|
Biomedical Spectroscopy
Biomedical spectroscopy is a multidisciplinary research field involving spectroscopic tools for applications in the field of biomedical science. Vibrational spectroscopy such as Raman or infrared spectroscopy is used to determine the chemical composition of a material based on detection of vibrational modes of constituent molecules. Some spectroscopic methods are routinely used in clinical settings for diagnosis of disease; an example is Magnetic resonance imaging Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and ... (MRI). Fourier transform infrared (FTIR) spectroscopic imaging is a form of chemical imaging for which the contrast is provided by composition of the material. NOCISCAN – The first, evidence-supported, SaaS platform to leverage MR Spectroscopy to noninvasively help ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectroscopy
Spectroscopy is the field of study that measures and interprets electromagnetic spectra. In narrower contexts, spectroscopy is the precise study of color as generalized from visible light to all bands of the electromagnetic spectrum. Spectroscopy, primarily in the electromagnetic spectrum, is a fundamental exploratory tool in the fields of astronomy, chemistry, materials science, and physics, allowing the composition, physical structure and electronic structure of matter to be investigated at the atomic, molecular and macro scale, and over astronomical distances. Historically, spectroscopy originated as the study of the wavelength dependence of the absorption by gas phase matter of visible light dispersed by a prism. Current applications of spectroscopy include biomedical spectroscopy in the areas of tissue analysis and medical imaging. Matter waves and acoustic waves can also be considered forms of radiative energy, and recently gravitational waves have been associa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raman Spectroscopy
Raman spectroscopy () (named after physicist C. V. Raman) is a Spectroscopy, spectroscopic technique typically used to determine vibrational modes of molecules, although rotational and other low-frequency modes of systems may also be observed. Raman spectroscopy is commonly used in chemistry to provide a structural fingerprint by which molecules can be identified. Raman spectroscopy relies upon inelastic scattering of photons, known as Raman scattering. A source of monochromatic light, usually from a laser in the visible spectrum, visible, near infrared, or ultraviolet, near ultraviolet range is used, although X-ray Raman scattering, X-rays can also be used. The laser light interacts with molecular vibrations, phonons or other excitations in the system, resulting in the energy of the laser photons being shifted up or down. The shift in energy gives information about the vibrational modes in the system. Time-resolved spectroscopy and infrared spectroscopy typically yields similar y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infrared Spectroscopy
Infrared spectroscopy (IR spectroscopy or vibrational spectroscopy) is the measurement of the interaction of infrared radiation with matter by absorption, emission, or reflection. It is used to study and identify chemical substances or functional groups in solid, liquid, or gaseous forms. It can be used to characterize new materials or identify and verify known and unknown samples. The method or technique of infrared spectroscopy is conducted with an instrument called an infrared spectrometer (or spectrophotometer) which produces an infrared spectrum. An IR spectrum can be visualized in a graph of infrared light absorbance (or transmittance) on the vertical axis vs. frequency, wavenumber or wavelength on the horizontal axis. Typical units of wavenumber used in IR spectra are reciprocal centimeters, with the symbol cm−1. Units of IR wavelength are commonly given in micrometers (formerly called "microns"), symbol μm, which are related to the wavenumber in a reciprocal way ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Society Of Chemistry
The Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC) is a learned society and professional association in the United Kingdom with the goal of "advancing the chemistry, chemical sciences". It was formed in 1980 from the amalgamation of the Chemical Society, the Royal Institute of Chemistry, the Faraday Society, and the Society for Analytical Chemistry with a new Royal Charter and the dual role of learned society and professional body. At its inception, the Society had a combined membership of 49,000 in the world. The headquarters of the Society are at Burlington House, Piccadilly, London. It also has offices in Thomas Graham House in Cambridge (named after Thomas Graham (chemist), Thomas Graham, the first president of the Chemical Society) where ''RSC Publishing'' is based. The Society has offices in the United States, on the campuses of The University of Pennsylvania and Drexel University, at the University City Science Center in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in both Beijing and Shanghai, People' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic Resonance Imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to generate pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes inside the body. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, magnetic field gradients, and radio waves to form images of the organs in the body. MRI does not involve X-rays or the use of ionizing radiation, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT) and positron emission tomography (PET) scans. MRI is a medical application of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) which can also be used for imaging in other NMR applications, such as NMR spectroscopy. MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging and follow-up of disease. Compared to CT, MRI provides better contrast in images of soft tissues, e.g. in the brain or abdomen. However, it may be perceived as less comfortable by patients, due to the usually longer and louder measurements with the subject in a long, confining tube, although ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
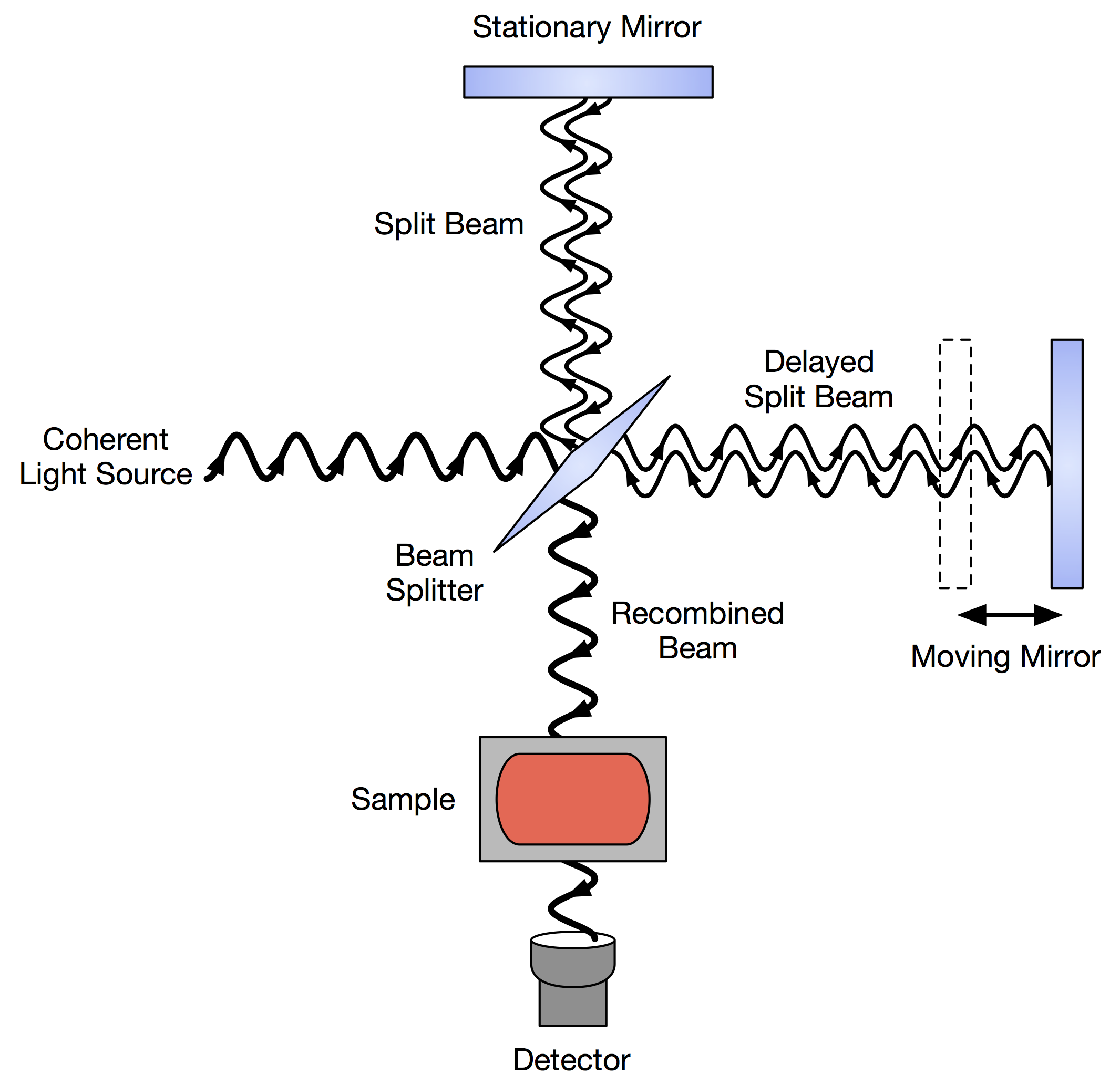
Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) is a technique used to obtain an infrared Electromagnetic spectrum, spectrum of Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption or Emission (electromagnetic radiation), emission of a solid, liquid, or gas. An FTIR spectrometer simultaneously collects high-resolution spectral data over a wide spectral range. This confers a significant advantage over a Dispersion (optics), dispersive spectrometer, which measures intensity over a narrow range of wavelengths at a time. The term ''Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy'' originates from the fact that a Fourier transform (a mathematical process) is required to convert the raw data into the actual spectrum. Conceptual introduction The goal of absorption spectroscopy techniques (FTIR, Ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy, ultraviolet-visible ("UV-vis") spectroscopy, etc.) is to measure how much light a sample absorbs at each wavelength. The most straightforward way to do this, the "dispe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |