|
Bifurcated Ligament
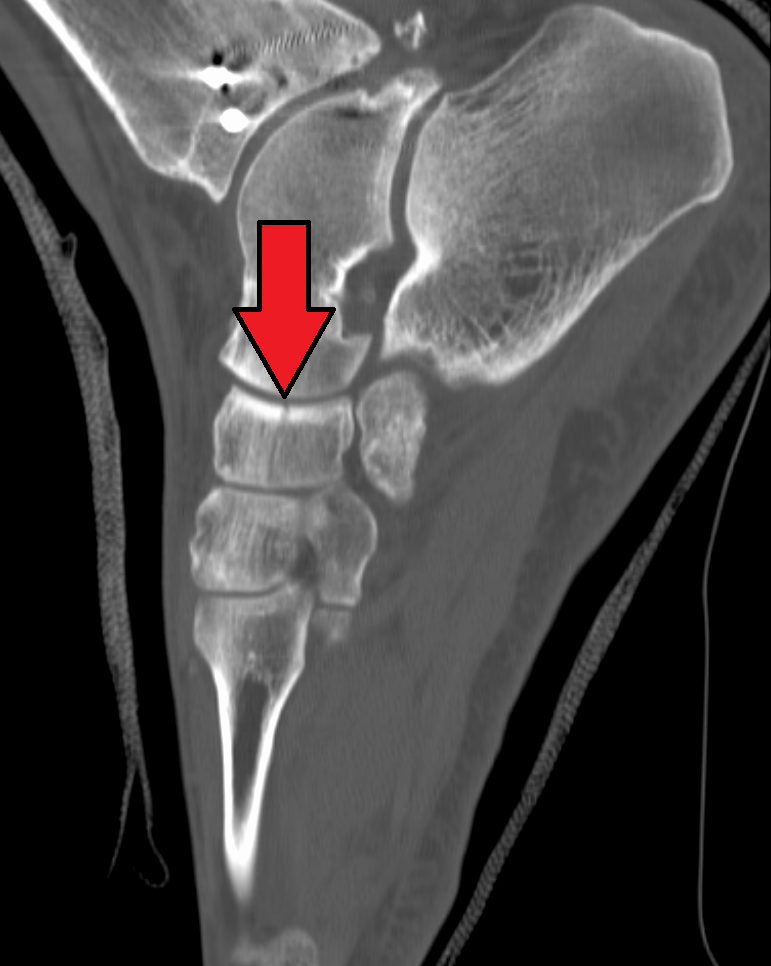
The bifurcated ligament (internal calcaneocuboid, interosseous ligament or bifurcate ligament) is a strong band, attached behind to the deep hollow on the upper surface of the calcaneus and dividing in front in a Y-shaped manner into a calcaneocuboid and a calcaneonavicular part. * The calcaneocuboid ligament (''ligamentum calcaneocuboideum'') is fixed to the medial side of the cuboid and forms one of the principal bonds between the first and second rows of the tarsal bones. * The calcaneonavicular ligament (''ligamentum calcaneonaviculare'') is attached to the lateral side of the navicular. (Note this is NOT the spring ligament which is commonly called the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament). It is commonly injured in "sprain-type" inversion injuries producing an avulsion fracture at the anterolateral process of the calcaneus In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talocalcaneal Articulation
In human anatomy, the subtalar joint, also known as the talocalcaneal joint, is a joint of the foot. It occurs at the meeting point of the talus and the calcaneus. The joint is classed structurally as a synovial joint, and functionally as a plane joint. Structure The talus is oriented slightly obliquely on the anterior surface of the calcaneus. There are three points of articulation between the two bones: two anteriorly and one posteriorly. The three articulations are known as facets, and they are the posterior, middle and anterior facets. * At the ''anterior and middle talocalcaneal articulation'', convex areas of the talus fits on to concave surfaces of the calcaneus. * The ''posterior talocalcaneal articulation'' is formed by a concave surface of the talus and a convex surface of the calcaneus. The sustentaculum tali forms the floor of middle facet, and the anterior facet articulates with the head of the talus, and sits lateral and congruent to the middle facet. In some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talocalcaneonavicular Articulation
The talocalcaneonavicular joint is a ball and socket joint in the foot; the rounded head of the talus is received into the concavity formed by the posterior surface of the navicular, the anterior articular surface of the calcaneus, and the upper surface of the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament. Structure As its shape suggests, this joint is a synovial ball-and-socket joint. It is composed of three articular surfaces: * The articulation between the medial talar articular surface on the sustentaculum tali of the superior calcaneus and the corresponding medial facet found inferiorly on the talus neck * The articulation between the anterior talar articular surface of the superior calcaneus and the anterior facet of the corresponding talus found inferiorly on the talar head * The articulation between the articular surface of navicular and the head of talus (talonavicular joint) Ligaments The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament also called the spring ligament forms the whole floor o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talus Bone
The talus (; Latin for ankle or ankle bone; : tali), talus bone, astragalus (), or ankle bone is one of the group of Foot#Structure, foot bones known as the tarsus (skeleton), tarsus. The tarsus forms the lower part of the ankle joint. It transmits the entire weight of the body from the lower legs to the foot.Platzer (2004), p 216 The talus has joints with the two bones of the lower leg, the tibia and thinner fibula. These leg bones have two prominences (the Lateral malleolus, lateral and Medial malleolus, medial malleoli) that articulation (anatomy), articulate with the talus. At the foot end, within the tarsus, the talus articulates with the calcaneus (heel bone) below, and with the curved navicular bone in front; together, these foot articulations form the Ball-and-socket joint, ball-and-socket-shaped talocalcaneonavicular joint. The talus is the second largest of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones; it is also one of the bones in the human body with the highest percentage of i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock (anatomy), hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubercle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the Abductor hallucis muscle, abductor hallucis and Abductor di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cuboid Bone
In the human body, the cuboid bone is one of the seven tarsal bones of the foot. Structure The cuboid bone is the most lateral of the bones in the distal row of the tarsus. It is roughly cubical in shape, and presents a prominence in its inferior (or plantar) surface, the tuberosity of the cuboid. The bone provides a groove where the tendon of the peroneus longus muscle passes to reach its insertion in the first metatarsal and medial cuneiform bones. Surfaces The dorsal surface, directed upward and lateralward, is rough, for the attachment of ligaments. The plantar surface presents in front a deep groove, the peroneal sulcus, which runs obliquely forward and medialward; it lodges the tendon of the peroneus longus, and is bounded behind by a prominent ridge, to which the long plantar ligament is attached. The ridge ends laterally in an eminence, the tuberosity, the surface of which presents an oval facet; on this facet glides the sesamoid bone or cartilage frequently found ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navicular Bone
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals. Human anatomy The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat, caused by the strongly concave Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, proximal joint, articular surface. The term ''navicular bone'' or ''hand navicular bone'' was formerly used for the scaphoid bone, one of the Carpal bones, carpal bones of the wrist. The navicular bone in humans is located on the Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, medial side of the foot, and articulates proximally with the Talus bone, talus, Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, distally with the three cuneiform bones, and Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, laterally with the Cuboid bone, cuboid. It is the last of the foot bones to start ossification and does not tend to do so until the end of the third year in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel; : calcanei or calcanea) or heel bone is a bone of the Tarsus (skeleton), tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock (anatomy), hock. Structure In humans, the calcaneus is the largest of the tarsal bones and the largest bone of the foot. Its long axis is pointed forwards and laterally. The talus bone, calcaneus, and navicular bone are considered the proximal row of tarsal bones. In the calcaneus, several important structures can be distinguished:Platzer (2004), p 216 There is a large calcaneal tuberosity located posteriorly on plantar surface with medial and lateral tubercles on its surface. Besides, there is another peroneal tubercle on its lateral surface. On its lower edge on either side are its lateral and medial processes (serving as the origins of the Abductor hallucis muscle, abductor hallucis and Abductor di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneocuboid Ligament
The calcaneocuboid ligament is a fibrous band that connects the superior surface of the calcaneus to the dorsal surface of the cuboid bone. It forms part of the bifurcated ligament The bifurcated ligament (internal calcaneocuboid, interosseous ligament or bifurcate ligament) is a strong band, attached behind to the deep hollow on the upper surface of the calcaneus and dividing in front in a Y-shaped manner into a calcaneocub .... References Foot Ligaments {{ligament-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calcaneonavicular Ligament
The plantar calcaneonavicular ligament (also known as the spring ligament or spring ligament complex) is a complex of three ligaments on the underside of the foot that connect the calcaneus with the navicular bone. Structure The plantar calcaneonavicular ligamentous complex is a broad and thick band with three constituent ligaments. These connect the anterior margin of the sustentaculum tali of the calcaneus to the plantar surface of the navicular bone. Its individual components are the: * superomedial calcaneonavicular ligament. * medioplantar oblique ligament. * inferior calcaneonavicular ligament. These ligament components attach to different parts of the navicular bone. The dorsal or superomedial component of the ligament presents a fibrocartilaginous facet, lined by the synovial membrane, upon which a portion of the head of the talus rests. Its plantar surface, consisting of the intermedial and lateral ligaments, is supported by the tendon of the tibialis posterior; i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Navicular
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals. Human anatomy The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsus (skeleton), tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat, caused by the strongly concave Anatomical terms of location#Proximal and distal, proximal joint, articular surface. The term ''navicular bone'' or ''hand navicular bone'' was formerly used for the scaphoid bone, one of the Carpal bones, carpal bones of the wrist. The navicular bone in humans is located on the Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, medial side of the foot, and articulates proximally with the Talus bone, talus, Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, distally with the three cuneiform bones, and Anatomical terms of location#Relative directions, laterally with the Cuboid bone, cuboid. It is the last of the foot bones to start ossification and does not tend to do so until the end of the third year in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprained Ankle
A sprained ankle (twisted ankle, rolled ankle, turned ankle, etc.) is an injury where sprain occurs on one or more ligaments of the ankle. It is the most commonly occurring injury in sports, mainly in ball sports (basketball, volleyball, and football) as well as racquet sports (tennis, badminton and pickleball). Signs and symptoms Knowing the symptoms that can be experienced with a sprain is important in determining that the injury is not really a break in the bone. When a sprain occurs, hematoma occurs within the tissue that surrounds the joint, causing a bruise. White blood cells responsible for inflammation migrate to the area, and blood flow increases as well. Along with this inflammation, swelling and pain is experienced. The nerves in the area become more sensitive when the injury is suffered, so pain is felt as throbbing and will worsen if there is pressure placed on the area. Warmth and redness are also seen as blood flow is increased. There is also decreased ability t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avulsion Fracture
An avulsion fracture is a bone fracture which occurs when a fragment of bone tears away from the main mass of bone as a result of physical trauma. This can occur at the ligament by the application of forces external to the body (such as a fall or pull) or at the tendon by a muscular contraction that is stronger than the forces holding the bone together. Generally muscular avulsion is prevented by the neurological limitations placed on muscle contractions. Highly trained Athlete, athletes can overcome this neurological inhibition of strength and produce a much greater force output capable of breaking or avulsing a bone. Types Dental avulsion dental trauma, Traumatic complete displacement of a tooth from its socket in alveolar bone. It is a serious dental emergency in which Treatment of knocked-out (avulsed) teeth, prompt management (within 20–40 minutes of injury) affects the prognosis of the tooth. Tuberosity avulsion of the 5th metatarsal file:Proximal fractures of 5th me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |