|
Bioregionalism
Bioregionalism is a philosophy that suggests that political, cultural, and economic systems are more sustainable and just if they are organized around naturally defined areas called '' bioregions'' (similar to ''ecoregions''). Bioregions are defined through physical and environmental features, including watershed boundaries and soil and terrain characteristics. Bioregionalism stresses that the determination of a bioregion is also a cultural phenomenon, and emphasizes local populations, knowledge, and solutions. Bioregionalism is a concept that goes beyond national boundaries—an example is the concept of Cascadia, a region that is sometimes considered to consist of most of Oregon and Washington, the Alaska Panhandle, the far north of California and the West Coast of Canada, sometimes also including some or all of Idaho and western Montana. Another example of a bioregion, which does not cross national boundaries, but does overlap state lines, is the Ozarks, a bioregion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
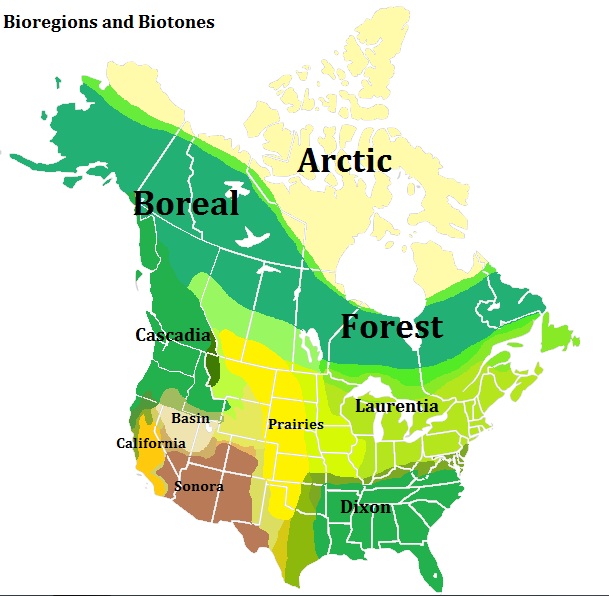
Bioregions And Biotones Of North America
A bioregion is a geographical area, on land or at sea, defined not by administrative boundaries, but by distinct characteristics such as plant and animal species, ecological systems, soils and landforms, human settlements, and topographic features such as watersheds. The idea of bioregions were adopted and popularized in the mid-1970s by a school of philosophy called bioregionalism, which includes the concept that human culture, in practice, can influence bioregional definitions due to its affect on non-cultural factors. Bioregions are part of a nested series of ecological scales, generally starting with local watersheds, growing into larger river systems, then Level III or IV ecoregions (or regional ecosystems), bioregions, then biogeographical realm, followed by the continental-scale and ultimately the biosphere. Within the life sciences, there are numerous methods used to define the physical limits of a bioregion based on the spatial extent of mapped ecological phenomena—f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cascadia Movement
The Cascadia movement is a bioregional independence movement based in the Cascadia bioregion of western North America. Potential boundaries differ, with some drawn along existing political state and provincial lines, and others drawn along larger ecological, cultural, political, and economic boundaries. The proposed country or region largely would consist of the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. states of Washington, Idaho and Oregon, including the major cities of Seattle, Vancouver, Boise and Portland. When all parts of the bioregion are included, Cascadia would stretch from coastal Alaska in the north into Northern California in the south, and inland to include parts of Montana, Nevada, Utah, Wyoming, and Yukon. More conservative advocates propose borders that include the land west of the crest of the Cascade Range (named after the long-gone Cascades Rapids), while some advocates propose borders as far north as Alaska and the Yukon region. As measured onl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Berg (bioregionalist)
Peter Stephen Berg (October 1, 1937 – July 28, 2011) was an environmental writer, best known as an advocate of the concept of bioregionalism. In the early 1960s, he was a member of the San Francisco Mime Troupe and the Diggers. He is the founder of the Planet Drum Foundation. Early life and education Born on October 1, 1937, in Jamaica, Queens, New York, Berg was raised in Florida after moving there at age six, which was where he first became interested in the environment as a child. He began attending the University of Florida at age 16, after winning a scholarship to study psychology. He dropped out at age 17, hitchhiked to San Francisco, and then enlisted and served in the army. After his discharge, he moved back to New York. After becoming active in the civil rights movement, he hitchhiked to San Francisco in 1964. In San Francisco, he joined the San Francisco Mime Troupe and met Judy Goldhaft. He also became a founder of the Artists Liberation Front and the Diggers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Localism
Localism is a range of political philosophies which prioritize the local. Generally, localism supports local production and consumption of goods, local control of government, and promotion of local history, local culture and local identity. Localism can be contrasted with regionalism and centralized government, with its opposite being found in unitarism. Localism can also refer to a systematic approach to organizing a central government so that local autonomy is retained rather than following the usual pattern of government and political power becoming centralized over time. On a conceptual level, there are important affinities between localism and deliberative democracy. This concerns mainly the democratic goal of engaging citizens in decisions that affect them. Consequently, localism will encourage stronger democratic and political participatory forums and widening public sphere connectivity. History Localists assert that throughout the world's history, most social and e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Drainage Basin
A drainage basin is an area of land in which all flowing surface water converges to a single point, such as a river mouth, or flows into another body of water, such as a lake or ocean. A basin is separated from adjacent basins by a perimeter, the drainage divide, made up of a succession of elevated features, such as ridges and hills. A basin may consist of smaller basins that merge at river confluences, forming a hierarchical pattern. Other terms for a drainage basin are catchment area, catchment basin, drainage area, river basin, water basin, and impluvium. In North America, they are commonly called a watershed, though in other English-speaking places, " watershed" is used only in its original sense, that of the drainage divide line. A drainage basin's boundaries are determined by watershed delineation, a common task in environmental engineering and science. In a closed drainage basin, or endorheic basin, rather than flowing to the ocean, water converges toward the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkpatrick Sale
Kirkpatrick Sale (born June 27, 1937) is an American author who has written prolifically about political decentralism, environmentalism, luddism and technology. He has been described as having a "philosophy unified by decentralism" and as being "a leader of the Neo-Luddites," an " anti-globalization leftist," and "the theoretician for a new secessionist movement." Early life and education Sale grew up in Ithaca, New York, where he later said he "spent most of my first twenty years there, and that has made an imprint on me—on my philosophy, social attitudes, certainly on my politics—that has lasted powerfully for the rest of my life." Sale's brother, Roger Sale, was a literary critic and a professor of English at the University of Washington. He graduated from Cornell University, majoring in English and history, in 1958. He served as associate editor and editor-in-chief of the student-owned and managed newspaper, '' The Cornell Daily Sun''. Sale was one of the leaders ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) is an ecological and geographic area that exists on multiple different levels, defined by type, quality, and quantity of environmental resources. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of land or water, and contain characteristic, geographically distinct assemblages of natural communities and species. The biodiversity of flora, fauna and ecosystems that characterise an ecoregion tends to be distinct from that of other ecoregions. In theory, biodiversity or conservation ecoregions are relatively large areas of land or water where the probability of encountering different species and communities at any given point remains relatively constant, within an acceptable range of variation (largely undefined at this point). Ecoregions are also known as "ecozones" ("ecological zones"), although that term may also refer to biogeographic realms. Three caveats are appropriate for all bio-geographic mapping approaches. Firstly, no single bio-geographic fram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Ozarks
The Ozarks, also known as the Ozark Mountains, Ozark Highlands or Ozark Plateau, is a physiographic region in the U.S. states of Missouri, Arkansas, and Oklahoma, as well as a small area in the southeastern corner of Kansas. The Ozarks cover a significant portion of northern Arkansas and most of the southern half of Missouri, extending from Interstate 40 in central Arkansas to Interstate 70 in central Missouri. There are two mountain ranges in the Ozarks: the Boston Mountains of Arkansas and Oklahoma, as well as the St. Francois Mountains of Missouri. Wahzhazhe Summit (formerly known as Buffalo Lookout), is the highest point in the Ozarks at , and is located in the Boston Mountains, in the westernmost part of Newton County, Arkansas, east of Boston, Madison County, Arkansas. Geologically, the area is a broad dome with the exposed core in the ancient St. Francois Mountains. The Ozarks cover nearly , making it the most extensive highland region between the Appalachians and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Google Books
Google Books (previously known as Google Book Search, Google Print, and by its code-name Project Ocean) is a service from Google that searches the full text of books and magazines that Google has scanned, converted to text using optical character recognition (OCR), and stored in its digital database.The basic Google book link is found at: https://books.google.com/ . The "advanced" interface allowing more specific searches is found at: https://books.google.com/advanced_book_search Books are provided either by publishers and authors through the Google Books Partner Program, or by Google's library partners through the Library Project. Additionally, Google has partnered with a number of magazine publishers to digitize their archives. The Publisher Program was first known as Google Print when it was introduced at the Frankfurt Book Fair in October 2004. The Google Books Library Project, which scans works in the collections of library partners and adds them to the digital inventory, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raymond F
Raymond is a male given name of Germanic origin. It was borrowed into English from French (older French spellings were Reimund and Raimund, whereas the modern English and French spellings are identical). It originated as the Germanic ᚱᚨᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Raginmund'') or ᚱᛖᚷᛁᚾᛗᚢᚾᛞ (''Reginmund''). ''Ragin'' ( Gothic) and ''regin'' ( Old German) meant "counsel". The Old High German ''mund'' originally meant "hand", but came to mean "protection". This etymology suggests that the name originated in the Early Middle Ages, possibly from Latin. Alternatively, the name can also be derived from Germanic Hraidmund, the first element being ''Hraid'', possibly meaning "fame" (compare ''Hrod'', found in names such as Robert, Roderick, Rudolph, Roland, Rodney and Roger) and ''mund'' meaning "protector". Despite the German and French origins of the English name, some of its early uses in English documents appear in Latinized form. As a surname, its first record ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Culture
Culture ( ) is a concept that encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, Attitude (psychology), attitudes, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tylor, Edward. (1871). ''Primitive Culture''. Vol 1. New York: J. P. Putnam's Son Culture often originates from or is attributed to a specific region or location. Humans acquire culture through the learning processes of enculturation and socialization, which is shown by the diversity of cultures across societies. A cultural norm codifies acceptable conduct in society; it serves as a guideline for behavior, dress, language, and demeanor in a situation, which serves as a template for expectations in a social group. Accepting only a monoculturalism, monoculture in a social group can bear risks, just as a single species can wither in the face of environmental change, for lack of functional respo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |