|
Big Joe (Project Mercury)
Big Joe 1 (Atlas-10D) launched an uncrewed boilerplate Mercury capsule from Cape Canaveral, Florida on 9 September 1959. The purposes of the Big Joe 1 were to test the Mercury spacecraft ablative heat shield, afterbody heating, reentry dynamics attitude control and recovery capability. It was also the first launch of a spacecraft in Project Mercury. Two flight readiness firings (FRF) were performed on Big Joe 1. The first, on 1 September 1959, ended immediately after T-0 because the ignition stage delay timer commanded shutdown of the rocket engines when neither sustainer nor main engine ignition followed normal vernier ignition. There was no booster or stand damage. The second FRF was successfully completed on 3 September 1959, with normal ignition, transition to main stage and shutdown by the engine timer after approximately 19 seconds of running time. The prelaunch countdown went relatively smoothly, with one delay caused by the Atlas's LOX fill and drain valve failing to clo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the federal government of the United States, US federal government responsible for the United States's civil list of government space agencies, space program, aeronautics research and outer space, space research. National Aeronautics and Space Act, Established in 1958, it succeeded the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA) to give the American space development effort a distinct civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. It has since led most of America's space exploration programs, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968–1972 Apollo program missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. Currently, NASA supports the International Space Station (ISS) along with the Commercial Crew Program and oversees the development of the Orion (spacecraft), Orion spacecraft and the Sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
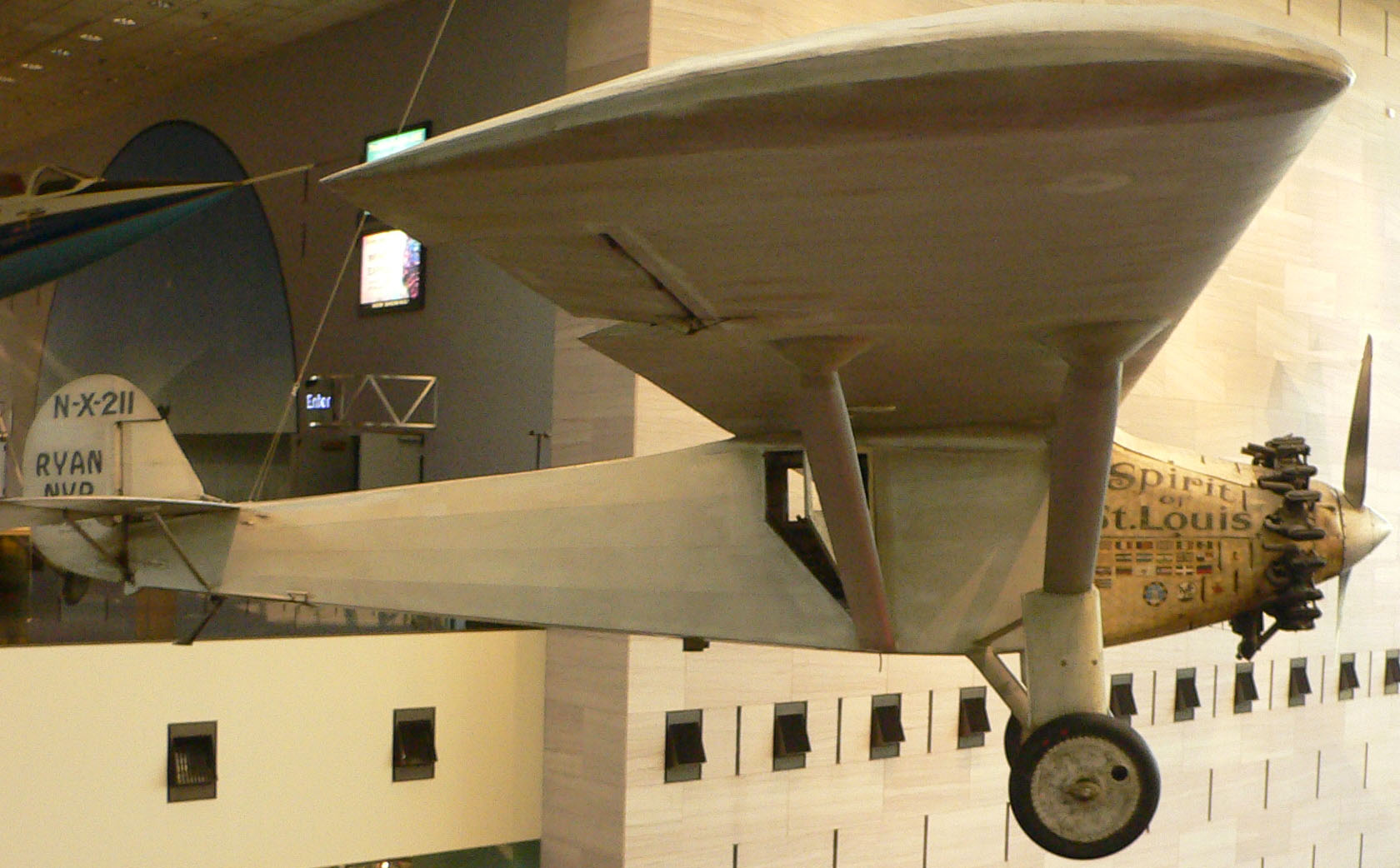
20180328 Big Joe Mercury Capsule Udvar-Hazy
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number) * One of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Science * Argon, a noble gas in the periodic table * 18 Melpomene, an asteroid in the asteroid belt Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. * ''18'' (Jeff Beck and Johnny Depp album), 2022 Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1959 In Spaceflight
Luna 1 was the first spacecraft to leave the gravitational influence of Earth. Also in 1959, Luna 2 was the first spacecraft to reach the surface of another celestial body, impacting the Moon, and Luna 3 returned the first images of the far side of the Moon. Overview Orbital and suborbital launches Deep Space Rendezvous Orbital launch statistics By country By rocket By orbit See also *Timeline of spaceflight This is a timeline of known spaceflights, both crewed and uncrewed, sorted chronologically by launch date. Due to its large size, the timeline has been split into smaller articles, one for each year since 1951. There is a separate list for ... References Footnotes {{Orbital launches in 1959 1959 in spaceflight Spaceflight by year ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
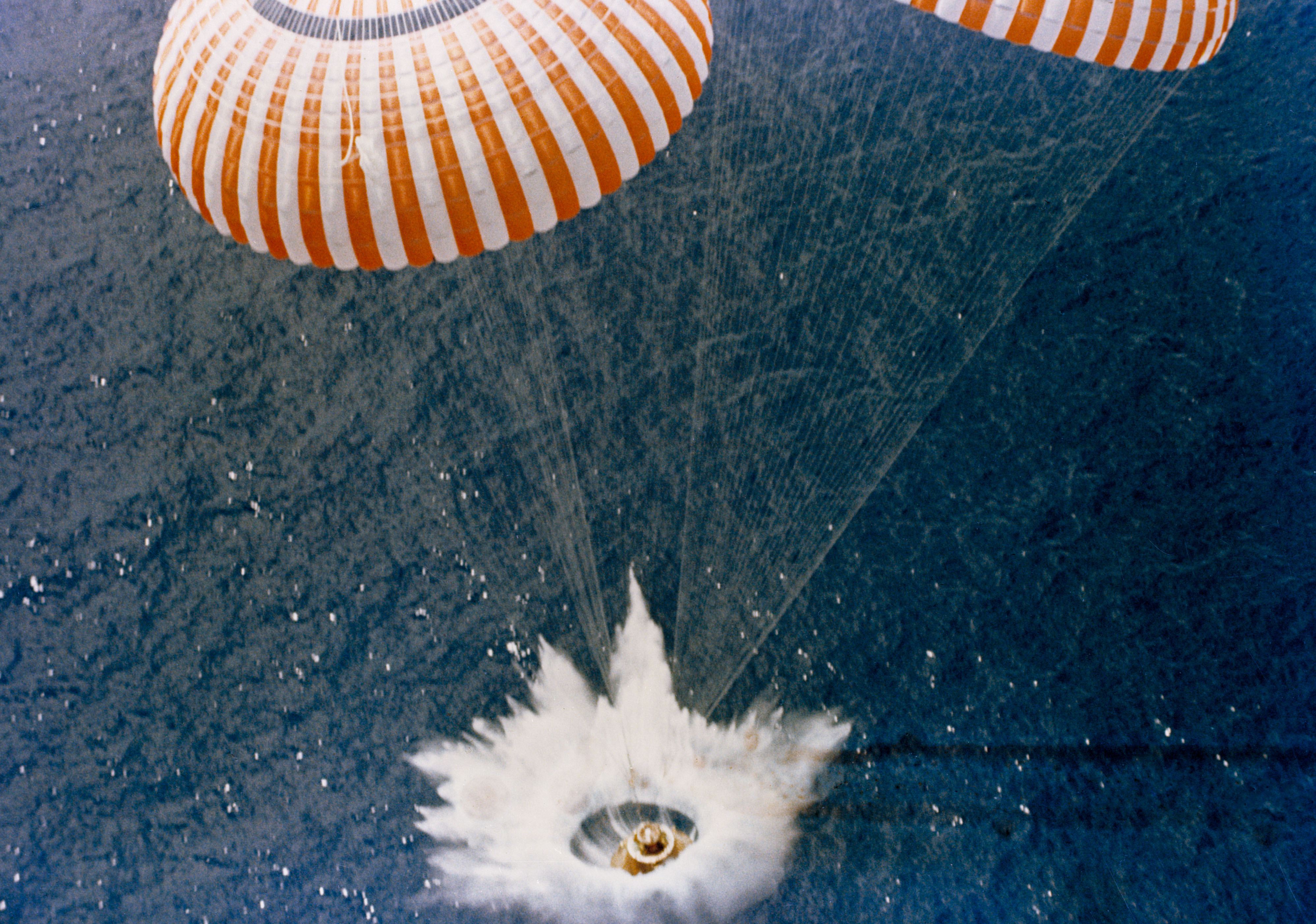
Splashdown
Splashdown is the method of landing a spacecraft or launch vehicle in a body of water, usually by parachute. This has been the primary recovery method of American capsules including NASA’s Mercury, Gemini, Apollo and Orion along with the private SpaceX Dragon. It is also possible for the Boeing Starliner, Russian Soyuz, and the Chinese Shenzhou crewed capsules to land in water in case of contingency. NASA recovered the Space Shuttle solid rocket boosters (SRBs) via splashdown, as is done for Rocket Lab's Electron first stage. As the name suggests, the vehicle parachutes into an ocean or other large body of water. Due to its low density and viscosity, water cushions the spacecraft enough that there is no need for a braking rocket to slow the final descent as is the case with Russian and Chinese crewed space capsules or airbags as is the case with the Starliner. The American practice came in part because American launch sites are on the coastline and launch primaril ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Little Joe (rocket)
Little Joe was a solid-fueled booster rocket used by NASA for eight launches from 1959 to 1961 from Wallops Island, Virginia to test the launch escape system and heat shield for Project Mercury capsules, as well as the name given to the test program using the booster. The first rocket designed solely for crewed spacecraft qualifications, Little Joe was also one of the pioneer operational launch vehicles using the rocket cluster principle. The Little Joe name has been attributed to Maxime Faget at NASA's Langley Research Center in Hampton, Virginia. He based the name on four large fins which reminded him of a slang term for a roll of four in craps#Rolling, craps. A successor, Little Joe II, was used for flight testing of the Apollo program, Apollo launch escape system from 1963 to 1966. Background When NASA needed a booster for Project Mercury, the agency found that the Atlas (rocket), Atlas rockets would cost approximately US$2.5 million each and that even the PGM-11 Redsto ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chantilly, Virginia
Chantilly is a census-designated place (CDP) in western Fairfax County, Virginia, United States. The population was 24,301 as of the 2020 census. Chantilly is named after an early-19th-century mansion and farm, which in turn took the name of an 18th-century plantation that was located in Westmoreland County, Virginia. The name "Chantilly" originated in France with the Château de Chantilly, about 28 miles north of Paris. Located in the Northern Virginia portion of the Washington metropolitan area, Chantilly sits approximately west of Washington, D.C., via Interstate 66 and U.S. Route 50. It is located between Centreville, Virginia, Centreville to the south, Herndon, Virginia, Herndon and Reston, Virginia, Reston to the north and northeast, respectively, and Fairfax, Virginia, Fairfax to the southeast. U.S. Route 50 and Virginia State Route 28 intersect in Chantilly, and these highways provide access to the Dulles International Airport, Dulles/Reston/Tysons Corner, Virginia, Ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Steven F
Stephen or Steven is an English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; he is widely regarded as the first martyr (or " protomartyr") of the Christian Church. The name, in both the forms Stephen and Steven, is often shortened to Steve or Stevie. In English, the female version of the name is Stephanie. Many surnames are derived from the first name, including Stephens, Stevens, Stephenson, and Stevenson, all of which mean "Stephen's (son)". In modern times the name has sometimes been given with intentionally non-standard spelling, such as Stevan or Stevon. A common variant of the name used in English is Stephan ( ); related names that have found some currency or significance in English include Stefan (pronounced or in English), Esteban (often pronounced ), and the Shakespearean Stephano ( ). Origins The name "Stephen" (and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Air And Space Museum
The National Air and Space Museum (NASM) of the Smithsonian Institution is a museum in Washington, D.C., in the United States, dedicated to history of aviation, human flight and space exploration. Established in 1946 as the National Air Museum, its main building opened on the National Mall near L'Enfant Plaza in 1976. In 2023, the museum welcomed 3.1 million visitors, making it the list of most-visited museums in the United States, fourth-most visited museum in the United States and List of most-visited museums, eleventh-most in the world. The museum is a center for research into the history and science of aviation and spaceflight, as well as planetary science and terrestrial geology and geophysics. Almost all of its spacecraft and aircraft on display are original primary or backup craft (rather than facsimiles). Its collection includes the Apollo 11 Command module Columbia, Command Module ''Columbia'', the Mercury-Atlas 6, ''Friendship 7'' capsule which was flown by John Glenn, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Convair
Convair, previously Consolidated Vultee Aircraft Corporation, was an American aircraft-manufacturing company that later expanded into rockets and spacecraft. The company was formed in 1943 by the merger of Consolidated Aircraft and Vultee Aircraft. In 1953, it was purchased by General Dynamics, and operated as their Convair Division for most of its corporate history. Convair is best known for its military aircraft; it produced aircraft such as the Convair B-36 Peacemaker and Convair B-58 Hustler strategic bombers, and the Convair F-102 Delta Dagger and Convair F-106 Delta Dart interceptors. It also manufactured the first Atlas rockets, including the rockets that were used for the crewed orbital flights of Project Mercury. The company's subsequent Atlas-Centaur design continued this success and derivatives of the design remain in use as of 2025. The company also entered the jet airliner business with its Convair 880 and Convair 990 designs. These were smaller than conte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atlas-Able
The Atlas-Able was an American expendable launch system derived from the SM-65 Atlas missile. It was a member of the Atlas family of rockets, and was used to launch several Pioneer spacecraft towards the Moon. Of the five Atlas-Able rockets built, two failed during static firings, and the other three failed to reach orbit. The Atlas-Able was a three-and-a-half-stage rocket, with a stage-and-a-half Atlas missile as the first stage, an Able second stage, and an Altair third stage. The first Atlas-Able used an Atlas C as the first stage, and was intended to carry Pioneer P-1, but exploded during a static fire test on 24 September 1959. The remaining Pioneer launches used Atlas D missiles. Launches were conducted from Launch Complexes 12 and 14 at the Cape Canaveral Air Force Station Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida. Headqu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reaction Control System
A reaction control system (RCS) is a spacecraft system that uses Thrusters (spacecraft), thrusters to provide Spacecraft attitude control, attitude control and translation (physics), translation. Alternatively, reaction wheels can be used for attitude control, rather than RCS. Use of diverted engine thrust to provide stable attitude control of a V/STOL, short-or-vertical takeoff and landing aircraft below conventional winged flight speeds, such as with the Hawker Siddeley Harrier#Controls and handling, Harrier "jump jet", may also be referred to as a reaction control system. Reaction control systems are capable of providing small amounts of thrust in any desired direction or combination of directions. An RCS is also capable of providing torque to allow control of rotation (aircraft principal axes, roll, pitch, and yaw). Reaction control systems often use combinations of large and small (vernier thruster, vernier) thrusters, to allow different levels of response. Uses Spacecr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercury Spacecraft
Project Mercury was the first human spaceflight program of the United States, running from 1958 through 1963. An early highlight of the Space Race, its goal was to put a man into Earth orbital spaceflight, orbit and return him safely, ideally before the Soviet Union. Taken over from the US Air Force by the newly created civilian space agency NASA, it conducted 20 uncrewed developmental flights (some using animals), and six successful flights by astronauts. The program, which took its name from Mercury (mythology), Roman mythology, cost $ (adjusted for inflation). The astronauts were collectively known as the "Mercury Seven", and each spacecraft was given a name ending with a "7" by its pilot. The Space Race began with the 1957 launch of the Soviet satellite Sputnik 1. This came as a shock to the American public, and led to the creation of NASA to expedite existing US space exploration efforts, and place most of them under civilian control. After the successful launch of the Ex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |