|
Bisabolol
Bisabolol, or more formally α-(−)-bisabolol or also known as levomenol, is a natural monocyclic sesquiterpene alcohol. It is a colorless viscous oil that is the primary constituent of the essential oil from German chamomile (''Matricaria recutita'') and ''Myoporum crassifolium''. High concentrations of bisabolol can also be found in certain medicinal cannabis cultivars. It is poorly soluble in water and glycerine, but soluble in ethanol. The enantiomer, α-(+)-bisabolol, is also found naturally but is rare. Synthetic bisabolol is usually a racemic mixture of the two, α-(±)-bisabolol. It is the terpenoid responsible for distinctive aroma of chamomile flowers, and when isolated, its scent has also has been likened to apples, sugar and honey. Bisabolol has a weak sweet floral aroma and is used in various fragrances. It has also been used for hundreds of years in cosmetics because of its skin healing properties including reducing wrinkles, skin toughness and repairing sun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Chamomile
''Matricaria chamomilla'' (synonym: ''Matricaria recutita''), commonly known as chamomile (also spelled camomile), German chamomile, Hungarian chamomile (kamilla), wild chamomile, blue chamomile, or scented mayweed, is an annual plant of the composite family Asteraceae. Commonly, the name ''M. recutita'' is applied to the most popular source of the herbal product chamomile, although other species are also used as chamomile. Chamomile is known mostly for its use against gastrointestinal problems; additionally, it can be used to treat irritation of the skin. Description ''Matricaria chamomilla'' is a member of the Asteraceae family, native to southern and eastern Europe. Today the plant can be found on all continents. It has a branched, erect and smooth stem, which grows to a height of . The long and narrow leaves are bipinnate or tripinnate. The flowers are borne in paniculate flower heads (capitula). The white ray florets are furnished with a ligule, while the disc floret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Myoporum Crassifolium
''Myoporum crassifolium'' is a plant in the figwort family, Scrophulariaceae. It is a shrub or small tree with thick, fleshy leaves and small groups of white flowers spotted with pink or purple. It is endemic to New Caledonia, Vanuatu and the Loyalty Islands and is a rich source of the essential oil, bisabolol. Description ''Myoporum crassifolium'' is a shrub or small tree which grows to a height of . The leaves are arranged alternately and are long, wide, glabrous, thick and fleshy. They are elliptic to egg-shaped, sometimes with the narrower end towards the base, shiny on both surfaces with the mid-vein more prominent on the lower surface. The flowers are arranged in groups of 3 to 6 in the axils of the leaves and have 5 sepals and 5 white, spotted pink petals joined at their base to form a tube. The tube is long and the lobes are spreading and long. There are 4 stamens which extend slightly beyond the petals. The fruit is a pale purple to mauve, roughly spherical d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesquiterpene
Sesquiterpenes are a class of terpenes that consist of three isoprene units and often have the molecular formula C15H24. Like monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes may be cyclic or contain rings, including many unique combinations. Biochemical modifications such as oxidation or rearrangement produce the related sesquiterpenoids. Sesquiterpenes are found naturally in plants and insects, as semiochemicals, e.g. defensive agents or pheromones. Biosynthesis and examples The reaction of geranyl pyrophosphate with isopentenyl pyrophosphate results in the 15-carbon farnesyl pyrophosphate (FPP), which is an intermediate in the biosynthesis of sesquiterpenes such as farnesene. Cyclic sesquiterpenes are more common than cyclic monoterpenes because of the increased chain length and additional double bond in the sesquiterpene precursors. In addition to common six-membered ring systems such as the ones found in zingiberene and bisacurone, cyclization of one end of the chain to the other en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
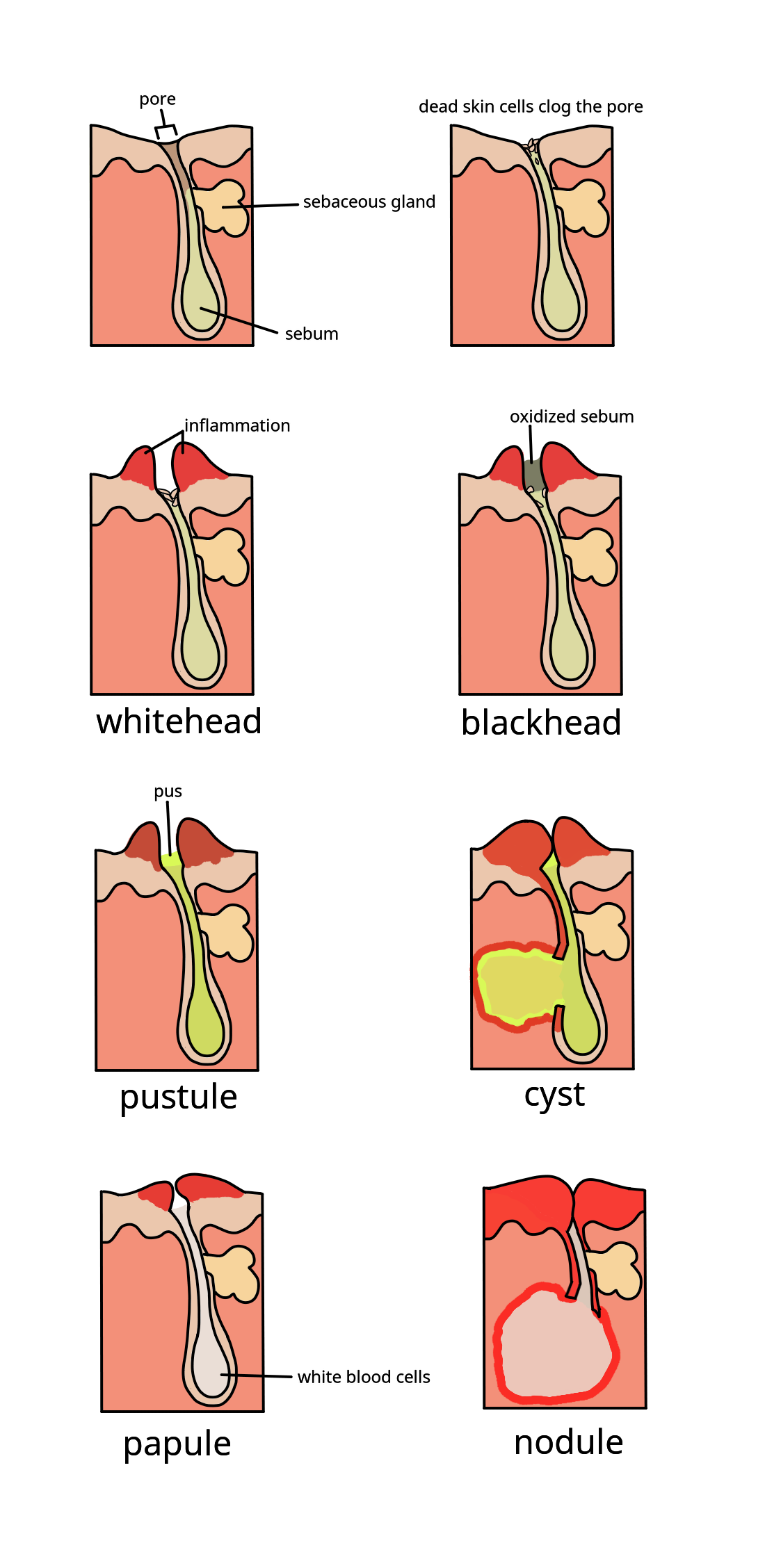
Acne
Acne, also known as ''acne vulgaris'', is a long-term skin condition that occurs when dead skin cells and oil from the skin clog hair follicles. Typical features of the condition include blackheads or whiteheads, pimples, oily skin, and possible scarring. It primarily affects skin with a relatively high number of oil glands, including the face, upper part of the chest, and back. The resulting appearance can lead to anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and, in extreme cases, depression or thoughts of suicide. Susceptibility to acne is primarily genetic in 80% of cases. The roles of diet and cigarette smoking in the condition are unclear, and neither cleanliness nor exposure to sunlight appear to play a part. In both sexes, hormones called androgens appear to be part of the underlying mechanism, by causing increased production of sebum. Another common factor is the excessive growth of the bacterium '' Cutibacterium acnes'', which is present on the skin. Treatments for ac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmetics Chemicals
Cosmetics are constituted mixtures of chemical compounds derived from either Natural product, natural sources, or synthetically created ones. Cosmetics have various purposes. Those designed for personal care and skin care can be used to Cleaning, cleanse or protect the body or skin. Cosmetics designed to enhance or alter one's appearance (makeup) can be used to conceal blemishes, enhance one's natural features (such as the eyebrows and eyelashes), add color to a person's face, or change the appearance of the face entirely to resemble a different person, creature or object. Cosmetics can also be designed to add fragrance to the body. Definition and etymology The word ''cosmetics'' derives from the Ancient Greek, Greek (), meaning "technique of dress and ornament", from (), "skilled in ordering or arranging" and that from (), meaning "order" and "ornament". Cosmetics are constituted from a mixture of chemical compounds derived from either natural sources, or synthetical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perfume Ingredients
Perfume (, ; french: parfum) is a mixture of fragrant essential oils or aroma compounds (fragrances), fixatives and solvents, usually in liquid form, used to give the human body, animals, food, objects, and living-spaces an agreeable scent. The 1939 Nobel Laureate for Chemistry, Leopold Ružička stated in 1945 that "right from the earliest days of scientific chemistry up to the present time, perfumes have substantially contributed to the development of organic chemistry as regards methods, systematic classification, and theory." Ancient texts and archaeological excavations show the use of perfumes in some of the earliest human civilizations. Modern perfumery began in the late 19th century with the commercial synthesis of aroma compounds such as vanillin or coumarin, which allowed for the composition of perfumes with smells previously unattainable solely from natural aromatics. History The word ''perfume'' derives from the Latin ''perfumare'', meaning "to smoke through" ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tertiary Alcohols
In chemistry, an alcohol is a type of organic compound that carries at least one hydroxyl () functional group bound to a saturated carbon atom. The term ''alcohol'' originally referred to the primary alcohol ethanol (ethyl alcohol), which is used as a drug and is the main alcohol present in alcoholic drinks. An important class of alcohols, of which methanol and ethanol are the simplest examples, includes all compounds which conform to the general formula . Simple monoalcohols that are the subject of this article include primary (), secondary () and tertiary () alcohols. The suffix ''-ol'' appears in the IUPAC chemical name of all substances where the hydroxyl group is the functional group with the highest priority. When a higher priority group is present in the compound, the prefix ''hydroxy-'' is used in its IUPAC name. The suffix ''-ol'' in non-IUPAC names (such as paracetamol or cholesterol) also typically indicates that the substance is an alcohol. However, some compo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
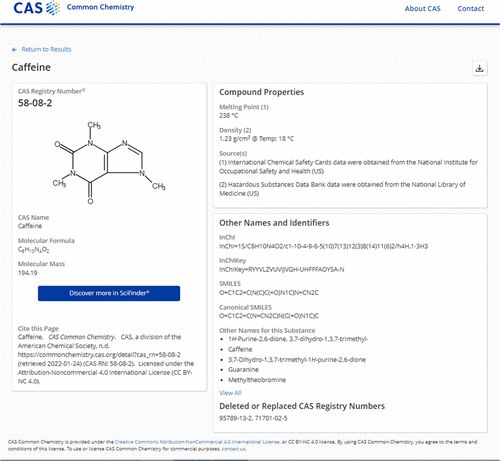
CAS Registry Number
A CAS Registry Number (also referred to as CAS RN or informally CAS Number) is a unique identification number assigned by the Chemical Abstracts Service (CAS), US to every chemical substance described in the open scientific literature. It includes all substances described from 1957 through the present, plus some substances from as far back as the early 1800s. It is a chemical database that includes organic and inorganic compounds, minerals, isotopes, alloys, mixtures, and nonstructurable materials (UVCBs, substances of unknown or variable composition, complex reaction products, or biological origin). CAS RNs are generally serial numbers (with a check digit), so they do not contain any information about the structures themselves the way SMILES and InChI strings do. The registry maintained by CAS is an authoritative collection of disclosed chemical substance information. It identifies more than 182 million unique organic and inorganic substances and 68 million protein and D ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skin
Skin is the layer of usually soft, flexible outer tissue covering the body of a vertebrate animal, with three main functions: protection, regulation, and sensation. Other cuticle, animal coverings, such as the arthropod exoskeleton, have different cellular differentiation, developmental origin, structure and chemical composition. The adjective cutaneous means "of the skin" (from Latin ''cutis'' 'skin'). In mammals, the skin is an organ (anatomy), organ of the integumentary system made up of multiple layers of ectodermal tissue (biology), tissue and guards the underlying muscles, bones, ligaments, and internal organs. Skin of a different nature exists in amphibians, reptiles, and birds. Skin (including cutaneous and subcutaneous tissues) plays crucial roles in formation, structure, and function of extraskeletal apparatus such as horns of bovids (e.g., cattle) and rhinos, cervids' antlers, giraffids' ossicones, armadillos' osteoderm, and os penis/os clitoris. All mammals have som ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Penetration Enhancer
Penetration may refer to: Science and technology * Passage through a partition or wall by a wire, cable, or other electrically conductive object * Penetration (firestop), an opening in a wall or floor assembly required to have a fire-resistance rating, for the purpose of accommodating the passage of a mechanical, electrical, or structural penetrant * Penetration (weapons), the ability to pierce the target's armor or other protection * Penetration depth of light or any electromagnetic radiation in a physical medium * Penetrating trauma, injury that occurs when an object pierces the skin and enters a tissue of the body * In roofing, pipes, conduits, and HVAC supports passing through the roof * An unauthorized act of bypassing access control Arts and media * Penetration (band), a punk rock band * "Penetration", a song on Iggy and the Stooges' album ''Raw Power'' * "Penetration", a song on Pedro the Lion's album ''Control'' * "Penetration", a song by The Pyramids * ''Body of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |