|
Biplane
A biplane is a fixed-wing aircraft with two main wings stacked one above the other. The first powered, controlled aeroplane to fly, the Wright Flyer, used a biplane wing arrangement, as did many aircraft in the early years of aviation. While a biplane wing structure has a structural advantage over a monoplane, it produces more drag than a monoplane wing. Improved structural techniques, better materials and higher speeds made the biplane configuration obsolete for most purposes by the late 1930s. Biplanes offer several advantages over conventional cantilever monoplane designs: they permit lighter wing structures, low wing loading and smaller span for a given wing area. However, interference between the airflow over each wing increases drag substantially, and biplanes generally need extensive bracing, which causes additional drag. Biplanes are distinguished from tandem wing arrangements, where the wings are placed forward and aft, instead of above and below. The term is als ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interplane Strut
In aeronautics, bracing comprises additional structural members which stiffen the functional airframe to give it rigidity and strength under load. Bracing may be applied both internally and externally, and may take the form of struts, which act in compression or tension as the need arises, and/or wires, which act only in tension. In general, bracing allows a stronger, lighter structure than one which is unbraced, but external bracing in particular adds drag which slows down the aircraft and raises considerably more design issues than internal bracing. Another disadvantage of bracing wires is that they require routine checking and adjustment, or rigging, even when located internally. During the early years of aviation, bracing was a universal feature of all forms of aeroplanes, including the monoplanes and biplanes, which were then equally common. Today, bracing in the form of lift struts is still used for some light commercial designs where a high wing and light weight are more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Travel Air 2000
The Travel Air 2000 is an open-cockpit biplane aircraft produced in the United States in the late 1920s by the Travel Air, Travel Air Manufacturing Company. During the period from 1924–1929, Travel Air produced more aircraft than any other American manufacturer, including over 1,000 biplanes. While an exact number is almost impossible to ascertain due to the number of conversions and rebuilds, some estimates for Travel Air as a whole range from 1,200 to nearly 2,000 aircraft.Wilkinson, 28 February 2014, pp.? Design and development The Travel Air Model A was engineered chiefly by Lloyd Stearman, with input from Travel Air co-founders Walter Beech, Clyde Cessna, and Bill Snook and could trace its ancestry back to the Swallow New Swallow biplane. The Travel Air, however, replaced the New Swallow's wooden fuselage structure with welded steel tubes. An interim design, the Winstead Special, was developed by the Winstead brothers from a metal fuselage frame developed at Swallow b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fighter Aircraft
Fighter aircraft (early on also ''pursuit aircraft'') are military aircraft designed primarily for air-to-air combat. In military conflict, the role of fighter aircraft is to establish air supremacy, air superiority of the battlespace. Domination of the airspace above a battlefield permits bombers and attack aircraft to engage in tactical bombing, tactical and strategic bombing of enemy targets, and helps prevent the enemy from doing the same. The key performance features of a fighter include not only its firepower but also its high speed and maneuverability relative to the target aircraft. The success or failure of a combatant's efforts to gain air superiority hinges on several factors including the skill of its pilots, the tactical soundness of its doctrine for deploying its fighters, and the numbers and performance of those fighters. Many modern fighter aircraft also have secondary capabilities such as ground-attack aircraft, ground attack and some types, such as fighter-b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
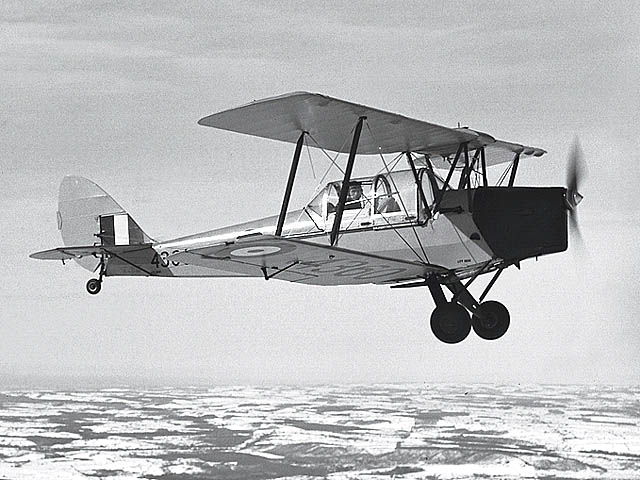
De Havilland Tiger Moth
The de Havilland DH.82 Tiger Moth is a 1930s British biplane designed by Geoffrey de Havilland and built by the de Havilland, de Havilland Aircraft Company. It was operated by the Royal Air Force (RAF) and other operators as a primary trainer (aircraft), trainer aircraft. In addition to the type's principal use for ''ab initio'' training, the World War II, Second World War had RAF Tiger Moths operating in other capacities, including Maritime patrol aircraft, maritime surveillance and defensive anti-invasion preparations; some aircraft were even outfitted to function as armed light bombers. The Tiger Moth remained in service with the RAF until it was replaced by the de Havilland Canada DHC-1 Chipmunk, de Havilland Chipmunk during the early 1950s. Many of the military surplus aircraft subsequently entered into civilian operation. Many nations have used the Tiger Moth in both military and civilian applications, and it remains in widespread use as a recreational aircraft. It is s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aileron
An aileron (French for "little wing" or "fin") is a hinged flight control surface usually forming part of the trailing edge of each wing of a fixed-wing aircraft. Ailerons are used in pairs to control the aircraft in roll (or movement around the aircraft's longitudinal axis), which normally results in a change in flight path due to the tilting of the lift vector. Movement around this axis is called rolling or banking. Considerable controversy exists over credit for the invention of the aileron. The Wright brothers and Glenn Curtiss fought a years-long legal battle over the Wright patent of 1906, which described a method of wing-warping to achieve lateral control. The brothers prevailed in several court decisions which found that Curtiss's use of ailerons violated the Wright patent. Ultimately, the First World War compelled the U.S. Government to legislate a legal resolution. A much earlier aileron concept was patented in 1868 by British scientist Matthew Piers Watt Boul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoplane
A monoplane is a fixed-wing aircraft configuration with a single mainplane, in contrast to a biplane or other types of multiplanes, which have multiple wings. A monoplane has inherently the highest efficiency and lowest drag of any wing configuration and is the simplest to build. However, during the early years of flight, these advantages were offset by its greater weight and lower manoeuvrability, making it relatively rare until the 1930s. Since then, the monoplane has been the most common form for a fixed-wing aircraft. Characteristics Support and weight The inherent efficiency of the monoplane is best achieved in the cantilever wing, which carries all structural forces internally. However, to fly at practical speeds the wing must be made thin, which requires a heavy structure to make it strong and stiff enough. External bracing can be used to improve structural efficiency, reducing weight and cost. For a wing of a given size, the weight reduction allows it to fly slowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tandem Wing
QAC Quickie Q2 A tandem wing is a wing configuration in which a flying craft or animal has two or more sets of wings set one behind another. All the wings contribute to lift. The tandem wing is distinct from the biplane in which the wings are stacked one above another, or from the canard or "tail-first" configuration where the forward surface is much smaller and does not contribute significantly to the overall lift. In aviation, tandem wings have long been experimented with, but few designs have ever been put into production. Tandem wings in nature occur only in insects and flying fish, although in the past there have been tandem-wing flying reptiles. Design principles A tandem wing configuration has two main wing planes, with one located forward and the other to the rear. The difference is greater than the wing chord, so there is a clear gap between them and the aircraft centre of gravity (CG) lies between the wings.Bottomley (1977) Compared to the conventional layout, whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antonov An2 Ha-mkf Arp
Antonov ( d/b/a Antonov Company, formerly the Aeronautical Scientific-Technical Complex named after Antonov or Antonov ASTC, and earlier the Antonov Design Bureau, for its chief designer, Oleg Antonov) is a Ukrainian aircraft manufacturing and services company. Antonov's particular expertise is in the fields of very large aeroplanes and aeroplanes using unprepared runways. Antonov (model prefix "An-") has built a total of approximately 22,000 aircraft, and thousands of its planes are operating in the former Soviet Union and in developing countries. Antonov Company is a state-owned commercial company originally established in Novosibirsk, Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR). In 1952, the company relocated to Kyiv, Ukrainian SSR, then part of the Soviet Union. On 12 May 2015, it was transferred from the Ministry of Economic Development and Trade to the Ukroboronprom (Ukrainian Defense Industry). In June 2016, Ukraine's major state-owned arms manufacturer Uk ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeroplane
An airplane (American English), or aeroplane (Commonwealth English), informally plane, is a fixed-wing aircraft that is propelled forward by thrust from a jet engine, Propeller (aircraft), propeller, or rocket engine. Airplanes come in a variety of sizes, shapes, and wing configurations. The broad spectrum of uses for airplanes includes recreation, air transportation, transportation of goods and people, military aviation, military, and Experimental aircraft, research. Worldwide, commercial aviation transports more than four billion passengers annually on airliners and transports more than 200 billion tonne-kilometersMeasured in RTKs—an RTK is one tonne of revenue freight carried one kilometer. of cargo annually, which is less than 1% of the world's cargo movement. Most airplanes are flown by a pilot on board the aircraft, but some are designed to be unmanned aerial vehicle, remotely or computer-controlled such as drones. The Wright brothers invented and flew the Wright Flyer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
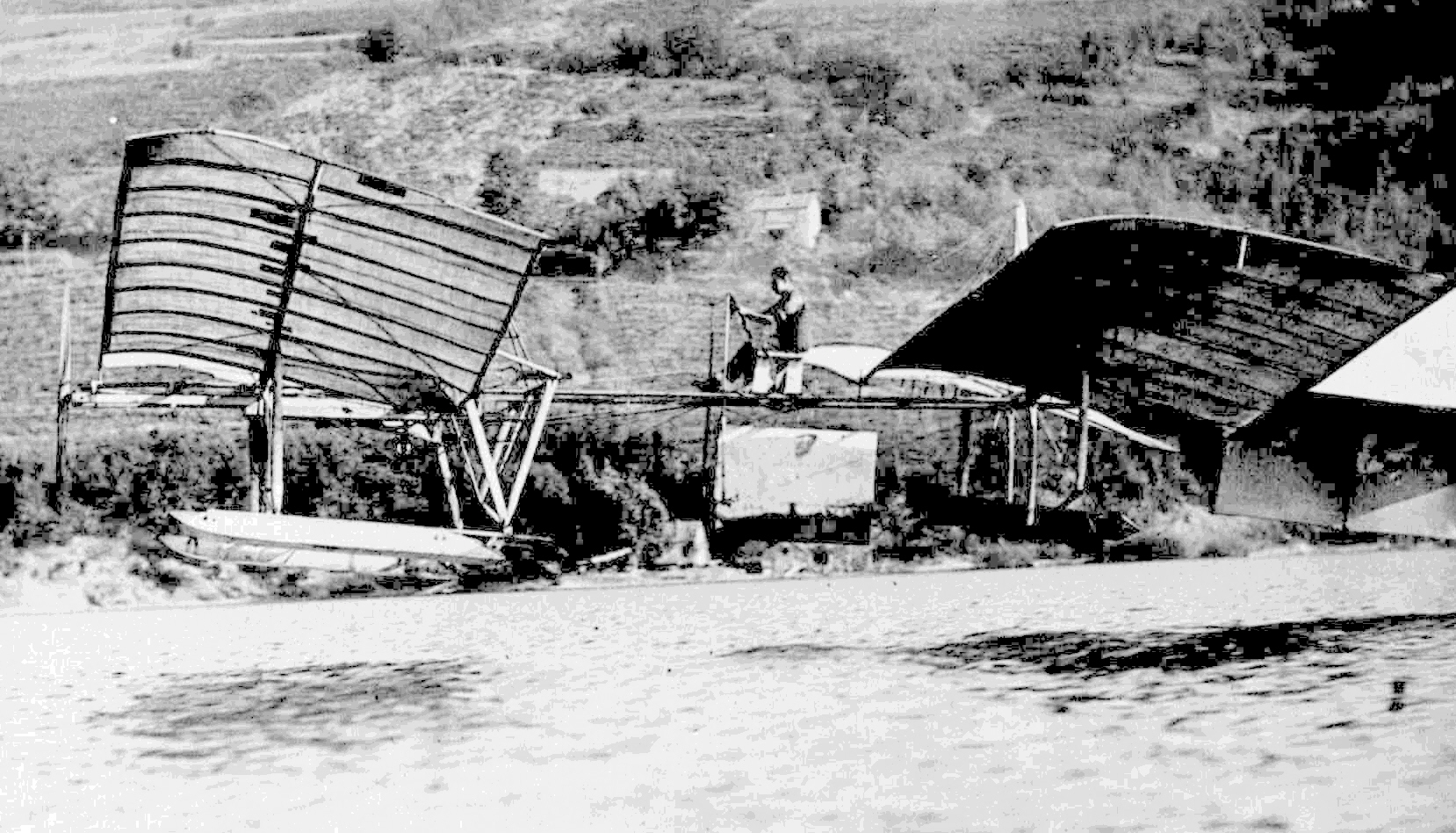
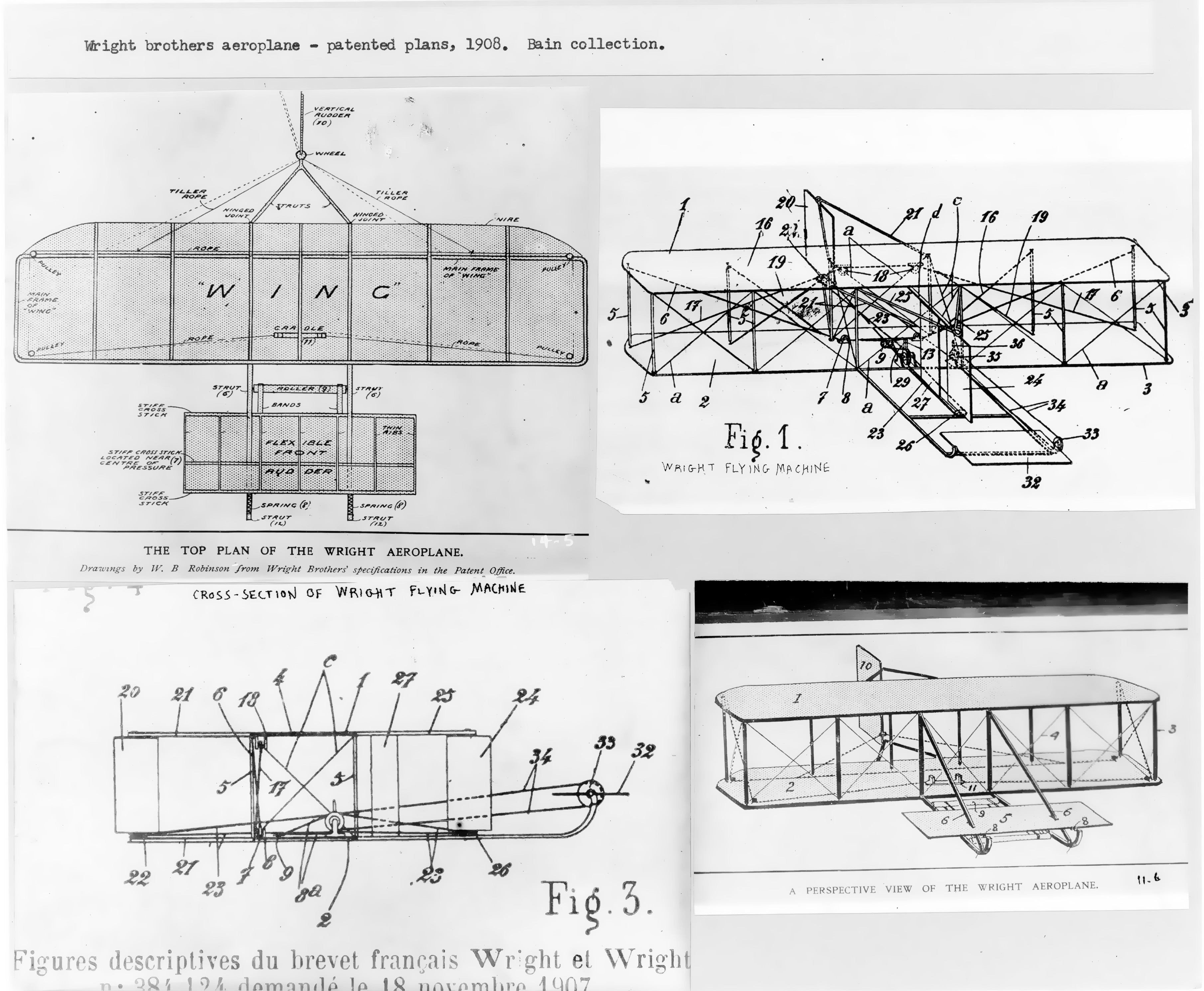
Wright Flyer
The ''Wright Flyer'' (also known as the ''Kitty Hawk'', ''Flyer'' I or the 1903 ''Flyer'') made the first sustained flight by a manned heavier-than-air powered and controlled aircraft on December 17, 1903. Invented and flown by brothers Wright brothers, Orville and Wilbur Wright, it marked the beginning of the Aviation in the pioneer era, pioneer era of aviation. The aircraft is a single-place biplane design with Dihedral (aeronautics)#Anhedral and polyhedral, anhedral (drooping) wings, front double Elevator (aeronautics), elevator (a canard (aeronautics), canard) and rear double rudder. It used a gasoline engine powering two pusher propellers. Employing "wing warping", it was relatively unstable and very difficult to fly. The Wright brothers flew it four times in a location now part of the town of Kill Devil Hills, North Carolina, Kill Devil Hills, about south of Kitty Hawk, North Carolina. The airplane flew on its fourth and final flight, but was damaged on landing, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed-wing Aircraft
A fixed-wing aircraft is a heavier-than-air aircraft, such as an airplane, which is capable of flight using aerodynamic lift. Fixed-wing aircraft are distinct from rotary-wing aircraft (in which a rotor mounted on a spinning shaft generates lift), and ornithopters (in which the wings oscillate to generate lift). The wings of a fixed-wing aircraft are not necessarily rigid; kites, hang gliders, variable-sweep wing aircraft, and airplanes that use wing morphing are all classified as fixed wing. Gliding fixed-wing aircraft, including free-flying gliders and tethered kites, can use moving air to gain altitude. Powered fixed-wing aircraft (airplanes) that gain forward thrust from an engine include powered paragliders, powered hang gliders and ground effect vehicles. Most fixed-wing aircraft are operated by a pilot, but some are unmanned or controlled remotely or are completely autonomous (no remote pilot). History Kites Kites were used approximately 2,800 years ago ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |