|
Bio-based Materials
A bio-based material is a material intentionally made, either wholly or partially, from substances derived from living (or once-living) organisms, such as plants, animals, enzymes, and microorganisms, including bacteria, fungi and yeast. Due to their main characteristics of being renewable and to their ability to store carbon over their growth, recent years assisted to their upsurge as a valid alternative compared to more traditional materials in view of climate mitigation. In European context, more specifically, European Union, which has set 2050 as a target date to reach climate neutrality, is trying to implement, among other measures, the production and utilization of bio-based materials in many diverse sectors. Indeed, several European regulations, such as the European Industrial Strategy, the EU Biotechnology and Biomanufacturing Initiative and the Circular Action Plan, emphasize bio-materials. These regulations aim to support innovation, investment, and market adoption of bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organism
An organism is any life, living thing that functions as an individual. Such a definition raises more problems than it solves, not least because the concept of an individual is also difficult. Many criteria, few of them widely accepted, have been proposed to define what an organism is. Among the most common is that an organism has autonomous reproduction, Cell growth, growth, and metabolism. This would exclude viruses, despite the fact that they evolution, evolve like organisms. Other problematic cases include colonial organisms; a colony of eusocial insects is organised adaptively, and has Germ-Soma Differentiation, germ-soma specialisation, with some insects reproducing, others not, like cells in an animal's body. The body of a siphonophore, a jelly-like marine animal, is composed of organism-like zooids, but the whole structure looks and functions much like an animal such as a jellyfish, the parts collaborating to provide the functions of the colonial organism. The evolutiona ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plastic
Plastics are a wide range of synthetic polymers, synthetic or Semisynthesis, semisynthetic materials composed primarily of Polymer, polymers. Their defining characteristic, Plasticity (physics), plasticity, allows them to be Injection moulding, molded, Extrusion, extruded, or Compression molding, pressed into a diverse range of solid forms. This adaptability, combined with a wide range of other properties such as low weight, durability, flexibility, chemical resistance, low toxicity, and low-cost production, has led to their widespread use around the world. While most plastics are produced from natural gas and petroleum, a growing minority are produced from renewable resources like polylactic acid. Between 1950 and 2017, 9.2 billion metric tons of plastic are estimated to have been made, with more than half of this amount being produced since 2004. In 2023 alone, preliminary figures indicate that over 400 million metric tons of plastic were produced worldwide. If global trends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Performance Index
The Environmental Performance Index (EPI) is a method of quantifying and numerically marking the environmentalism, environmental performance of a state's policies, highlightning the degradation of the planet's life-supporting systems on which humanity depends. A world economy that continues to rely heavily on fossil fuels translates into ongoing air and water pollution, acidification of the oceans, and rising concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. These changes threaten the survival of species already suffering from widespread habitat loss, pushing them closer to extinction. Recent analyses show that humanity has already transgressed six out of nine critical planetary boundaries that define Earth's safe operating space — and is close to crossing a seventh. The Environmental Performance Index (EPI) was started in 2002 by World Economic Forum in association with the Yale Center for Environmental Law & Policy (Yale University) and Earth Institute, Center for Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organic Food
Organic food, also known as ecological or biological food, refers to foods and beverages produced using methods that comply with the standards of organic farming. Standards vary worldwide, but organic farming features practices that cycle resources, promote ecological balance, and conserve biodiversity. Organizations regulating organic products may restrict the use of certain pesticides and fertilizers in the farming methods used to produce such products. Organic foods are typically not processed using irradiation, industrial solvents, or synthetic food additives. In the 21st century, the European Union, the United States, Canada, Mexico, Japan, and many other countries require producers to obtain special certification to market their food as ''organic''. Although the produce of kitchen gardens may actually be organic, selling food with an organic label is regulated by governmental food safety authorities, such as the National Organic Program of the US Department of Agricu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anaerobic Digestion
Anaerobic digestion is a sequence of processes by which microorganisms break down biodegradable material in the absence of oxygen. The process is used for industrial or domestic purposes to Waste management, manage waste or to produce fuels. Much of the Fermentation (biochemistry), fermentation used industrially to produce food and drink products, as well as home fermentation, uses anaerobic digestion. Anaerobic digestion occurs naturally in some soils and in lake and oceanic basin sediments, where it is usually referred to as "anaerobic activity". This is the source of Methane#Occurrence, marsh gas methane as discovered by Alessandro Volta in 1776. Anaerobic digestion comprises four stages: * Hydrolysis *Acidogenesis *Acetogenesis *Methanogenesis The digestion process begins with bacterial hydrolysis of the input materials. Insoluble organic polymers, such as carbohydrates, are broken down to soluble derivatives that become available for other bacteria. Acidogenesis, Acidogen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Compost
Compost is a mixture of ingredients used as plant fertilizer and to improve soil's physical, chemical, and biological properties. It is commonly prepared by Decomposition, decomposing plant and food waste, recycling organic materials, and manure. The resulting mixture is rich in plant nutrients and beneficial organisms, such as bacteria, protozoa, nematodes, and fungi. Compost improves soil fertility in gardens, landscaping, horticulture, urban agriculture, and organic farming, reducing dependency on commercial chemical fertilizers. The benefits of compost include providing nutrients to crops as fertilizer, acting as a soil conditioner, increasing the humus or Humic acids, humic acid contents of the soil, and introducing beneficial microbes that help to suppress pathogens in the soil and reduce soil-borne diseases. At the simplest level, composting requires gathering a mix of green waste (nitrogen-rich materials such as leaves, grass, and food scraps) and brown waste (woody ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Material
A material is a matter, substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an Physical object, object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical property, physical and chemical property, chemical properties, or on their geological origin or biological function. Materials science is the study of materials, their properties and their applications. Raw materials can be processed in different ways to influence their properties, by purification, shaping or the introduction of other materials. New materials can be produced from raw materials by Chemical synthesis, synthesis. In Industrial sector, industry, materials are inputs to list of manufacturing processes, manufacturing processes to produce products or more complex materials, and the nature and quantity of materials used may form part of the calculation for the cost of a product or delivery under contract, such as where contract costs are calculated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
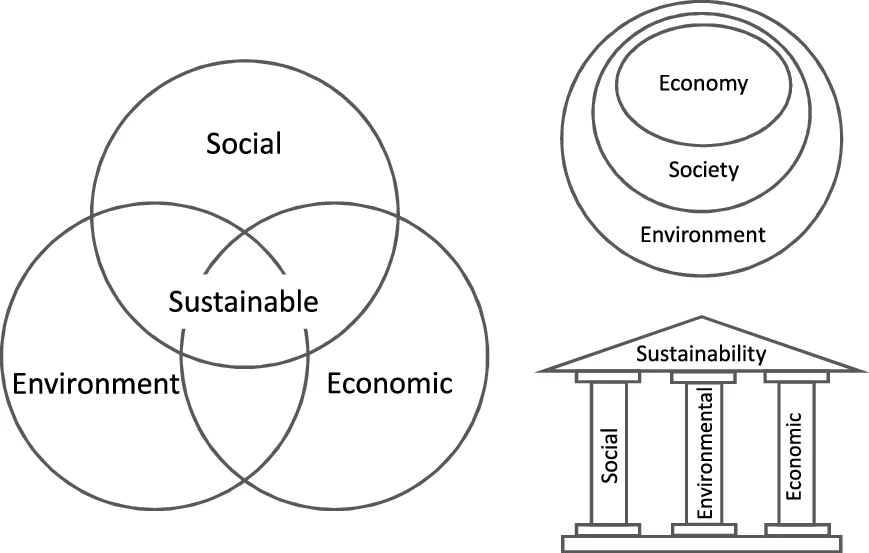
Sustainability
Sustainability is a social goal for people to co-exist on Earth over a long period of time. Definitions of this term are disputed and have varied with literature, context, and time. Sustainability usually has three dimensions (or pillars): environmental, economic, and social. Many definitions emphasize the environmental dimension. This can include addressing key environmental problems, including climate change and biodiversity loss. The idea of sustainability can guide decisions at the global, national, organizational, and individual levels. A related concept is that of sustainable development, and the terms are often used to mean the same thing. UNESCO distinguishes the two like this: "''Sustainability'' is often thought of as a long-term goal (i.e. a more sustainable world), while ''sustainable development'' refers to the many processes and pathways to achieve it." Details around the economic dimension of sustainability are controversial. Scholars have discussed this under ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biodegradable
Biodegradation is the breakdown of organic matter by microorganisms, such as bacteria and fungi. It is generally assumed to be a natural process, which differentiates it from composting. Composting is a human-driven process in which biodegradation occurs under a specific set of circumstances. The process of biodegradation is threefold: first an object undergoes biodeterioration, which is the mechanical weakening of its structure; then follows biofragmentation, which is the breakdown of materials by microorganisms; and finally assimilation, which is the incorporation of the old material into new cells. In practice, almost all chemical compounds and materials are subject to biodegradation, the key element being time. Things like vegetables may degrade within days, while glass and some plastics take many millennia to decompose. A standard for biodegradability used by the European Union is that greater than 90% of the original material must be converted into , water and minerals b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biotic Material
Biotic material or biological derived material is any material that originates from living organisms. Most such materials contain carbon and are capable of decay. The earliest form of life on Earth arose at least 3.5 billion years ago.Schopf, J.W., Kudryavtsev, A.B., Czaja, A.D., and Tripathi, A.B. (2007). "Evidence of some Archean life: Stromatolites and microfossils." ''Precambrian Research''. 158:141–155.Schopf, J.W. (2006). "Fossil evidence of Archaean life." ''Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. Biol. Sci.'' 29;361(1470) 869–885. Earlier physical evidences of life include graphite, a biogenic substance, in 3.7 billion-year-old metasedimentary rocks discovered in southwestern Greenland, as well as, "remains of biotic life" found in 4.1 billion-year-old rocks in Western Australia. Early edition, published online before print. Earth's biodiversity has expanded continually except when interrupted by mass extinctions. Although scholars estimate that over 99 percent of all spec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Additive Synthesis
Additive synthesis is a sound synthesis technique that creates timbre by adding sine waves together. The timbre of musical instruments can be considered in the light of Fourier series, Fourier theory to consist of multiple harmonic or inharmonic ''Harmonic series (music)#Partial, partials'' or overtones. Each partial is a sine wave of different frequency and amplitude that swells and decays over time due to modulation from an ADSR envelope or low frequency oscillator. Additive synthesis most directly generates sound by adding the output of multiple sine wave generators. Alternative implementations may use pre-computed Wavetable synthesis, wavetables or the inverse fast Fourier transform. Explanation The sounds that are heard in everyday life are not characterized by a single frequency. Instead, they consist of a sum of pure sine frequencies, each one at a different amplitude. When humans hear these frequencies simultaneously, we can recognize the sound. This is true for both ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, or substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. powder coatings. Paints and lacquers are coatings that mostly have dual uses, which are protecting the substrate and being decorative, although some artists paints are only for decoration, and the paint on large industrial pipes is for identification (e.g. blue for process water, red for fire-fighting control) in addition to preventing corrosion. Along with corrosion resistance, functional coatings may also be applied to change the surface properties of the substrate, such as adhesion, wettability, or wear resistance.Howarth G.A "Synthesis of a legislation compliant corrosion protection coating system based on urethane, oxazolidine and waterborne epoxy technology" Master of Science Thesis April 1997 Imperial College London In other cases the coating adds a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |