|
Bifolium From The
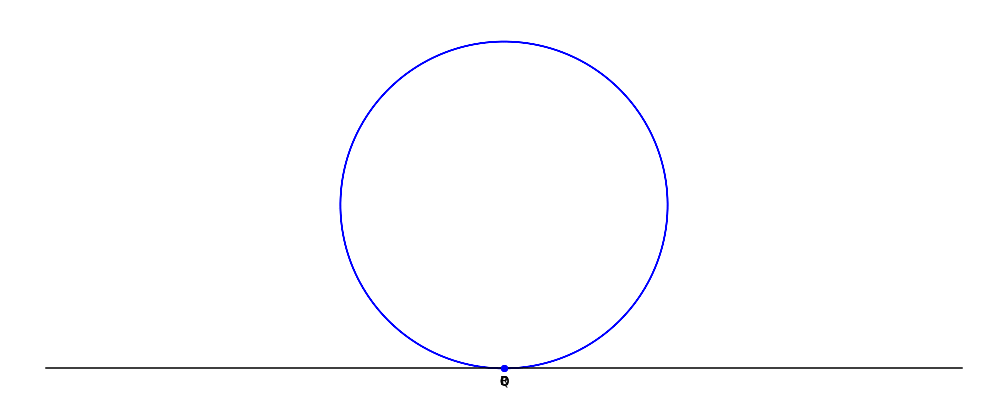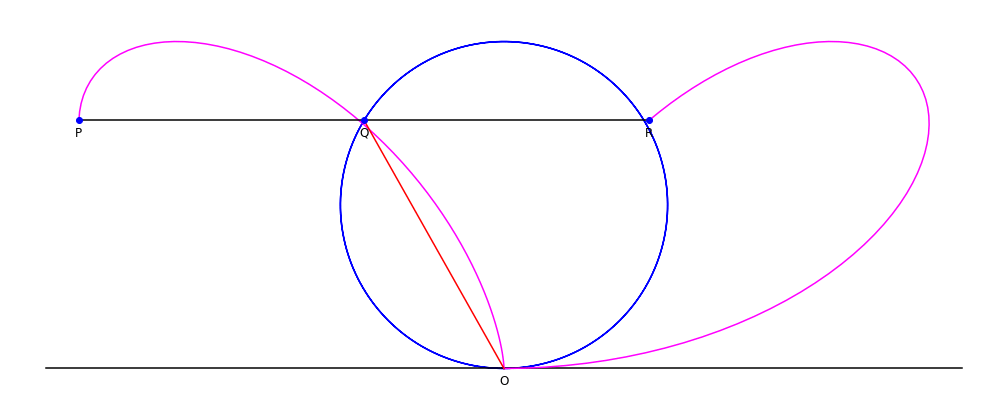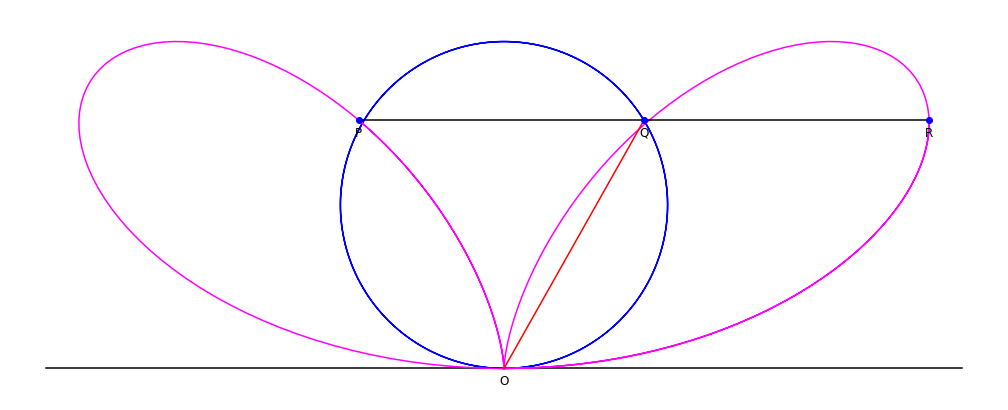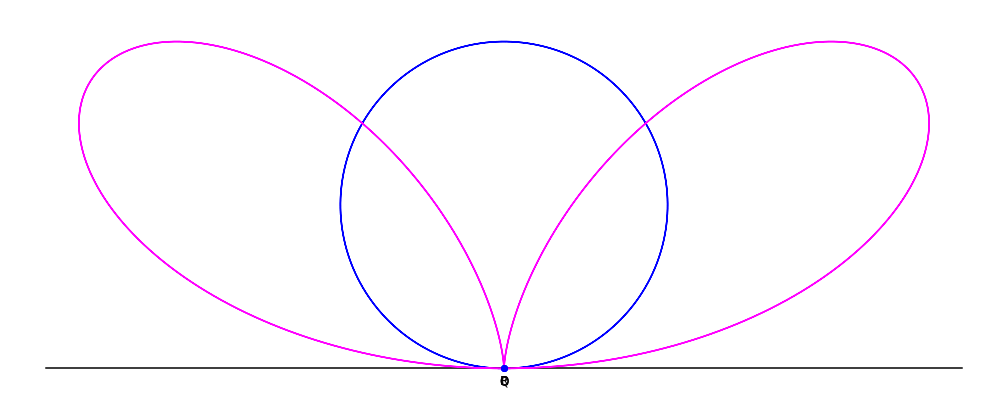
A bifolium is a quartic plane curve with equation in Cartesian coordinates: :(x^2 + y^2)^2 = ax^2y. Construction and equations Given a circle C through a point O, and line L tangent to the circle at point O: for each point Q on C, define the point P such that PQ is parallel to the tangent line L, and PQ = OQ. The collection of points P forms the bifolium. In polar coordinates, the bifolium's equation is :\rho=a\sin\theta\cdot\cos^2\theta, :while (first eqn.) :\rho^=a\cdot x^2y,\,\,\rho^2=\pm x\cdot(ay)^. For ''a'' = 1, the total included area is approximately 0.10. See also * Folium of Descartes * Trifolium curve Clovers, also called trefoils, are plants of the genus ''Trifolium'' (), consisting of about 300 species of flowering plants in the legume family Fabaceae originating in Europe. The genus has a cosmopolitan distribution with the highest diversity ... Reference {{Reflist External linkBifolium at MathWorldby Wolfram Plane curves Algebraic curves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quartic Plane Curve
In algebraic geometry, a quartic plane curve is a plane algebraic curve of the fourth degree. It can be defined by a bivariate quartic equation: :Ax^4+By^4+Cx^3y+Dx^2y^2+Exy^3+Fx^3+Gy^3+Hx^2y+Ixy^2+Jx^2+Ky^2+Lxy+Mx+Ny+P=0, with at least one of not equal to zero. This equation has 15 constants. However, it can be multiplied by any non-zero constant without changing the curve; thus by the choice of an appropriate constant of multiplication, any one of the coefficients can be set to 1, leaving only 14 constants. Therefore, the space of quartic curves can be identified with the real projective space It also follows, from Cramer's theorem on algebraic curves, that there is exactly one quartic curve that passes through a set of 14 distinct points in general position, since a quartic has 14 degrees of freedom. A quartic curve can have a maximum of: * Four connected components * Twenty-eight bi-tangents * Three ordinary double points. One may also consider quartic curves over oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cartesian Coordinate
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular oriented lines, called '' coordinate lines'', ''coordinate axes'' or just ''axes'' (plural of ''axis'') of the system. The point where the axes meet is called the '' origin'' and has as coordinates. The axes directions represent an orthogonal basis. The combination of origin and basis forms a coordinate frame called the Cartesian frame. Similarly, the position of any point in three-dimensional space can be specified by three ''Cartesian coordinates'', which are the signed distances from the point to three mutually perpendicular planes. More generally, Cartesian coordinates specify the point in an -dimensional Euclidean space for any dimension . These coordinates are the signed distances from the point to mutually perpendicular fixed h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bifolium
A bifolium is a quartic plane curve with equation in Cartesian coordinates: :(x^2 + y^2)^2 = ax^2y. Construction and equations Given a circle C through a point O, and line L tangent to the circle at point O: for each point Q on C, define the point P such that PQ is parallel to the tangent line L, and PQ = OQ. The collection of points P forms the bifolium. In polar coordinates, the bifolium's equation is :\rho=a\sin\theta\cdot\cos^2\theta, :while (first eqn.) :\rho^=a\cdot x^2y,\,\,\rho^2=\pm x\cdot(ay)^. For ''a'' = 1, the total included area is approximately 0.10. See also * Folium of Descartes In geometry, the folium of Descartes (; named for René Descartes) is an algebraic curve defined by the implicit equation x^3+y^3-3a\cdot xy=0. dy/dx=(x^2-ay)/(ax-y^2), \,dx/dy=(ax-y^2)/(x^2-ay). History The curve was first proposed and studi ... * Trifolium curve Reference {{Reflist External linkBifolium at MathWorldby Wolfram Plane curves Algebraic curves [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is called the radius. The length of a line segment connecting two points on the circle and passing through the centre is called the diameter. A circle bounds a region of the plane called a Disk (mathematics), disc. The circle has been known since before the beginning of recorded history. Natural circles are common, such as the full moon or a slice of round fruit. The circle is the basis for the wheel, which, with related inventions such as gears, makes much of modern machinery possible. In mathematics, the study of the circle has helped inspire the development of geometry, astronomy and calculus. Terminology * Annulus (mathematics), Annulus: a ring-shaped object, the region bounded by two concentric circles. * Circular arc, Arc: any Connected ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Point (geometry)
In geometry, a point is an abstract idealization of an exact position, without size, in physical space, or its generalization to other kinds of mathematical spaces. As zero-dimensional objects, points are usually taken to be the fundamental indivisible elements comprising the space, of which one-dimensional curves, two-dimensional surfaces, and higher-dimensional objects consist. In classical Euclidean geometry, a point is a primitive notion, defined as "that which has no part". Points and other primitive notions are not defined in terms of other concepts, but only by certain formal properties, called axioms, that they must satisfy; for example, ''"there is exactly one straight line that passes through two distinct points"''. As physical diagrams, geometric figures are made with tools such as a compass, scriber, or pen, whose pointed tip can mark a small dot or prick a small hole representing a point, or can be drawn across a surface to represent a curve. A po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Line (geometry)
In geometry, a straight line, usually abbreviated line, is an infinitely long object with no width, depth, or curvature, an idealization of such physical objects as a straightedge, a taut string, or a ray (optics), ray of light. Lines are space (mathematics), spaces of dimension one, which may be Embedding, embedded in spaces of dimension two, three, or higher. The word ''line'' may also refer, in everyday life, to a line segment, which is a part of a line delimited by two Point (geometry), points (its ''endpoints''). Euclid's Elements, Euclid's ''Elements'' defines a straight line as a "breadthless length" that "lies evenly with respect to the points on itself", and introduced several postulates as basic unprovable properties on which the rest of geometry was established. ''Euclidean line'' and ''Euclidean geometry'' are terms introduced to avoid confusion with generalizations introduced since the end of the 19th century, such as Non-Euclidean geometry, non-Euclidean, Project ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangent Line
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points on the curve. More precisely, a straight line is tangent to the curve at a point if the line passes through the point on the curve and has slope , where ''f'' is the derivative of ''f''. A similar definition applies to space curves and curves in ''n''-dimensional Euclidean space. The point where the tangent line and the curve meet or intersect is called the ''point of tangency''. The tangent line is said to be "going in the same direction" as the curve, and is thus the best straight-line approximation to the curve at that point. The tangent line to a point on a differentiable curve can also be thought of as a '' tangent line approximation'', the graph of the affine function that best approximates the original function at the given p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parallel (geometry)
In geometry, parallel lines are coplanar infinite straight line (geometry), lines that do not intersecting lines, intersect at any point. Parallel planes are plane (geometry), planes in the same three-dimensional space that never meet. ''Parallel curves'' are curves that do not tangent, touch each other or intersect and keep a fixed minimum distance. In three-dimensional Euclidean space, a line and a plane that do not share a point are also said to be parallel. However, two noncoplanar lines are called ''skew lines''. Line segments and Euclidean vectors are parallel if they have the same direction (geometry), direction or opposite direction (geometry), opposite direction (not necessarily the same length). Parallel lines are the subject of Euclid's parallel postulate. Parallelism is primarily a property of affine geometry, affine geometries and Euclidean geometry is a special instance of this type of geometry. In some other geometries, such as hyperbolic geometry, lines can have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system specifies a given point (mathematics), point in a plane (mathematics), plane by using a distance and an angle as its two coordinate system, coordinates. These are *the point's distance from a reference point called the ''pole'', and *the point's direction from the pole relative to the direction of the ''polar axis'', a ray (geometry), ray drawn from the pole. The distance from the pole is called the ''radial coordinate'', ''radial distance'' or simply ''radius'', and the angle is called the ''angular coordinate'', ''polar angle'', or ''azimuth''. The pole is analogous to the origin in a Cartesian coordinate system. Polar coordinates are most appropriate in any context where the phenomenon being considered is inherently tied to direction and length from a center point in a plane, such as spirals. Planar physical systems with bodies moving around a central point, or phenomena originating from a central point, are often simpler and more in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Area (geometry)
Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while ''surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-dimensional object. Area can be understood as the amount of material with a given thickness that would be necessary to fashion a model of the shape, or the amount of paint necessary to cover the surface with a single coat. It is the two-dimensional analogue of the length of a curve (a one-dimensional concept) or the volume of a solid (a three-dimensional concept). Two different regions may have the same area (as in squaring the circle); by synecdoche, "area" sometimes is used to refer to the region, as in a "polygonal area". The area of a shape can be measured by comparing the shape to squares of a fixed size. In the International System of Units (SI), the standard unit of area is the square metre (written as m2), which is the area of a square ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Folium Of Descartes
In geometry, the folium of Descartes (; named for René Descartes) is an algebraic curve defined by the implicit equation x^3+y^3-3a\cdot xy=0. dy/dx=(x^2-ay)/(ax-y^2), \,dx/dy=(ax-y^2)/(x^2-ay). History The curve was first proposed and studied by René Descartes in 1638. Its claim to fame lies in an incident in the development of calculus. Descartes challenged Pierre de Fermat to find the tangent line to the curve at an arbitrary point, since Fermat had recently discovered a method for finding tangent lines. Fermat solved the problem easily, something Descartes was unable to do. Since the invention of calculus, the slope of the tangent line can be found easily using implicit differentiation. Mayor Johan(nes) Hudde's second letter on maxima and minima (1658) mentions his calculation of the maximum width of the closed loop, part of ''Mathematical Exercitions'', 5 books (1656/57 Leyden) p. 498, by Frans van Schooten Jnr. Graphing the curve The folium of Descartes can be expr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |