|
Bishop Head Pawn
In shogi, the Bishop Head Pawn or Bishop's Head Pawn Push (角頭歩 or 角頭歩突き ) is a surprise opening Opening may refer to: * Al-Fatiha, "The Opening", the first chapter of the Qur'an * The Opening (album), live album by Mal Waldron * Backgammon opening * Chess opening * A title sequence or opening credits * , a term from contract bridge * , .... The opening is characterized by advancing early in the game the bishop's head pawn on 87 to 86 if played by Black or on 23 to 24 if played by White, in which it is undefended. This is a daring move since the head of the bishop (the 87 or 23 square) needs to be defended from a Static Rook attack and moving the bishop's head pawn forward increases the vulnerability of the bishop's head. It can be developed into a Ranging Rook position and is played against a Static Rook position. The opening was used by professional Kunio Yonenaga in tournament play in the 1960s and 1970s. Development 1. P-76 P-34. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, '' chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and '' janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Opening
A shogi opening ( ) is the sequence of initial moves of a shogi game before the middle game. The more general Japanese term for the beginning of the game is ()''.'' A '' jōseki'' () is the especially recommended sequence of moves for a given opening that was considered balanced play at one point in time for both sides by professional players. (However, some ''s'' have become outdated when they are reevaluated to no longer give balanced play.) ''s'' also typically include commentary about the possible reasons to deviate from the especially regarding blunders. Note that not all openings have ''s''. For example, trap openings like Demon Slayer, while they may have standard moves, are considered to favor one player and are not balanced play. Thus, the Demon Slayer opening is not a jōseki. Introduction The very first opening moves in most games are pawn pushes. In particular, most games start with two types of pawn pushes. A player can move the rook pawn forward (P-26) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
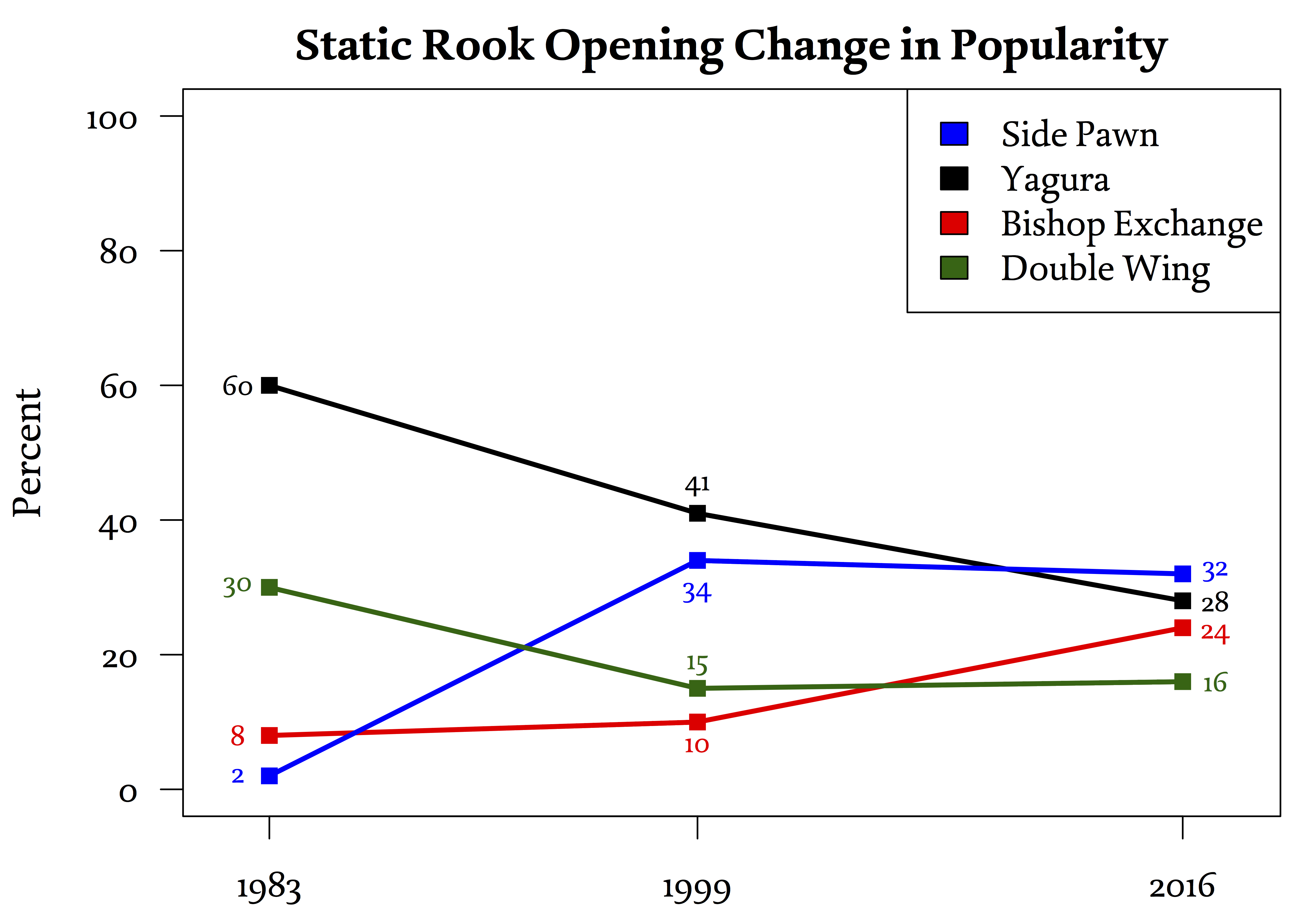
Static Rook
Static Rook (居飛車 ''ibisha'') openings in shogi typically have the player's rook at its start position, which is the second file (on the 28 square) for Black and the eighth file (on the 82 square) for White. Explanation Static Rook is a set of openings in which the rook remains on its starting square, which is the 28 square if played by Black and the 82 square if played by White. It is also possible to include other openings where the rook moves to another file that is still on the players right side of the board, such as the third file or the fourth file. The reason for including these other openings where the rook is not technically ''static'' is because the typical castle fortifications constructed to the protect the Static Rook player's king are usually the same for these openings. Nonetheless, some shogi theory does categorize these openings with right side rook movement into the same group as Ranging Rook openings despite the disparity in castle formation. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranging Rook
Ranging Rook or Swinging Rook (振り飛車 ''furibisha'') openings in shogi position the rook to the center or left of the player's board to support an attack there. Ranging Rook strategies used in Ranging Rook vs Static Rook are among the oldest of shogi strategies attested in the historical documents that first describe the rules of shogi around 1600. Description Types of Ranging Rook Traditionally, Ranging Rook has been used as a defensive strategy for White against Static Rook openings played by Black. White's rook can be moved flexibly to counteract Black's attacks. These types of White openings are named simply Ranging Rook (振り飛車 ''furibisha''). In describing the game positions of both opponents, the term is Static Rook vs Ranging Rook (居飛車対振り飛車 ''ibisha tai furibisha''). In these games, Black has the initiative, and White quickly builds a defense by castling the king and seeks counterattacking opportunities. By default, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kunio Yonenaga
was a Japanese professional shogi player and president of Japan Shogi Association (May, 2005 - December 18, 2012). He received an honorary title Lifetime Kisei due to his remarkable results in the Kisei title tournament. He is a former Meijin and 10- dan. Biography Yonenaga was born in Masuho, Yamanashi in 1943. He became a disciple of shogi professional Yūji Sase and moved to Tokyo to live with his teacher to become a professional. Yonenaga became a professional in 1963, and was promoted to 9 dan in 1979. Yonenaga was regarded as one of the best shogi players through the 1970s and 1980s. He won Kisei, his first titleholder championship in 1973 and dominated four of the seven shogi titles in 1984. He was awarded as Best Shogi Player of the Year thrice (1978, 1983 and 1984), though he had not won a Meijin title, then regarded the supreme tournament, for decades. He finally won Meijin in 1993 when he was 49 (the oldest on record), but he was defeated by Yoshiharu Habu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shogi Openings
, also known as Japanese chess, is a strategy board game for two players. It is one of the most popular board games in Japan and is in the same family of games as Western chess, ''chaturanga, Xiangqi'', Indian chess, and ''janggi''. ''Shōgi'' means general's (''shō'' ) board game (''gi'' ). Western chess is sometimes called (''Seiyō Shōgi'' ) in Japan. Shogi was the earliest chess-related historical game to allow captured pieces to be returned to the board by the capturing player. This drop rule is speculated to have been invented in the 15th century and possibly connected to the practice of 15th century mercenaries switching loyalties when captured instead of being killed. The earliest predecessor of the game, chaturanga, originated in India in the sixth century, and the game was likely transmitted to Japan via China or Korea sometime after the Nara period."Shogi". ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. 2002. Shogi in its present form was played as early as the 16th century, whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranging Rook Openings
Length measurement, distance measurement, or range measurement (ranging) refers to the many ways in which length, distance, or range can be measured. The most commonly used approaches are the rulers, followed by transit-time methods and the interferometer methods based upon the speed of light. For objects such as crystals and diffraction gratings, diffraction is used with X-rays and electron beams. Measurement techniques for three-dimensional structures very small in every dimension use specialized instruments such as ion microscopy coupled with intensive computer modeling. Standard rulers The ruler the simplest kind of length measurement tool: lengths are defined by printed marks or engravings on a stick. The metre was initially defined using a ruler before more accurate methods became available. Gauge blocks are a common method for precise measurement or calibration of measurement tools. For small or microscopic objects, microphotography where the length is calibrated u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |