|
Bi-hemispherical Reflectance
Bi-hemispherical reflectance is the reflectance of a surface under diffuse illumination (with no direct component). Bi-hemispherical reflectance is an important part of the Bidirectional reflectance distribution function over all viewing and illumination directions of a hemisphere. It is sometimes called "white-sky albedo". See also *Directional-hemispherical reflectance Directional-hemispherical reflectance is the reflectance of a surface under direct illumination (with no diffuse component). Directional-hemispherical reflectance is the integral of the bidirectional reflectance distribution function over all viewin ... References Electromagnetic radiation {{Optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
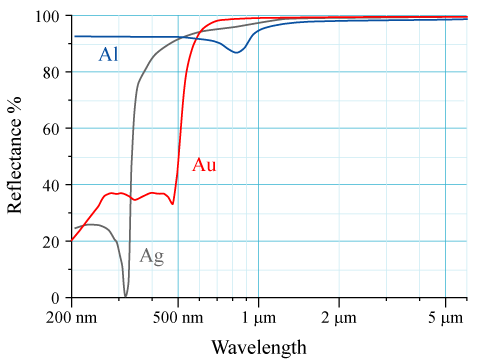
Reflectivity
The reflectance of the surface of a material is its effectiveness in reflecting radiant energy. It is the fraction of incident electromagnetic power that is reflected at the boundary. Reflectance is a component of the response of the electronic structure of the material to the electromagnetic field of light, and is in general a function of the frequency, or wavelength, of the light, its polarization, and the angle of incidence. The dependence of reflectance on the wavelength is called a ''reflectance spectrum'' or ''spectral reflectance curve''. Mathematical definitions Hemispherical reflectance The ''hemispherical reflectance'' of a surface, denoted , is defined as R = \frac, where is the radiant flux ''reflected'' by that surface and is the radiant flux ''received'' by that surface. Spectral hemispherical reflectance The ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in frequency'' and ''spectral hemispherical reflectance in wavelength'' of a surface, denoted and respectively, ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffuse Reflection
Diffuse reflection is the reflection of light or other waves or particles from a surface such that a ray incident on the surface is scattered at many angles rather than at just one angle as in the case of specular reflection. An ''ideal'' diffuse reflecting surface is said to exhibit Lambertian reflection, meaning that there is equal luminance when viewed from all directions lying in the half-space adjacent to the surface. A surface built from a non-absorbing powder such as plaster, or from fibers such as paper, or from a polycrystalline material such as white marble, reflects light diffusely with great efficiency. Many common materials exhibit a mixture of specular and diffuse reflection. The visibility of objects, excluding light-emitting ones, is primarily caused by diffuse reflection of light: it is diffusely-scattered light that forms the image of the object in the observer's eye. Mechanism Diffuse reflection from solids is generally not due to surface roughness. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bidirectional Reflectance Distribution Function
The bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF; f_(\omega_,\, \omega_) ) is a function of four real variables that defines how light is reflected at an opaque surface. It is employed in the optics of real-world light, in computer graphics algorithms, and in computer vision algorithms. The function takes an incoming light direction, \omega_, and outgoing direction, \omega_ (taken in a coordinate system where the surface normal \mathbf n lies along the ''z''-axis), and returns the ratio of reflected radiance exiting along \omega_ to the irradiance incident on the surface from direction \omega_. Each direction \omega is itself parameterized by azimuth angle \phi and zenith angle \theta, therefore the BRDF as a whole is a function of 4 variables. The BRDF has units sr−1, with steradians (sr) being a unit of solid angle. Definition The BRDF was first defined by Fred Nicodemus around 1965. The definition is: f_(\omega_,\, \omega_) \,=\, \frac \,=\, \frac\frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sphere
A sphere () is a Geometry, geometrical object that is a solid geometry, three-dimensional analogue to a two-dimensional circle. A sphere is the Locus (mathematics), set of points that are all at the same distance from a given point in three-dimensional space.. That given point is the centre (geometry), centre of the sphere, and is the sphere's radius. The earliest known mentions of spheres appear in the work of the Greek mathematics, ancient Greek mathematicians. The sphere is a fundamental object in many fields of mathematics. Spheres and nearly-spherical shapes also appear in nature and industry. Bubble (physics), Bubbles such as soap bubbles take a spherical shape in equilibrium. spherical Earth, The Earth is often approximated as a sphere in geography, and the celestial sphere is an important concept in astronomy. Manufactured items including pressure vessels and most curved mirrors and lenses are based on spheres. Spheres rolling, roll smoothly in any direction, so mos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Directional-hemispherical Reflectance
Directional-hemispherical reflectance is the reflectance of a surface under direct illumination (with no diffuse component). Directional-hemispherical reflectance is the integral of the bidirectional reflectance distribution function over all viewing directions. It is sometimes called "black-sky albedo Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that refl ...". References See also * Bi-hemispherical reflectance Electromagnetic radiation Climatology {{Optics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |