|
Bieresel
A ''bieresel'' ()Ranke (1927): ''Bieresel''. In: Hanns Bächtold-Stäubli, Eduard Hoffmann-Krayer (1927): ''Handwörterbuch des Deutschen Aberglaubens: Band 1 Aal-Butzemann''. Berlin/New York 2000 p. 1282. ("beer donkey"; sg., pl.; ; English mythological literature also offers the corrupted forms Biersal, Bieresal, and Bierasal not found in German literature) is a type of kobold (house spirit) of German folklore. General description The ''bieresel'' is mentioned in the ''Die gestriegelte Rockenphilosophie'' (first published 1705) by apothecary and natural historian , where the "bier esel" is described as a devil or kobold taking on a shape of a donkey and drinking beer by night, and seen in many places. The term ''bieresel'' is attested as an insult dated 1597 in Bürgel. Generally, the bieresel is described as a spirit with donkey legs, sometimes only three, hence the name meaning "beer donkey". In Ruhla, Thuringia, a ''bieresel'' (with the appearance of a three- or four-leg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kobold
A kobold (; ''kobolt'', ''kobolde'', cobold) is a general or generic name for the household spirit (''hausgeist'') in German folklore. It may invisibly make noises (i.e., be a poltergeist), or helpfully perform kitchen chores or stable work. But it can be a prankster as well. It may expect a bribe or offering of milk, etc. for its efforts or good behaviour. When mistreated (cf. fig. right), its reprisal can be utterly cruel. A () meaning "little hat" is one subtype; this and other kobold sprites are known for its pointy red cap, such as the ''niss'' (cognate of Nisse (folklore), nisse of Norway) or ''puk'' (cognate of Puck (folklore), puck fairy) which are attested in Northern Germany, alongside ''drak'', a dragon-type name, as the sprite is sometimes said to appear as a shaft of fire, with what looks like a head. There is also the combined form Nis Puk. A house sprite Hinzelmann is a shape-shifter assuming many forms, such as a feather or animals. The name supposedly refer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Folklore
German folklore is the folk tradition which has developed in Germany over a number of centuries. Seeing as Germany was divided into numerous polities for most of its history, this term might both refer to the folklore of Germany proper and of all German-speaking countries, this wider definition including folklore of Austria and Liechtenstein as well as the German-speaking parts of Switzerland, Luxembourg, Belgium, and Italy. Characteristics It shares many characteristics with Nordic folklore and English folklore due to their origins in a common Germanic mythology. It reflects a similar mix of influences: a pre-Christian pantheon and other beings equivalent to those of Norse mythology; magical characters (sometimes recognizably pre-Christian) associated with Christian festivals, and various regional 'character' stories. As in Scandinavia, when belief in the old gods disappeared, remnants of the mythos persisted: There are: * Frau Holle or Perchta, a "supernatural" patron o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bier
A bier is a stand on which a corpse, coffin, or casket containing a corpse is placed to lie in state or to be carried to its final disposition.''The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language'' (American Heritage Publishing Co., Inc., New York, 1973), s.v., "bier" In Christian burial, the bier is often placed in the centre of the nave with candles surrounding it, and remains in place during the funeral. The bier is a flat frame, traditionally wooden but sometimes of other materials. In antiquity it was often a wooden board on which the dead were placed, covered with a shroud. In modern times, the corpse is rarely carried on the bier without being first placed in a coffin or casket, though the coffin or casket is sometimes kept open. A bier is often draped with cloth to lend dignity to the funeral service. The modern funeral industry uses a collapsible aluminium bier on wheels, known as a "church truck" to move the coffin to and from the church or funeral home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schrat
The ''Schrat'' () or ''Schratt'', also ''Schraz'' or ''Waldschrat'' (forest ''Schrat''), is a rather diverse German folklore, German and Slavic mythology, Slavic legendary creature with aspects of either a wild man, wood sprite, Household deity, domestic sprite and a nightmare Mare (folklore), demon. In other languages it is further known as ''Skrat''. Etymology The word ''Schrat'' originates in the cognate, same word root as Old Norse ''skrati'', ''skratti'' (sorcerer, giant), Icelandic language, Icelandic ' (devil) and ''vatnskratti'' (water sprite), Swedish language, Swedish ' (fool, sorcerer, devil), and English language, English ' (devil). The German term entered Slavic languages and (via North Germanic languages) Finno-Ugric languages, Finno-Ugric ones as well. Examples are Polish language, Polish ''skrzat'', ''skrzot'' (domestic sprite, dwarf), Czech language, Czech (domestic sprite, gold bringing devil/gnome, mining sprite), Slovene language, Slovene (domestic sprit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grape Treading
Grape-treading or grape-stomping is part of the method of Maceration (wine), maceration used in traditional wine-making.Clarke, Oz (2009). ''Oz Clarke's Pocket Wine Guide 2010.'' Sterling Publishing Company, Cheap, BA (2010). ''Mr. Cheap's Guide to Wine.'' Adams Media, Rather than being crushed in a wine press or by another mechanized method, grapes are repeatedly trampled in vats by barefoot participants to release their juices and begin Fermentation (wine), fermentation. Grape-treading was widespread in the history of winemaking, but with the introduction of industrial methods, it now survives mostly as a recreational or competitive activity at cultural festivals. History One of the earliest extant visual representations of the practice appears on a Roman Empire sarcophagus from the 3rd century AD, which depicts an idealized pastoral scene with a group of Erotes harvesting and stomping grapes at Vindemia, a rural festival.Wight, Karol (2008)Roman sarcophagus, c. 290-300 AD.The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
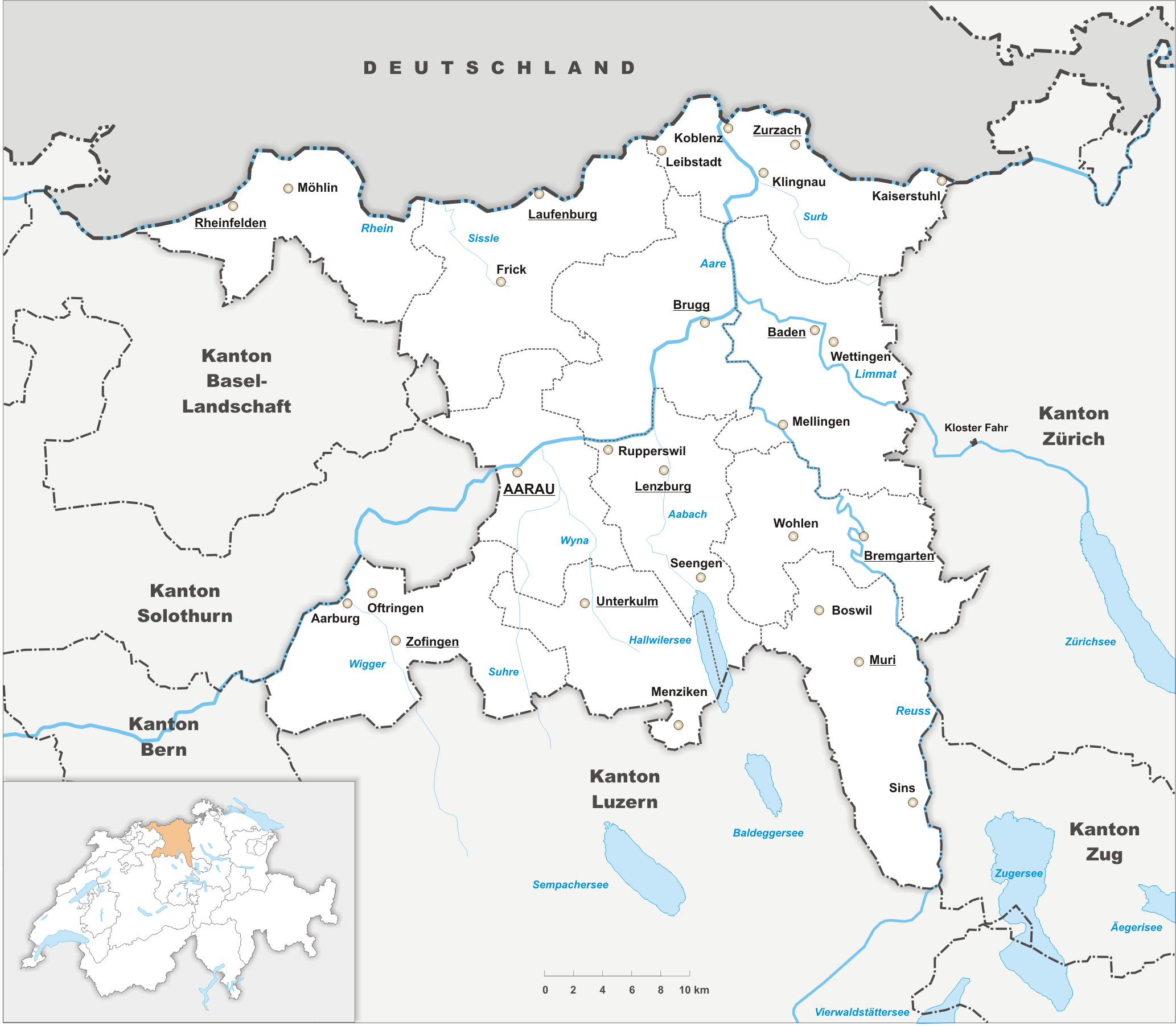
Aargau
Aargau ( ; ), more formally the Canton of Aargau (; ; ; ), is one of the Canton of Switzerland, 26 cantons forming the Switzerland, Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capital is Aarau. Aargau is one of the most northerly cantons of Switzerland, by the lower course of the Aare River, which is why it is called ''Aar-Gau (country subdivision), gau'' ("Aare province"). It is one of the most densely populated regions of Switzerland. History Early history The area of Aargau and the surrounding areas were controlled by the Helvetians, a tribe of Celts, as far back as 200 BC. It was eventually occupied by the Roman Empire, Romans and then by the 6th century, the Franks. The Romans built a major settlement called Vindonissa, near the present location of Brugg. Medieval Aargau The reconstructed Old High German name of Aargau is ''Argowe'', first unambiguously attested (in the spelling ''Argue'') in 795. The term described a territory only loosely eq ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oberflachs
Oberflachs is a former municipalities of Switzerland, municipality in the district of Brugg (district), Brugg in Canton Aargau in Switzerland. It is located about 6 km south west of the town of Brugg, Aargau, Brugg. On 1 January 2014 the former municipalities of Oberflachs and Schinznach-Dorf merged into the new municipality of Schinznach.Nomenklaturen – Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz . Retrieved 13 December 2014 History While various Switzerland in the Roman era, Roman era bricks and coins have been discovered, the first record of Oberflachs is in 1342 as ''Obreflaht''. From the Middle Ages until 1732, Schloss Kasteln, Kasteln Castle held the rights to High, middle and low justice, lo ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kurt Ranke
Kurt Ranke (14 April 1908 – 6 June 1985) was a German ethnologist who specialized in the study of fairy tales. Biography Kurt Ranke was born in Blankenburg, Germany on 14 April 1908. His father was a postal inspector. Growing up in Essen, Ranke studied Germanistics, ethnology and history at the universities of Bonn and Munich from 1927 to 1930. Ranke subsequently transferred to the University of Kiel, where he in 1933 gained a PhD on fairy tales under the supervision of Karl Wesle. He completed his habilitation on comparative religion, ethnology and ancient history in 1938 at Kiel under the supervision of Wesle. His habilitation thesis centered on the cult of the dead in Indo-European religion. After gaining his habilitation, Ranke lectured at Kiel on ethnology and ancient history, but was drafted into the Wehrmacht during World War II. In 1951 he resumed lecturing at Kiel. He began publishing the ''Encyclopedia of Fairy Tales'' in 1957, and founded the journal '' Fabula'' in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and its largest city is Leipzig. Saxony is the List of German states by area, tenth largest of Germany's sixteen states, with an area of , and the List of German states by population, sixth most populous, with more than 4 million inhabitants. The term Saxony (other), Saxony has been in use for more than a millennium. It was used for the medieval Duchy of Saxony, the Electorate of Saxony of the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of Saxony, and twice for a republic. The first Free State of Saxony was established in 1918 as a constituent state of the Weimar Republic. After World War II, it was under Soviet occupation before it became part of communist East Germany and was abolished by the government in 1952. Following German reunificat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Germanic Mythology
Germanic mythology consists of the body of myths native to the Germanic peoples, including Norse mythology, Anglo-Saxon paganism#Mythology, Anglo-Saxon mythology, and Continental Germanic mythology. It was a key element of Germanic paganism. Origins As the Germanic languages developed from Proto-Indo-European language, Germanic mythology is ultimately a development of Proto-Indo-European mythology. Archaeological remains, such as petroglyphs in Scandinavia, suggest continuity in Germanic mythology since at least the Nordic Bronze Age. Sources The earliest written sources on Germanic mythology include literature by Ancient Rome, Roman writers. This includes ''Commentaries on the Gallic War'' by Julius Caesar, ''Geographica'' by Strabo, and ''Germania (book), Germania'' by Tacitus. Later Latin-language sources on Germanic mythology include ''Getica'' by Jordanes, ''History of the Lombards'' by Paul the Deacon, ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' by Bede, ''Vita Ansga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sprite (entity)
A sprite is a supernatural entity in European mythology. They are often depicted as fairy-like creatures or as an ethereal entity. Etymology The word ''sprite'' is derived from the Latin ''spiritus'' ("spirit"), via the French '' esprit''. Variations on the term include ''spright'' and the Celtic ''spriggan''. The term is chiefly used with regard to elves and fairies in European folklore, and in modern English is rarely used in reference to spirits. Belief in sprites The belief in diminutive beings such as sprites, elves, fairies, etc. has been common in many parts of the world, and might to some extent still be found within neo-spiritual and religious movements such as "neo-druidism" and Ásatrú. In some elemental magics, the sprite is often believed to be the elemental of air (see also sylph). Water sprite A water sprite (also called a water fairy or water faery) is a general term for an elemental spirit associated with water, according to alchemist Paracelsus. Wat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |