Bifolium on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A bifolium is a
A bifolium is a
 Given a
Given a
Bifolium at MathWorld
by Wolfram Plane curves Algebraic curves
quartic plane curve
In algebraic geometry, a quartic plane curve is a plane algebraic curve of the fourth degree. It can be defined by a bivariate quartic equation:
:Ax^4+By^4+Cx^3y+Dx^2y^2+Exy^3+Fx^3+Gy^3+Hx^2y+Ixy^2+Jx^2+Ky^2+Lxy+Mx+Ny+P=0,
with at least one of ...
with equation in Cartesian coordinate
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular o ...
s:
:
Construction and equations
 Given a
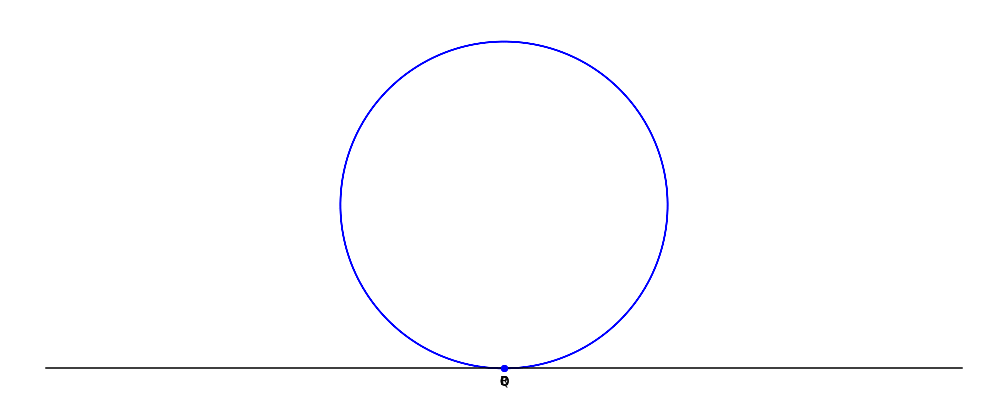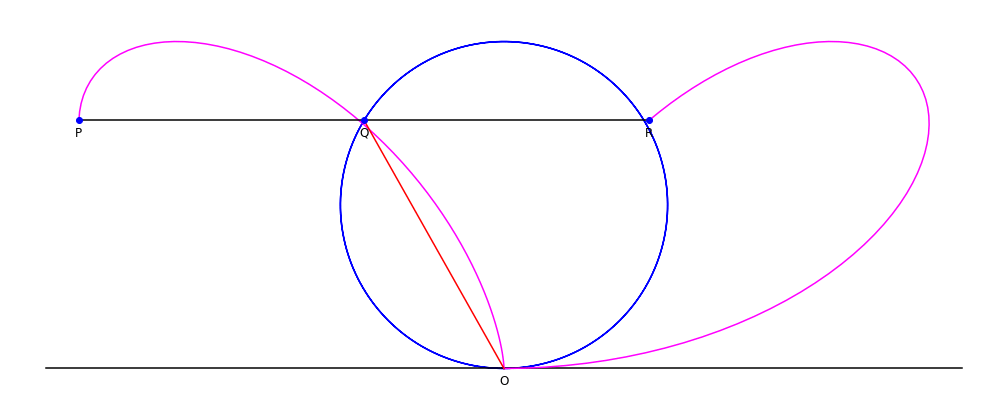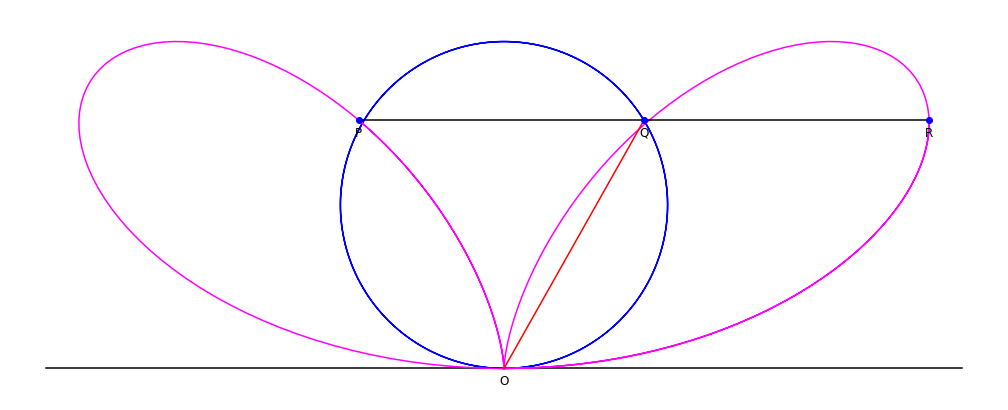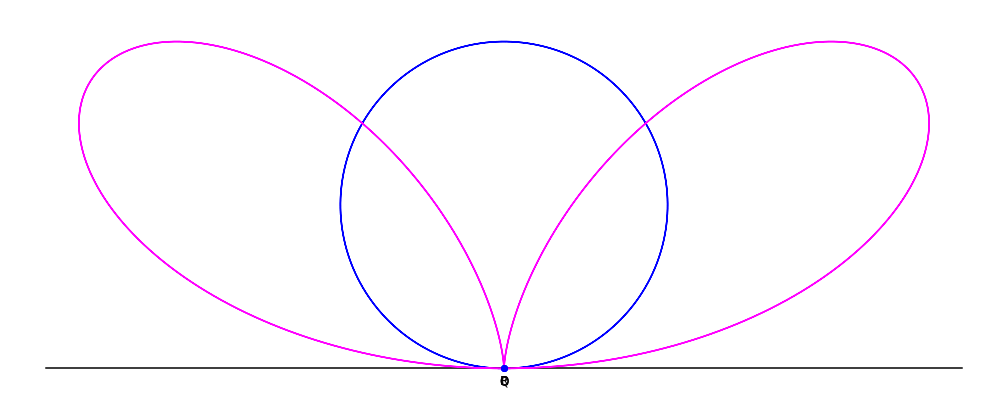
Given a circle
A circle is a shape consisting of all point (geometry), points in a plane (mathematics), plane that are at a given distance from a given point, the Centre (geometry), centre. The distance between any point of the circle and the centre is cal ...
C through a point O, and line L tangent
In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. Leibniz defined it as the line through a pair of infinitely close points o ...
to the circle at point O: for each point Q on C, define the point P such that PQ is parallel
Parallel may refer to:
Mathematics
* Parallel (geometry), two lines in the Euclidean plane which never intersect
* Parallel (operator), mathematical operation named after the composition of electrical resistance in parallel circuits
Science a ...
to the tangent line L, and PQ = OQ. The collection of points P forms the bifolium.
In polar coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system specifies a given point (mathematics), point in a plane (mathematics), plane by using a distance and an angle as its two coordinate system, coordinates. These are
*the point's distance from a reference ...
, the bifolium's equation is
:
:while (first eqn.)
:
For ''a'' = 1, the total included area
Area is the measure of a region's size on a surface. The area of a plane region or ''plane area'' refers to the area of a shape or planar lamina, while '' surface area'' refers to the area of an open surface or the boundary of a three-di ...
is approximately 0.10.
See also
*Folium of Descartes
In geometry, the folium of Descartes (; named for René Descartes) is an algebraic curve defined by the implicit equation
x^3+y^3-3a\cdot xy=0.
dy/dx=(x^2-ay)/(ax-y^2), \,dx/dy=(ax-y^2)/(x^2-ay). History
The curve was first proposed and studi ...
* Trifolium curve
Reference
{{ReflistExternal link
Bifolium at MathWorld
by Wolfram Plane curves Algebraic curves