|
Bilayer Graphene
Bilayer graphene is a material consisting of two layers of graphene. One of the first reports of bilayer graphene was in the seminal 2004 ''Science'' paper by Geim and colleagues, in which they described devices "which contained just one, two, or three atomic layers" Structure Bilayer graphene can exist in the AB, or Bernal-stacked form, where half of the atoms lie directly over the center of a hexagon in the lower graphene sheet, and half of the atoms lie over an atom, or, less commonly, in the AA form, in which the layers are exactly aligned. In Bernal stacked graphene, twin boundaries are common; transitioning from AB to BA stacking. Twisted layers, where one layer is rotated relative to the other, have also been extensively studied. Quantum Monte Carlo methods have been used to calculate the binding energies of AA- and AB-stacked bilayer graphene, which are 11.5(9) and 17.7(9) meV per atom, respectively. This is consistent with the observation that the AB-stacked structure ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Graphene
Graphene () is a carbon allotrope consisting of a Single-layer materials, single layer of atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, honeycomb planar nanostructure. The name "graphene" is derived from "graphite" and the suffix -ene, indicating the presence of double bonds within the carbon structure. Graphene is known for its exceptionally high Ultimate tensile strength, tensile strength, Electrical resistivity and conductivity, electrical conductivity, Transparency and translucency, transparency, and being the thinnest two-dimensional material in the world. Despite the nearly transparent nature of a single graphene sheet, graphite (formed from stacked layers of graphene) appears black because it absorbs all visible light wavelengths. On a microscopic scale, graphene is the strongest material ever measured. The existence of graphene was first theorized in 1947 by P. R. Wallace, Philip R. Wallace during his research on graphite's electronic properties, while the term ''graphen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harvard University
Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyman John Harvard (clergyman), John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States. Its influence, wealth, and rankings have made it one of the most prestigious universities in the world. Harvard was founded and authorized by the Massachusetts General Court, the governing legislature of Colonial history of the United States, colonial-era Massachusetts Bay Colony. While never formally affiliated with any Religious denomination, denomination, Harvard trained Congregationalism in the United States, Congregational clergy until its curriculum and student body were gradually secularized in the 18th century. By the 19th century, Harvard emerged as the most prominent academic and cultural institution among the Boston B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The City University Of New York
The City University of New York (CUNY, pronounced , ) is the public university system of New York City. It is the largest urban university system in the United States, comprising 25 campuses: eleven senior colleges, seven community colleges, and seven professional institutions. The university enrolls more than 275,000 students. CUNY alumni include thirteen Nobel Prize winners and twenty-four MacArthur Fellows. The oldest constituent college of CUNY, City College of New York, was originally founded in 1847 and became the first free public institution of higher learning in the United States. In 1960, John R. Everett became the first chancellor of the Municipal College System of New York City, later known as the City University of New York (CUNY). CUNY, established by New York state legislation in 1961 and signed into law by governor Nelson Rockefeller, was an amalgamation of existing institutions and a new graduate school. The system was governed by the Board of Higher Education ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Ion Batteries
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery that uses the reversible intercalation of Li+ ions into electronically conducting solids to store energy. Li-ion batteries are characterized by higher specific energy, energy density, and energy efficiency and a longer cycle life and calendar life than other types of rechargeable batteries. Also noteworthy is a dramatic improvement in lithium-ion battery properties after their market introduction in 1991; over the following 30 years, their volumetric energy density increased threefold while their cost dropped tenfold. In late 2024 global demand passed per year, while production capacity was more than twice that. The invention and commercialization of Li-ion batteries has had a large impact on technology, as recognized by the 2019 Nobel Prize in Chemistry. Li-ion batteries have enabled portable consumer electronics, laptop computers, cellular phones, and electric cars. Li-ion batteries also see significant use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Van Hove Singularity
In condensed matter physics, a Van Hove singularity is a singularity (non-smooth point) in the density of states (DOS) of a crystalline solid. The wavevectors at which Van Hove singularities occur are often referred to as critical points of the Brillouin zone. For three-dimensional crystals, they take the form of kinks (where the density of states is not differentiable). The most common application of the Van Hove singularity concept comes in the analysis of optical absorption spectra. The occurrence of such singularities was first analyzed by the Belgian physicist Léon Van Hove in 1953 for the case of phonon densities of states. Theory Consider a one-dimensional lattice of ''N'' particle sites, with each particle site separated by distance ''a'', for a total length of ''L'' = ''Na''. Instead of assuming that the waves in this one-dimensional box are standing waves, it is more convenient to adopt periodic boundary conditions: :k=\frac=n\frac where \lambda is wavelength, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
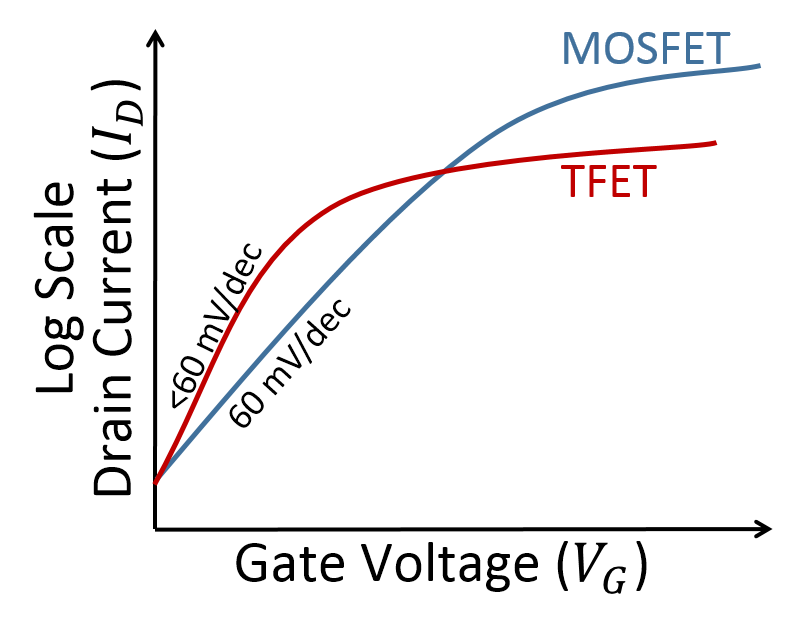
Tunnel Field-effect Transistor
The tunnel field-effect transistor (TFET) is an experimental type of transistor. Even though its structure is very similar to a metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET), the fundamental switching mechanism differs, making this device a promising candidate for low power electronics. TFETs switch by modulating quantum tunneling through a barrier instead of modulating thermionic emission over a barrier as in traditional MOSFETs. Because of this, TFETs are not limited by the thermal Maxwell–Boltzmann statistics, Maxwell–Boltzmann tail of carriers, which limits MOSFET drain current subthreshold slope, subthreshold swing to about 60 mV/Decade (log scale), decade of current at room temperature. TFET studies can be traced back to Stuetzer who in 1952 published first investigations of a transistor containing the basic elements of the TFET, a gated p-n junction. The reported surface conductivity control was, however, not related to tunneling. The first TFET was rep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Field-effect Transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the current through a semiconductor. It comes in two types: junction FET (JFET) and metal-oxide-semiconductor FET (MOSFET). FETs have three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs control the current by the application of a voltage to the gate, which in turn alters the conductivity between the drain and source. FETs are also known as unipolar transistors since they involve single-carrier-type operation. That is, FETs use either electrons (n-channel) or holes (p-channel) as charge carriers in their operation, but not both. Many different types of field effect transistors exist. Field effect transistors generally display very high input impedance at low frequencies. The most widely used field-effect transistor is the MOSFET (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistor). History The concept of a field-effect transistor (FET) was first patented by the Austr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twistronics
Twistronics (from ''twist'' and ''electronics'') is the study of how the angle (the twist) between layers of two-dimensional materials can change their electrical properties. Materials such as bilayer graphene have been shown to have vastly different electronic behavior, ranging from non-conductive to superconductive, that depends sensitively on the angle between the layers. The term was first introduced by the research group of Efthimios Kaxiras at Harvard University in their theoretical treatment of graphene superlattices. Pablo Jarillo-Herrero, Allan H. MacDonald and Rafi Bistritzer were awarded the 2020 Wolf Prize in Physics for their theoretical and experimental work on twisted bilayer graphene. History In 2007, National University of Singapore physicist Antonio H. Castro Neto hypothesized that pressing two misaligned graphene sheets together might yield new electrical properties, and separately proposed that graphene might offer a route to superconductivity, but he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The Next Big Future
''The'' is a grammatical article in English, denoting nouns that are already or about to be mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with nouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of the archaic pronoun ''thee'') ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rafi Bistritzer
Rafi Bistritzer (; born 1974 in Israel) is an Israeli physicist, and manager of an algorithms group at Applied Materials. He is the winner of the 2020 Wolf Prize in Physics, together with Pablo Jarillo-Herrero and Allan MacDonald, for "pioneering theoretical and experimental work on twisted bilayer graphene." Education Bistritzer received a bachelor's degree in physics from Tel Aviv University in 2000. He received an MSc in physics in 2003, and a PhD in physics in 2007, both from the Weizmann Institute of Science. He moved to the United States for a postdoctoral fellowship at the University of Texas at Austin, under the supervision of Alan H. MacDonald, where he studied the theoretical physics of bilayer graphene, and specifically twisted bilayer graphene. Their calculations predicted that two parallel graphene sheets twisted at an angle of 1.1 degrees relative to each other (an angle known as the "magic angle") would host flat moiré bands and thus possibly correlated states. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Allan H
Allan may refer to: People * Allan (given name), a list of people and characters with this given name * Allan (surname), a list of people and characters with this surname * Allan (footballer, born 1984) (Allan Barreto da Silva), Brazilian football striker * Allan (footballer, born 1989) (Allan dos Santos Natividade), Brazilian football forward * Allan (footballer, born 1991) (Allan Marques Loureiro), Brazilian football midfielder * Allan (footballer, born 1994) (Allan Christian de Almeida), Brazilian football midfielder * Allan (footballer, born 1997) (Allan Rodrigues de Souza), Brazilian football midfielder * Allan (footballer, born 2004) (Allan Andrade Elias), Brazilian football midfielder Places * Allan, Queensland, Australia * Allan, Saskatchewan, Canada * Allan Water (Ontario), a river * Allan, the Allaine river's lower course, in France * Allan, Drôme, town in France * Allan, Iran (other), places in Iran * Bridge of Allan, Central Scotland, a town ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yuan Cao
Yuan Cao () is a Chinese electrical engineer and physicist. His research is focused on the properties of two-dimensional materials. He discovered that a stack of two sheets of graphene, cooled to 1.7 K, could act as a superconductor or as an insulator when exposed to an electric field. In 2018, ''Nature'' chose him as one of 10 people who mattered that year in science, calling him a "graphene wrangler." Early life and education Cao was born in Chengdu, Sichuan, China, in 1996. He attended Shenzhen Yaohua Experimental School from 2007 to 2010. Cao was admitted to and started his undergraduate education at the Special Class for the Gifted Young of the University of Science and Technology of China in 2010. He traveled to the United States and studied at the University of Michigan as an undergraduate exchange student from 2012 to 2013. In 2014, Cao graduated from the University of Science and Technology of China, receiving a Bachelor of Science with a major in physics. He went ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |