|
Bioasphalt
Bioasphalt is an asphalt alternative made from non-petroleum based renewable resources. These sources include sugar, molasses and rice, corn and potato starches, natural tree and gum resins, natural latex rubber and vegetable oils, lignin, cellulose, palm oil waste, coconut waste, peanut oil waste, canola oil waste, dried sewerage effluent and so on. Bitumen can also be made from waste vacuum tower bottoms produced in the process of cleaning used motor oils, which are normally burned or dumped into land fills. Non-petroleum based bitumen binders can be colored, which can reduce the temperatures of road surfaces and reduce the Urban heat islands. Petroleum, environmental, and heat concerns Because of concerns over Peak oil, pollution and climate change, as well the oil price increases since 2003, non-petroleum alternatives have become more popular. This has led to the introduction of biobitumen alternatives that are more environmentally friendly and nontoxic. For millions of peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Renewable Resource
A renewable resource (also known as a flow resource) is a natural resource which will replenish to replace the portion depleted by usage and consumption, either through natural reproduction or other recurring processes in a finite amount of time in a human time scale. It is also known as non conventional energy resources. When the recovery rate of resources is unlikely to ever exceed a human time scale, these are called perpetual resources. Renewable resources are a part of Earth's natural environment and the largest components of its ecosphere. A positive life-cycle assessment is a key indicator of a resource's sustainability. Definitions of renewable resources may also include agricultural production, as in agricultural products and to an extent water resources.What are "Renewable Resourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asphalt Concrete
Asphalt concrete (commonly called asphalt, blacktop, or pavement in North America, and Tarmacadam, tarmac or bitumen macadam in the United Kingdom and the Republic of Ireland) is a composite material commonly used to surface road surface, roads, parking lots, airports, and the core of embankment dams. Asphalt mixtures have been used in pavement construction since the nineteenth century. It consists of Construction aggregate, mineral aggregate Binder (material), bound together with bitumen (a substance also independently known as asphalt, Pitch (resin), pitch, or tar), laid in layers, and compacted. The American English terms ''asphalt'' (or ''asphaltic'') ''concrete'', ''bituminous asphalt concrete'', and ''bituminous mixture'' are typically used only in engineering and construction documents, which define concrete as any composite material composed of mineral aggregate adhered with a binder. The abbreviation, ''AC'', is sometimes used for ''asphalt concrete'' but can also denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pavements
Pavement(s) or paving may refer to: Surfacing * Road surface, the durable surfacing of roads and walkways * Sidewalk, a walkway along the side of a road, called a pavement in British English * Asphalt concrete, a common form of road surface * Cool pavement, pavement that delivers higher solar reflectance than conventional dark pavement * Crazy paving, a means of hard-surfacing used outdoors * Nicolson pavement, a road surface material consisting of wooden blocks * Pavers (flooring), an outdoor floor done in blocks * Permeable paving, paving that enables stormwater to flow through it or between gaps * Portuguese pavement, the traditional paving used in most pedestrian areas in Portugal * Resin-bound paving, a mixture of aggregate stones and resin used to pave footpaths, driveways, etc. * Tactile paving, textured ground surface indicators to assist vision-impaired pedestrians * Whitetopping, the covering of an existing asphalt pavement with a layer of Portland cement concret ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Recycled Building Materials
Recycling is the process of converting waste materials into new materials and objects. This concept often includes the recovery of energy from waste materials. The recyclability of a material depends on its ability to reacquire the properties it had in its original state. It is an alternative to "conventional" waste disposal that can save material and help lower greenhouse gas emissions. It can also prevent the waste of potentially useful materials and reduce the consumption of fresh raw materials, reducing energy use, air pollution Air pollution is the presence of substances in the Atmosphere of Earth, air that are harmful to humans, other living beings or the environment. Pollutants can be Gas, gases like Ground-level ozone, ozone or nitrogen oxides or small particles li ... (from incineration) and water pollution (from landfilling). Recycling is a key component of modern waste reduction and represents the third step in the "Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle" waste hierarch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Building Materials
Building material is material used for construction. Many naturally occurring substances, such as clay, rocks, sand, wood, and even twigs and leaves, have been used to construct buildings and other structures, like bridges. Apart from naturally occurring materials, many man-made products are in use, some more and some less synthetic. The manufacturing of building materials is an established industry in many countries and the use of these materials is typically segmented into specific specialty trades, such as carpentry, Building insulation, insulation, plumbing, and roofing material, roofing work. They provide the make-up of :Human habitats, habitats and architecture, structures including homes. The total cost of building materials In history, there are trends in building materials from being natural to becoming more human-made and Composite material, composite; biodegradable to imperishable; indigenous (local) to being transported globally; repairable to disposable; chosen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biomass
Biomass is a term used in several contexts: in the context of ecology it means living organisms, and in the context of bioenergy it means matter from recently living (but now dead) organisms. In the latter context, there are variations in how biomass is defined, e.g., only from plants, from plants and algae, from plants and animals. The vast majority of biomass used for bioenergy does come from plants and fecal matter. Bioenergy is a type of renewable energy that the bioenergy industry claims has the potential to assist with climate change mitigation. Uses in different contexts Ecology * Biomass (ecology), the mass of living biological organisms in a given area or ecosystem at a given time. This can be the biomass of particular species or the biomass of a particular community or habitat. Energy * Biomass (energy), biomass used for energy production or in other words: biological mass used as a renewable energy source (usually produced through agriculture, forestry or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zeeland
Zeeland (; ), historically known in English by the Endonym and exonym, exonym Zealand, is the westernmost and least populous province of the Netherlands. The province, located in the southwest of the country, borders North Brabant to the east, South Holland to the north, as well as the country of Belgium to the south and west. It consists of a number of islands and peninsulas (hence its name, meaning "Sealand") and a strip bordering the Flanders, Flemish provinces of East Flanders, East and West Flanders. Its capital is Middelburg, Zeeland, Middelburg with a population of 48,544 as of November 2019, although the largest municipality in Zeeland is Terneuzen (population 54,589). Zeeland has two Port, seaports: Vlissingen and Terneuzen. Its area is , of which is water; it had a population of about 391,000 as of January 2023. Large parts of Zeeland are below sea level. The North Sea flood of 1953, last great flooding of the area was in 1953. Tourism is an important economic activ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wageningen University & Research Centre
Wageningen () is a municipality and a historic city in the central Netherlands, in the province of Gelderland. It is famous for Wageningen University, which specialises in life sciences. The municipality had a population of in , of which many thousands are students from over 150 countries. Demographics Inhabitants by nationality 71,68% is Dutch, 28,32% has a migration background. Geography Wageningen is situated on the north bank of the Nederrijn (the Dutch portion of the Lower Rhine) part of the and the Veluwe, of which the southwest hill is called the ''Wageningse Berg''. Wageningen can be reached by car from highways A12 via the N781, A15 via the N233 and N225, and A50 via the N225, and from the Ede-Wageningen railway station via a 20-minute bus drive to the Wageningen central terminal (see below)., ''Topographic map of the municipality of Wageningen, July 2013 (click to enlarge)'' History The oldest known settlements in the Wageningen area were located north of tod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iowa State University
Iowa State University of Science and Technology (Iowa State University, Iowa State, or ISU) is a Public university, public land-grant university, land-grant research university in Ames, Iowa, United States. Founded in 1858 as the Iowa Agricultural College and Model Farm, Iowa State became one of the nation's first designated land-grant institutions when the Iowa Legislature accepted the provisions of the 1862 Morrill Land-Grant Colleges Act, Morrill Act on September 11, 1862. On July 4, 1959, the college was officially renamed Iowa State University of Science and Technology. Iowa State is the second largest university in Iowa by total enrollment. The university's academic offerings are administered through eight colleges, including the Iowa State University College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, College of Agriculture and Life Sciences, the Iowa State University College of Veterinary Medicine, College of Veterinary Medicine, the Iowa State University College of Engineering, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bio-oil
Pyrolysis oil, sometimes also known as biocrude or bio-oil, is a synthetic fuel with few industrial applications and under investigation as substitute for petroleum. It is obtained by heating dried biomass without oxygen in a reactor at a temperature of about with subsequent cooling, separation from the aqueous phase and other processes. Pyrolysis oil is a kind of tar and normally contains levels of oxygen too high to be considered a pure hydrocarbon. This high oxygen content results in non-volatility, corrosiveness, partial miscibility with fossil fuels, thermal instability, and a tendency to polymerize when exposed to air. As such, it is distinctly different from petroleum products. Removing oxygen from bio-oil or nitrogen from algal bio-oil is known as upgrading. Standards There are few standards for pyrolysis oil because of few efforts to produce it. One is from ASTM. Feedstock decomposition Pyrolysis is a well established technique for decomposition of organic material ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
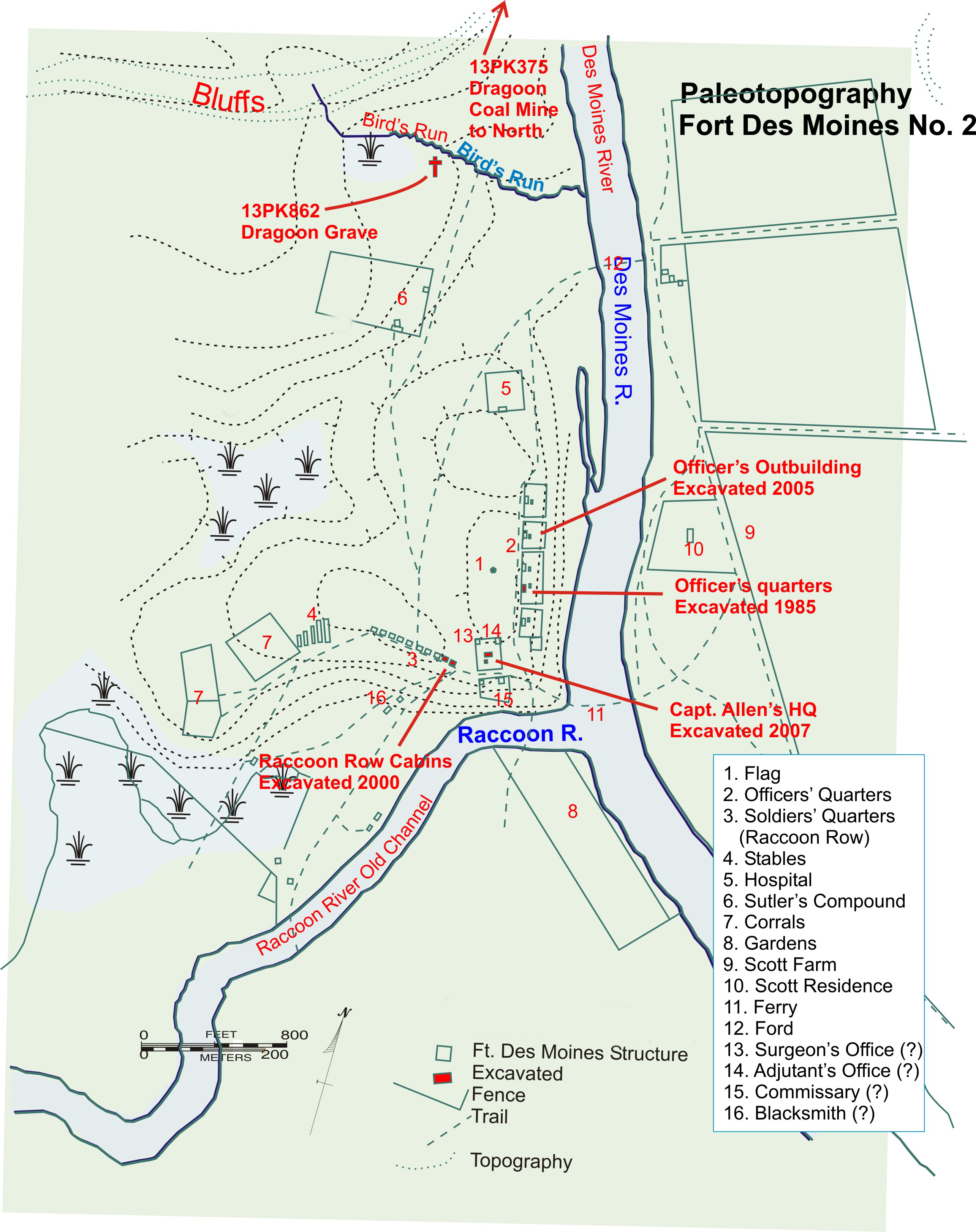
Des Moines, Iowa
Des Moines is the List of capitals in the United States, capital and List of cities in Iowa, most populous city in the U.S. state of Iowa. It is the county seat of Polk County, Iowa, Polk County with parts extending into Warren County, Iowa, Warren County. It is named after the Des Moines River, likely derived from the French "Rivière des Moines" meaning "River of the Monks." The city was incorporated in 1851 as Fort Des Moines and shortened to "Des Moines" in 1857. Its population was 214,133 at the 2020 United States census, 2020 census. The Des Moines metropolitan area, covering six counties, is the Metropolitan statistical area, 81st largest metropolitan area in the U.S. with about 750,000 residents, and is the largest metropolitan area entirely in Iowa. Des Moines is a major center of the United States insurance industry and has a sizable financial services and publishing business base. The city is the headquarters for the Principal Financial Group and Wellmark Blue Cross B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermoplastic Elastomer
Thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), sometimes referred to as thermoplastic rubbers (TPR), are a class of copolymers or a physical mix of polymers (usually a plastic and a rubber) that consist of materials with both thermoplastic and elastomeric properties. While most elastomers are thermosets, thermoplastic elastomers are not, in contrast making them relatively easy to use in manufacturing, for example, by injection moulding. Thermoplastic elastomers show advantages typical of both rubbery materials and plastic materials. The benefit of using thermoplastic elastomers is the ability to stretch to moderate elongations and return to its near original shape creating a longer life and better physical range than other materials. The principal difference between thermoset elastomers and thermoplastic elastomers is the type of cross-linking bond in their structures. In fact, crosslinking is a critical structural factor which imparts high elastic properties. Types There are six g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |