina and others. One national park is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivan Meštrović
Ivan Meštrović (; 15 August 1883 – 16 January 1962) was a Croatian and Yugoslav sculptor, architect, and writer. He was the most prominent modern Croatian sculptor and a leading artistic personality in contemporary Zagreb. He studied at Pavao Bilinić's Stone Workshop in Split and at the Academy of Fine Arts Vienna, where he was formed under the influence of the Secession. He traveled throughout Europe and studied the works of ancient and Renaissance masters, especially Michelangelo, and French sculptors Auguste Rodin, Antoine Bourdelle and Aristide Maillol. He was the initiator of the national-romantic group Medulić (he advocated the creation of art of national features inspired by the heroic folk songs). During the First World War, he lived in emigration. After the war, he returned to Croatia and began a long and fruitful period of sculpture and pedagogical work. In 1942 he emigrated to Italy, in 1943 to Switzerland and in 1947 to the United States. He was a professor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veliki Kozjak
Veliki Kozjak or just Kozjak is a mountain cliff in Croatia, located inland of Dalmatian Zagora. It belongs to Dinaric Alps, and stretches over the small village Kijevo between the towns of Vrlika and Knin Knin () is a city in the Šibenik-Knin County of Croatia, located in the Dalmatian hinterland near the source of the river Krka (Croatia), Krka, an important traffic junction on the rail and road routes between Zagreb and Split, Croatia, Split. .... The highest peak of this cliff is ''Bat'' (1,207 m), and its southeast peak is ''Kunica'' (1,101 m), over the small village of Maovice. Gallery Kozjak north.jpg, Kozjak from the north in winter See also * List of mountains in Croatia Mountains of Croatia Cliffs of Europe Landforms of Šibenik-Knin County {{Dalmatia-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serbian Cyrillic
The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet (, ), also known as the Serbian script, (, ), is a standardized variation of the Cyrillic script used to write the Serbian language. It originated in medieval Serbia and was significantly reformed in the 19th century by the Serbian philologist and linguist Vuk Karadžić. The Serbian Cyrillic alphabet is one of the two official scripts used to write modern standard Serbian, the other being Gaj's Latin alphabet. Karadžić based his reform on the earlier 18th-century Slavonic-Serbian script. Following the principle of "write as you speak and read as it is written" (''piši kao što govoriš, čitaj kao što je napisano''), he removed obsolete letters, eliminated redundant representations of iotated vowels, and introduced the letter from the Latin script. He also created new letters for sounds unique to Serbian phonology. Around the same time, Ljudevit Gaj led the standardization of the Latin script for use in western South Slavic languages, appl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |