|
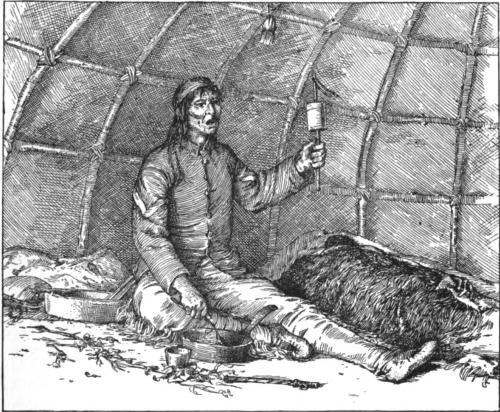
Big Indian Farms
Big Indian Farms is a remote clearing in the Chequamegon Forest west of Medford, Wisconsin where as many as 130 Potawatomi and others lived from around 1896 to 1908. In this isolated spot they were able to practice and preserve their ancestors' culture better than if they had lived under the direct influence of the Bureau of Indian Affairs on a reservation. The site was placed on the National Register of Historic Places in 1988. Background The forests and rivers of north-central Wisconsin were home to various Native Americans since shortly after the last glacier receded. The Ojibwe were the final native group to dominate the area, but they sold their land rights to the U.S. in the 1837 Treaty of St. Peters, also known as the "White Pine Treaty". This treaty was part of a general effort to move natives west of the Mississippi, to secure the east for mining, logging and white settlers. Most of the Ojibwe eventually withdrew to reservations to the north. By the late 1800s few In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perkinstown, Wisconsin
Perkinstown is an unincorporated community located in the town of Grover, Taylor County, Wisconsin, United States. Perkinstown is located on County Highway M in the Chequamegon National Forest, east-northeast of Gilman. History Logging began in the area around the 1860s. The first homesteaders staked their claims nearby in 1882. In 1892 Shaws started a leather tannery in Perkinstown, using hemlock bark from the surrounding forests, and for a time dumping the waste sludge in Kathryn Lake. By 1893 the town had six saloons. In 1900 the tannery shut down. In 1933 the Perkinstown CCC CCC may refer to: Arts and entertainment * Canada's Capital Cappies, the Critics and Awards Program in Ottawa, Ontario, Canada * ''Capcom Classics Collection'', a 2005 compilation of arcade games for the PlayStation 2 and Xbox * CCC, the pro ... Camp opened nearby, and helped build the Winter Sports Area, among other projects. References Further reading * More details on history are in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1821 Treaty Of Chicago
The Treaty of Chicago may refer to either of two treaties made and signed in the settlement that became Chicago, Illinois between the United States and the Odaawaa (anglicized Ottawa), Ojibwe (anglicized Chippewa), and Bodéwadmi (anglicized Potawatomi) (collectively, Council of Three Fires) Native American peoples. The first was in 1821 and the second in 1833. Background In 1795, in a then minor part of the Treaty of Greenville, a Native American confederation granted treaty rights to the United States in a six-mile parcel of land at the mouth of the Chicago River. This was followed by the 1816 Treaty of St. Louis, which ceded additional land in the Chicago area, including the Chicago Portage. 1821 Treaty of Chicago The first treaty of Chicago was signed by Michigan Territorial Governor Lewis Cass and Solomon Sibley for the United States and representatives of the Ottawa, Ojibwe, and Potawatomi (Council of Three Fires) on August 29, 1821, and proclaimed on March 25, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
White-tailed Deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced to New Zealand, all the Greater Antilles in the Caribbean (Cuba, Jamaica, Hispaniola, and Puerto Rico), and some countries in Europe, such as the Czech Republic, Finland, France, Germany, Romania and Serbia. In the Americas, it is the most widely distributed wild ungulate. In North America, the species is widely distributed east of the Rocky Mountains as well as in southwestern Arizona and most of Mexico, except Baja California peninsula, Lower California. It is mostly displaced by the black-tailed deer, black-tailed or mule deer (''Odocoileus hemionus'') from that point west except for mixed deciduous riparian corridors, river valley bottomlands, and lower foothills of the northern Rocky Mountain region from Wyoming west to eastern Washing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Muskrat
The muskrat (''Ondatra zibethicus'') is a medium-sized semiaquatic rodent native to North America and an introduced species in parts of Europe, Asia, and South America. The muskrat is found in wetlands over a wide range of climates and habitats. It has important effects on the ecology of wetlands, and is a resource of food and fur for humans. Adult muskrats weigh , with a body length of . They are covered with short, thick fur of medium to dark brown color. Their long tails, covered with scales rather than hair, are their main means of propulsion. Muskrats spend most of their time in the water and can swim under water for 12 to 17 minutes. They live in families, consisting of a male and female pair and their young. To protect themselves from the cold and from predators, they build nests that are often burrowed into the bank with an underwater entrance. Muskrats feed mostly on cattail and other aquatic vegetation but also eat small animals. ''Ondatra zibethicus'' is the only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Big Indian Farms Marshes
Big or BIG may refer to: * Big, of great size or degree Film and television * ''Big'' (film), a 1988 fantasy-comedy film starring Tom Hanks * ''Big!'', a Discovery Channel television show * ''Richard Hammond's Big'', a television show presented by Richard Hammond * ''Big'' (TV series), a 2012 South Korean TV series * ''Banana Island Ghost'', a 2017 fantasy action comedy film Music * '' Big: the musical'', a 1996 musical based on the film * Big Records, a record label * ''Big'' (album), a 2007 album by Macy Gray * "Big" (Dead Letter Circus song) * "Big" (Sneaky Sound System song) * "Big" (Rita Ora and Imanbek song) * "Big", a 1990 song by New Fast Automatic Daffodils * "Big", a 2021 song by Jade Eagleson from '' Honkytonk Revival'' *The Notorious B.I.G., an American rapper Places * Allen Army Airfield ( IATA code), Alaska, US * BIG, a VOR navigational beacon at London Biggin Hill Airport * Big River (other), various rivers (and other things) * Big Island (disambi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow River (Chippewa River)
The Yellow River in north central Wisconsin is a tributary of the Chippewa River. For the most part it is a mud and rock-bottomed river flowing through forest and farmland. It is one of four distinct rivers in the state bearing the name ''Yellow River''. Geography This Yellow River begins at Matt Ochs Lake and Perch Lake in the township of Molitor near Perkinstown in the Chequamegon National Forest. This area of small lakes and swamps is the terminal moraine left by the last glacier, which reached this far about 18,000 years ago. The river runs a short way before it forms Chequamegon Waters Flowage, locally known as Miller Dam. Below Miller Dam, there is one more dam, at Cadott, forming another small reservoir, before the river joins the Chippewa River when it flows into Lake Wissota at Moon Bay. Much of the Yellow is undeveloped - in particular the upper stretches through the Chequamegon Forest. In very few places will you see any sign of man. The only settlements ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleveland, Taylor County, Wisconsin
See Cleveland (other) Cleveland is a town in Taylor County, Wisconsin, United States. The population was 262 at the 2000 census. The unincorporated community of Hannibal is located in the town. Geography According to the United States Census Bureau, the town has a total area of 35.7 square miles (92.4 km2), of which 33.9 square miles (87.7 km2) is land and 1.8 square miles (4.7 km2) (5.07%) is water. Most of the water area is Chequamegon Waters, also known as Miller Dam, a man-made lake in the southeast corner of the town. History The six mile square that would become Cleveland was first surveyed in 1847 by a crew working for the U.S. government. Then in 1854 another crew marked all the section corners in the township, walking through the woods and slogging through the swamps on foot, measuring with chain and compass. When done, the deputy surveyor filed this general description: ''The Township contains several swamps. All(?) are unfit f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Boarding School At Lac Du Flambeau
The Government Boarding School at Lac du Flambeau in Lac du Flambeau, Wisconsin was a school where Native American children of the Ojibwe, Potowatomi and Odawa peoples were taught mainstream American culture from 1895 to 1932. It served grades 1-8, teaching both academic and practical subjects, intended to give children skills needed for their rural societies. The school was converted in 1932 to a day school, serving only Ojibwe children and those nearby of other tribes. After 1975 and passage of national legislation for self-determination, the Ojibwe tribe at Lac du Flambeau took over control of the school. They now use the boys' dormitory for offices for historic preservation, Ojibwe language, and cultural activities. The boys' dormitory is one of the remaining structures of what was a large multi-building complex on 300 acres. It had a variety of support buildings and, when a boarding school, raised its own produce and livestock. The school complex was added to the National ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Indian Boarding Schools
American Indian boarding schools, also known more recently as American Indian residential schools, were established in the United States from the mid 17th to the early 20th centuries with a primary objective of "civilizing" or assimilating Native American children and youth into Euro-American culture. In the process, these schools denigrated Native American culture and made children give up their languages and religion. At the same time the schools provided a basic Western education. These boarding schools were first established by Christian missionaries of various denominations. The missionaries were often approved by the federal government to start both missions and schools on reservations, especially in the lightly populated areas of the West. In the late 19th and early 20th centuries especially, the government paid religious orders to provide basic education to Native American children on reservations, and later established its own schools on reservations. The Bureau o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Midewiwin
The Midewiwin (in syllabics: , also spelled ''Midewin'' and ''Medewiwin'') or the Grand Medicine Society is a secretive religion of some of the indigenous peoples of the Maritimes The Maritimes, also called the Maritime provinces, is a region of Eastern Canada consisting of three provinces: New Brunswick, Nova Scotia, and Prince Edward Island. The Maritimes had a population of 1,899,324 in 2021, which makes up 5.1% of Ca ..., New England and Great Lakes regions in North America. Its practitioners are called ''Midew'', and the practices of ''Midewiwin'' are referred to as ''Mide''. Occasionally, male ''Midew'' are called ''Midewinini'', which is sometimes translated into English as "medicine man". Etymology The preverb ''mide'' can be translated as "mystery," "mysterious," "spiritual," "sanctified," "sacred," or "ceremonial", depending on the context of its use. The derived verb ''midewi'', thus means "be in/of ''mide''." The derived noun ''midewiwin'' then means "state o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cultural Assimilation Of Native Americans
The cultural assimilation of Native Americans refers to a series of efforts by the United States to assimilate Native Americans into mainstream European–American culture between the years of 1790 and 1920. George Washington and Henry Knox were first to propose, in the American context, the cultural assimilation of Native Americans. They formulated a policy to encourage the so-called "civilizing process". With increased waves of immigration from Europe, there was growing public support for education to encourage a standard set of cultural values and practices to be held in common by the majority of citizens. Education was viewed as the primary method in the acculturation process for minorities. Americanization policies were based on the idea that when indigenous people learned customs and values of the United States, they would be able to merge tribal traditions with American culture and peacefully join the majority of the society. After the end of the Indian Wars, in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebraska
Nebraska () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. It is bordered by South Dakota to the north; Iowa to the east and Missouri to the southeast, both across the Missouri River; Kansas to the south; Colorado to the southwest; and Wyoming to the west. It is the only triply landlocked U.S. state. Indigenous peoples, including Omaha, Missouria, Ponca, Pawnee, Otoe, and various branches of the Lakota (Sioux) tribes, lived in the region for thousands of years before European exploration. The state is crossed by many historic trails, including that of the Lewis and Clark Expedition. Nebraska's area is just over with a population of over 1.9 million. Its capital is Lincoln, and its largest city is Omaha, which is on the Missouri River. Nebraska was admitted into the United States in 1867, two years after the end of the American Civil War. The Nebraska Legislature is unlike any other American legislature in that it is unicameral, and its members a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |