|
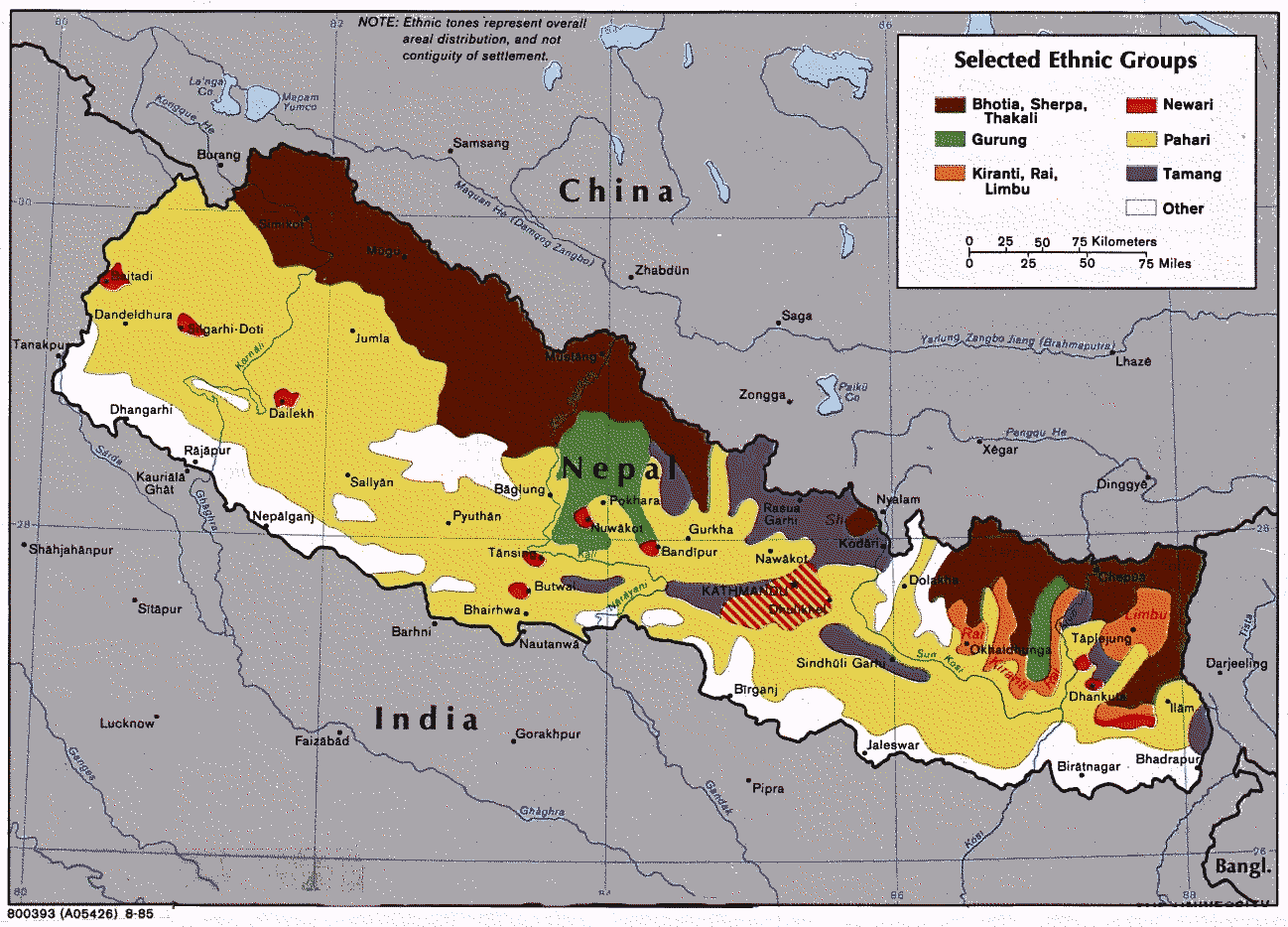
Bhutias
The Bhutias (exonym; Nepali: भुटिया, "People from Tibet") or Drejongpas (endonym; , THL: dre-jong pa, "People of the Rice Valley") are a Tibetan ethnic group native to the Indian state of Sikkim who speak Drejongke, a Tibetic language which descends from old Tibetan. The majority of Bhutias live in Sikkim, while a significant number also reside in the Darjeeling and Kalimpong districts of northern West Bengal and in countries such as Nepal and Bhutan. Language The language spoken by the Bhutias of Sikkim is Drejongke, a Tibetic language which has a lexical similarity of 65% with Dzongkha, the language of Bhutan. By comparison, Drejongke is only 42% lexically similar with Standard Tibetan. Sikkimese has also been influenced to some degree by the neighboring Yolmo and Tamang languages. History Migration from Tibet to Sikkim in small numbers occurred since the 8th century. However, the 13th century saw an increase in migrations as many clans came with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sikkim
Sikkim ( ; ) is a States and union territories of India, state in northeastern India. It borders the Tibet Autonomous Region of China in the north and northeast, Bhutan in the east, Koshi Province of Nepal in the west, and West Bengal in the south. Sikkim is also close to the Siliguri Corridor, which borders Bangladesh. Sikkim is the List of states and union territories of India by population, least populous and List of states and union territories of India by area, second-smallest among the Indian states. Situated in the Eastern Himalaya, Sikkim is notable for its biodiversity, including Alpine climate, alpine and subtropical climates, as well as being a host to Kangchenjunga, the List of mountains in India, highest peak in India and List of highest mountains on Earth, third-highest on Earth. Sikkim's Capital (political), capital and largest city is Gangtok. Almost 35% of the state is covered by Khangchendzonga National Park – a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The Kingdom of Si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ethnologue
''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'' is an annual reference publication in print and online that provides statistics and other information on the living languages of the world. It is the world's most comprehensive catalogue of languages. It was first issued in 1951 and is now published by SIL International, an American evangelical Parachurch organization, Christian non-profit organization. Overview and content ''Ethnologue'' has been published by SIL Global (formerly known as the Summer Institute of Linguistics), a Christian linguistics, linguistic service organization with an international office in Dallas, Texas. The organization studies numerous minority languages to facilitate language development, and to work with speakers of such language communities in translating portions of the Bible into their languages. Despite the Christian orientation of its publisher, ''Ethnologue'' is not ideologically or theologically biased. ''Ethnologue'' includes alternative names and Exo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old Tibetan
Old Tibetan refers to the earliest attested form of Tibetan language, reflected in documents from the adoption of writing by the Tibetan Empire in the mid-7th century to the early 9th century. In 816 CE, during the reign of Tibetan King Sadnalegs, literary Tibetan underwent comprehensive standardization, resulting in Classical Tibetan. Phonology Old Tibetan is characterised by many features that are lost in Classical Tibetan, including ''my-'' rather than ''m-'' before the vowels ''-i-'' and ''-e-'', the cluster ''sts-'' which simplifies to ''s-'' in Classical Tibetan, and a reverse form of the vowel letter for ''i'' (''gi-gu''). Aspiration was not phonemic and many words were written indiscriminately with consonants from the aspirated or unaspirated series. Most consonants could be palatalized, and the palatal series from the Tibetan script represents palatalized coronals. The sound conventionally transcribed with the letter འ ( Wylie: 'a) was a voiced velar fricative, while ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yellow Hat Sect
240px, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Bodh_Gaya.html" ;"title="Kalachakra ceremony, Bodh Gaya">Bodhgaya (India) The Gelug (, also Geluk; 'virtuous')Kay, David N. (2007). ''Tibetan and Zen Buddhism in Britain: Transplantation, Development and Adaptation,'' p. 39. Routledge. is the newest of the four major schools of Tibetan Buddhism. It was founded by Je Tsongkhapa (1357–1419), a Tibetan people, Tibetan philosopher, Vajrayana, tantric yogi and lama and further expanded and developed by his disciples (such as Khedrup Je, Gyaltsap Je, Dulzin Drakpa Gyaltsen, and Gendün Drubpa). The Gelug school is alternatively known as Kadam (''bKa’-gdams gsar-pa''), since it sees itself as a continuation of the Kadam tradition of Atisha (c. 11th century). The school of New Kadam, or New Kadampa is an offshoot of the Gelug-tradition. Furthermore, it is also called the Ganden school, after the first monastery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Red Hat Sect
''Red Hat sects'' is the English language translation of the Tibetic languages term ''shamar'' (uchen Tibetan script: ཞྭ་དམར)—"red hat" or "red hats"—collectively denoting the three oldest of the four primary sects of Tibetan Buddhism. These sects are termed "Red Hat" for the colour of their monks' hats as worn during formal occasions. The Red Hat sects are the Nyingma, Sakya and Kagyu schools of Tibetan Buddhism. The fourth school is Gelug file:DalaiLama0054 tiny.jpg, 240px, 14th Dalai Lama, The 14th Dalai Lama (center), the most influential figure of the contemporary Gelug tradition, at the 2003 Kalachakra ceremony, Bodh Gaya, Bodhgaya (India) The Gelug (, also Geluk; 'virtuous' ... and is known as the Yellow Hat sect. A minority considers the eldest school, the Nyingma school, to be the sole Red Hat sect. References Schools of Tibetan Buddhism {{Tibetan-Buddhism-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ), or Greater Tibet, is a region in the western part of East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are other ethnic groups such as Mongols, Monpa people, Monpa, Tamang people, Tamang, Qiang people, Qiang, Sherpa people, Sherpa, Lhoba people, Lhoba, and since the 20th century Han Chinese and Hui people, Hui. Tibet is the highest region on Earth, with an average elevation of . Located in the Himalayas, the highest elevation in Tibet is Mount Everest, Earth's highest mountain, rising above sea level. The Tibetan Empire emerged in the 7th century. At its height in the 9th century, the Tibetan Empire extended far beyond the Tibetan Plateau, from the Tarim Basin and Pamirs in the west, to Yunnan and Bengal in the southeast. It then divided into a variety of territories. The bulk of western and central Tibet (Ü-Tsang) was often at least nominally unified under a ser ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamang Language
Tamangic language is spoken mainly in Tamangsaling Land in Nepal, Sikkim, West Bengal (Darjeeling) and North-Eastern India. It comprises Eastern Tamang, Northwestern Tamang, Southwestern Tamang, Eastern Gorkha Tamang, and Western Tamang. Lexical similarity between Eastern Tamang (which is regarded as the most prominent) and other Tamang languages varies between 81% and 63%. For comparison, the lexical similarity between Spanish and Portuguese is estimated at 89%. Ethnologue report for Spanish Dialects ''Ethnologue'' divides Tamang into the following varieties due to mutual unintelligibility. *Eastern Tamang: 759,000 in Nepal (2000 WCD). Population total all countries: 773,000. Sub-dialects are as follows. **Outer-Eastern Tamang (Sailung Tamang) **Central-Eastern Tamang (Temal Tamang) **Southwestern Tamang (Kath-Bhotiya, Lama Bhote, Murmi, Rongba, Sain, Tamang Gyoi, Tamang Gyot, Tamang Lengmo, Tamang Tam) *Western Tamang: 323,000 (2000 WCD). Sub-dialects are as follows. ** ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yolmo Language
Yolmo (Hyolmo) or Helambu Sherpa, is a w:Tibeto-Burman languages, Tibeto-Burman language of the w:Yolmo people, Hyolmo people of Nepal (ISO 639-3: iso639-3:scp, scp, GlottoCodeyolm1234. Yolmo is spoken predominantly in the w:Helambu, Helambu and w:Melamchi, Melamchi valleys in northern w:Nuwakot District, Nuwakot District and northwestern w:Sindhupalchowk District, Sindhupalchowk District. Dialects are also spoken by smaller populations in w:Lamjung District, Lamjung District and w:Ilam District, Ilam District and also in w:Ramechhap District, Ramecchap District (where it is known as w:Kagate language, Syuba). It is very similar to w:Kyirong language, Kyirong Tibetan and less similar to w:Standard Tibetan, Standard Tibetan and w:Sherpa language, Sherpa. There are approximately 10,000 Yolmo speakers, although some dialects have larger populations than others. Language name Yolmo is both the name of the language (w:glottonym, glottonym), and the ethnic group of w:Yolmo people, p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lhasa Tibetan
Lhasa Tibetan or Standard Tibetan is a standardized dialect of Tibetan spoken by the people of Lhasa, the capital of the Tibetan Autonomous Region. It is an official language of the Tibet Autonomous Region. In the traditional "three-branched" classification of the Tibetic languages, the Lhasa dialect belongs to the Central Tibetan branch (the other two being Khams Tibetan and Amdo Tibetan). In terms of mutual intelligibility, speakers of Khams Tibetan are able to communicate at a basic level with Lhasa Tibetan, while Amdo speakers cannot. Both Lhasa Tibetan and Khams Tibetan evolved to become tonal and do not preserve the word-initial consonant clusters, which makes them very far from Classical Tibetan, especially when compared to the more conservative Amdo Tibetan. Registers Like many languages, Lhasa Tibetan has a variety of language registers: * ( Wylie: , literally " demotic language"): the vernacular speech. * ( Wylie: , "honorifics or deference, courtesy"): the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lexical Similarity
In linguistics, lexical similarity is a measure of the degree to which the word sets of two given languages are similar. A lexical similarity of 1 (or 100%) would mean a total overlap between vocabularies, whereas 0 means there are no common words. There are different ways to define the lexical similarity and the results vary accordingly. For example, ''Ethnologue''s method of calculation consists of comparing a regionally standardized wordlist (comparable to the Swadesh list) and counting those forms that show similarity in both form and meaning. Using such a method, English was evaluated to have a lexical similarity of 60% with German and 27% with French. Lexical similarity can be used to evaluate the degree of genetic relationship between two languages. Percentages higher than 85% usually indicate that the two languages being compared are likely to be related dialects. The lexical similarity is only one indication of the mutual intelligibility of the two languages, since t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhutan
Bhutan, officially the Kingdom of Bhutan, is a landlocked country in South Asia, in the Eastern Himalayas between China to the north and northwest and India to the south and southeast. With a population of over 727,145 and a territory of , Bhutan ranks List of countries and dependencies by area, 133rd in land area and List of countries and dependencies by population, 160th in population. Bhutan is a Democracy, democratic constitutional monarchy with a King of Bhutan, King as the head of state and a Prime Minister of Bhutan, prime minister as the head of government. The Je Khenpo is the head of the state religion, Vajrayana Buddhism. The Himalayas, Himalayan mountains in the north rise from the country's lush subtropical plains in the south. In the Mountains of Bhutan, Bhutanese Himalayas, there are peaks higher than above sea level. Gangkhar Puensum is Bhutan's highest peak and is the highest unclimbed mountain in the world. The wildlife of Bhutan is notable for its diversi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |