|
Bhumaka
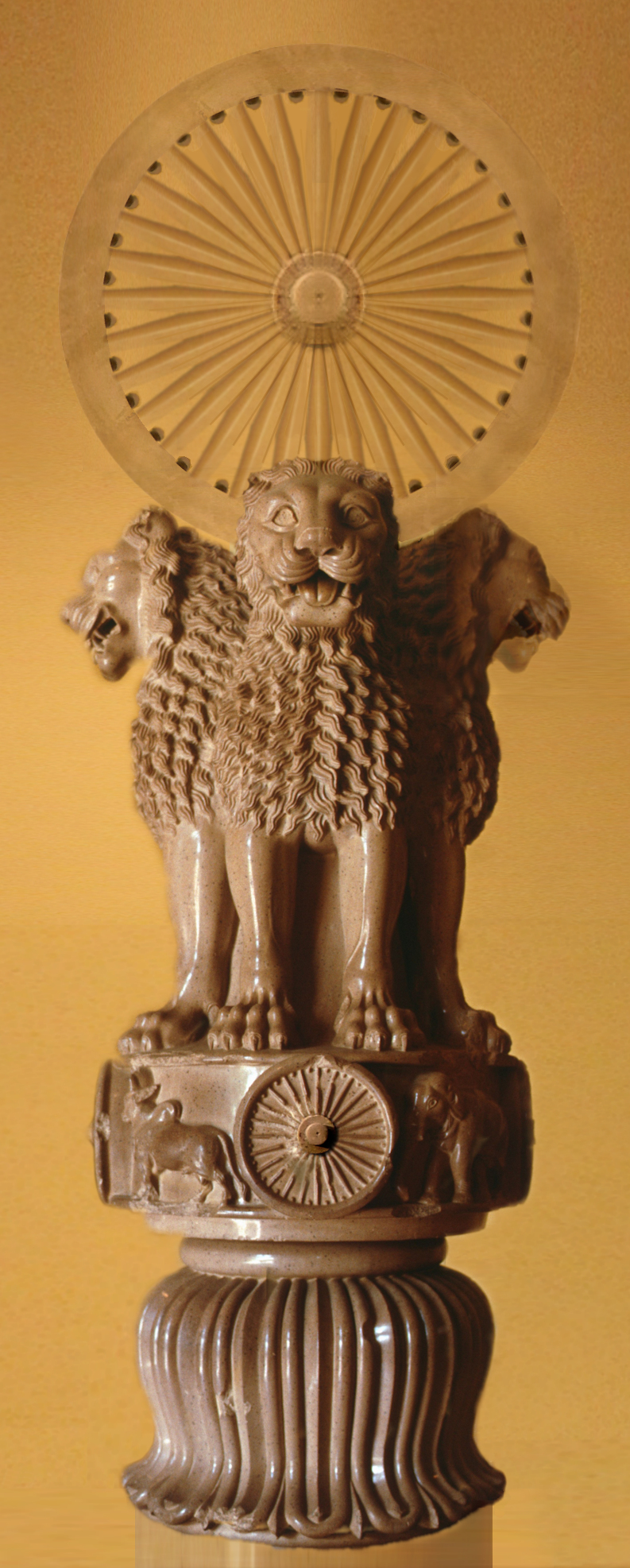
Bhumaka ( Kharosthi: , ; Brahmi: , ; r. 1st century CE) was a Western Kshatrapa ruler of the early 1st century CE. He was the father of the great ruler Nahapana, according to one of the latter's coins. He was preceded by Abhiraka (Aubhirakes), of whom a few coins are known. some scholars identify him with Ysamotika, the father of Chashtana. His coins bear Buddhist symbols, such as the eight-spoked wheel ( dharmachakra), or the lion seated on a capital, a representation of a pillar of Ashoka. Bhumaka's coins have been found in the regions of Gujarat Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ..., Kathiawad and Malwa.Some Early Dynasties of South India by Sudhakar Chattopadhyaya, Motilal Banarsidass Publ., 197p.54/ref> Notes Western Satraps 2nd-century Indian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Kshatrapa
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering modern-day Sindh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh states), between 35 and 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the " Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE. The power of the Western Satraps started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Saka rulers were defeated by the Emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni of the Satavahana dynasty. After this, the Saka kingdom revived, but was ultimately defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Satrap
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra (region), Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering modern-day Sindh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh states), between 35 and 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushan Empire, Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the "Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE. The power of the Western Satraps started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Saka rulers were defeated by the Emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni of the Satavahana dynasty. After this, the Saka kingdom re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Satraps
The Western Satraps, or Western Kshatrapas (Brahmi: , ''Mahakṣatrapa'', "Great Satraps") were Indo-Scythian (Saka) rulers of the western and central parts of India (extending from Saurashtra in the south and Malwa in the east, covering modern-day Sindh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh states), between 35 and 415 CE. The Western Satraps were contemporaneous with the Kushans who ruled the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, and were possibly vassals of the Kushans. They were also contemporaneous with the Satavahana who ruled in Central India. They are called "Western Satraps" in modern historiography in order to differentiate them from the " Northern Satraps", who ruled in Punjab and Mathura until the 2nd century CE. The power of the Western Satraps started to decline in the 2nd century CE after the Saka rulers were defeated by the Emperor Gautamiputra Satakarni of the Satavahana dynasty. After this, the Saka kingdom revived, but was ultimately defe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abhiraka
Abhiraka was an Abhira ruler from the Kshaharata dynasty, of the Western Satraps. He is known through his coins, which are found in the northern Pakistan area of Chukhsa, and then later in the south, suggesting a southern migration at some point, possibly in search for trade. His coins have been found in Afghanistan and as far as Arab states of the Persian Gulf.R.C. Senior, p.v The coinage, reminiscent of the coinage of the Indo-Greeks, has on the obverse a winged Nike with Greek legend "CATRAPATOY CATRAΠOY AYBIPAKOY" ("Abhiraka, Satrap of the Satraps"), and the reverse shows a lion or a horse facing a wheel, with Brahmi or Kharoshthi legend around ''Khaharatasa Khatrapasa Abhirakasa jayatasa Abhirakasa" ("The Khsaharata Satrap Abhiraka, victory to Abhiraka").'' Name Prior to R. C. Senior reading the name as Abhiraka (1998), the name had been misread as Aubhiraka, Aubhirakes, Aghudaka, Arta, and Ata. Coinage Coins of Abhiraka have been predominantly from modern-day Gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nahapana
Nahapana (Ancient Greek: ; Kharosthi: , ; Brahmi script, Brahmi: , ;), was a member of Western Satraps, Kshaharata dynasty in northwestern India, who ruled during the 1st or 2nd century CE. According to one of his coins, he was the son of Bhumaka. Name Nahapana's name appears on his coins in the Kharosthi form (), the Brahmi form (), and the Greek alphabet, Greek form (), which are derived from the Saka language, Saka name , which means "protector of the clan". Period The exact period of Nahapana is uncertain. A group of his inscriptions are dated to the years 41-46 of an unspecified era. Assuming that this era is the Shaka era (which starts in 78 CE), some scholars have assigned his reign to 119-124 CE. Some scholars argue that his reign lasted from 41 to 46 and assign his rule to a different period. For example, Krishna Chandra Sagar assigns his reign to 24-70 CE, while R.C.C. Fynes dates it to -71 CE, and Shailendra Bhandare regards 78 CE as the last year of his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chashtana
Chashtana (Greek: (epigraphic), ; Brahmi: ; Kharosthi: , ), also known as Tisman Ror was a Kardamaka dynasty ruler of the Saka Western Satraps in northwestern India during 78-130 CE, when he was the satrap of Ujjain. He was a descendant of Kardhaman, son of Raja Dhaj and son of Ysamotika. Name Chashtana's name is attested in the Greek forms () and (), in the Brahmi form () and the Kharosthi form (), which are derived from the Saka name , meaning "master". Reign Among modern scholars, the beginning of the Saka era is widely equated to the ascension of Chashtana (possibly to ''Mahakshatrapa'') in 78 CE. A statue found in Mathura together with statues of the Kushan king Kanishka and Vima Taktu, and bearing the name "Shastana" ( Middle Brahmi script of the Kushan period: ') is often attributed to Chashtana himself."The three letters give us a complete name, which I read as Ṣastana (vide facsimile and cast). Dr. Vogel read it as Mastana but that is incorrect for Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
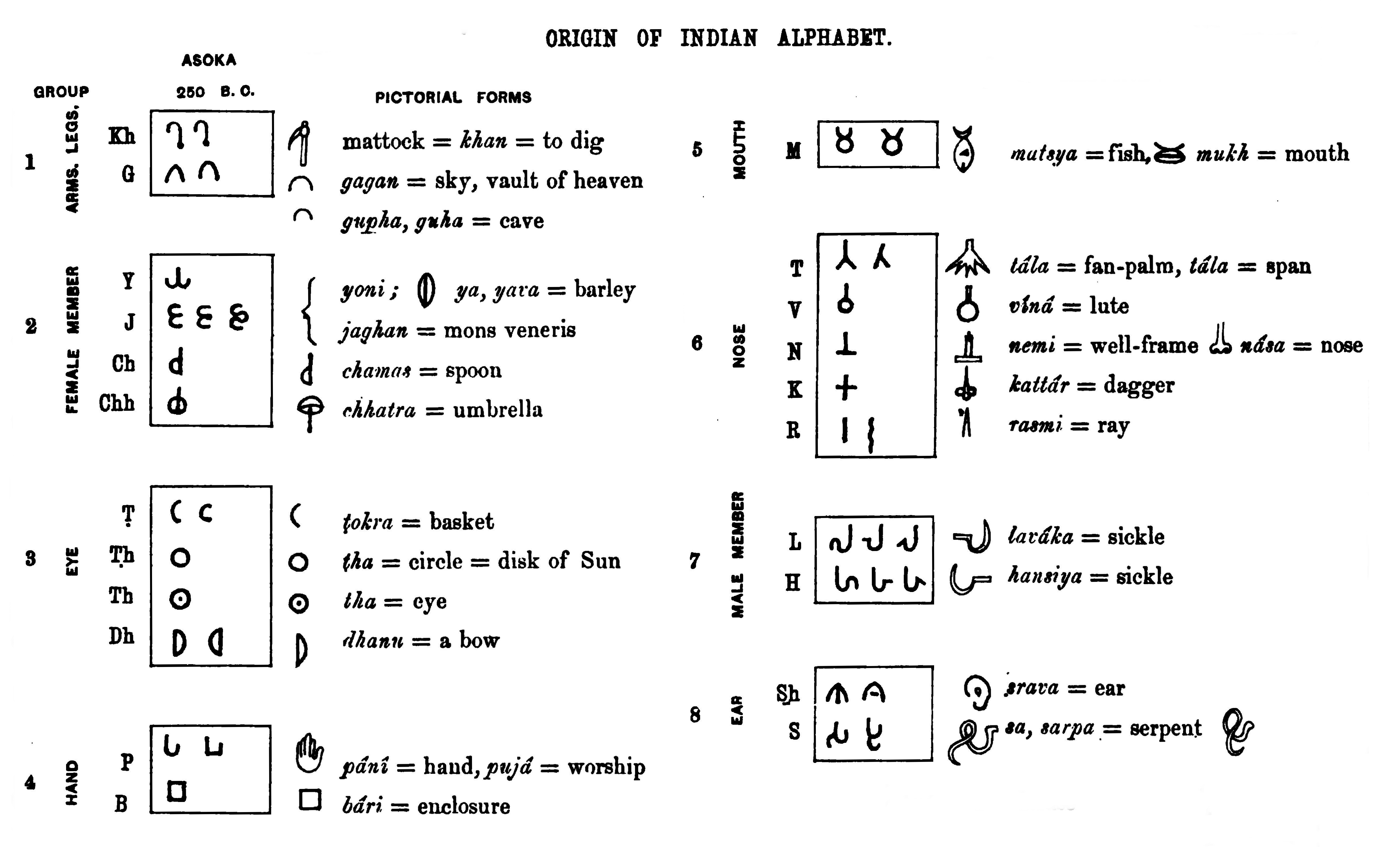
Kharoshthi
Kharosthi script (), also known as the Gandhari script (), was an ancient script originally developed in the Gandhara Region of modern-day Pakistan, between the 5th and 3rd century BCE. used primarily by the people of Gandhara alongside various parts of South Asia and Central Asia. it remained in use until it died out in its homeland around the 5th century CE. It was also in use in Bactria, the Kushan Empire, Sogdia, and along the Silk Road. There is some evidence it may have survived until the 7th century in Khotan and Niya, both cities in East Turkestan. History The name Kharosthi may derive from the Hebrew ''kharosheth'', a Semitic word for writing, or from Old Iranian ''*xšaθra-pištra'', which means "royal writing". The script was earlier also known as ''Indo-Bactrian script'', ''Kabul script'' and ''Arian-Pali''. Scholars are not in agreement as to whether the Kharosthi script evolved gradually, or was the deliberate work of a single inventor. An analysis of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dharmachakra
The dharmachakra (Sanskrit: धर्मचक्र, ) or wheel of dharma is a symbol used in the Dharmic religions. It has a widespread use in Buddhism.John C. Huntington, Dina Bangdel, ''The Circle of Bliss: Buddhist Meditational Art,'' p. 524. In Hinduism, the symbol is particularly used in places that underwent religious transformation. The symbol also finds its usage in modern India. Historically, the dharmachakra was often used as a decoration in East Asian statues and Epigraphy, inscriptions, beginning with the earliest period of Buddhism in Southeast Asia , East Asian culture to the present. It remains a major symbol of the Buddhist religion today. Etymology The Sanskrit noun ''dharma'' () is a derivation from the root ''dhṛ'' 'to hold, maintain, keep',Monier Williams, ''A Sanskrit Dictionary'' (1899): "to hold, bear (also: bring forth), carry, maintain, preserve, keep, possess, have, use, employ, practise, undergo" and means 'what is established or firm'. The word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brāhmī Script
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO 15919, ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern Aśokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi [''sc. lipi''], which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T[errien] de Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the Aśokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a fully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharosthi
Kharosthi script (), also known as the Gandhari script (), was an ancient script originally developed in the Gandhara Region of modern-day Pakistan, between the 5th and 3rd century BCE. used primarily by the people of Gandhara alongside various parts of South Asia and Central Asia. it remained in use until it died out in its homeland around the 5th century CE. It was also in use in Bactria, the Kushan Empire, Sogdia, and along the Silk Road. There is some evidence it may have survived until the 7th century in Khotan and Niya, both cities in East Turkestan. History The name Kharosthi may derive from the Hebrew ''kharosheth'', a Semitic word for writing, or from Old Iranian ''*xšaθra-pištra'', which means "royal writing". The script was earlier also known as ''Indo-Bactrian script'', ''Kabul script'' and ''Arian-Pali''. Scholars are not in agreement as to whether the Kharosthi script evolved gradually, or was the deliberate work of a single inventor. An analysis of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brahmi
Brahmi ( ; ; ISO: ''Brāhmī'') is a writing system from ancient India. "Until the late nineteenth century, the script of the Aśokan (non-Kharosthi) inscriptions and its immediate derivatives was referred to by various names such as 'lath' or 'Lat', 'Southern Aśokan', 'Indian Pali', 'Mauryan', and so on. The application to it of the name Brahmi 'sc. lipi'' which stands at the head of the Buddhist and Jaina script lists, was first suggested by T rriende Lacouperie, who noted that in the Chinese Buddhist encyclopedia ''Fa yiian chu lin'' the scripts whose names corresponded to the Brahmi and Kharosthi of the ''Lalitavistara'' are described as written from left to right and from right to left, respectively. He therefore suggested that the name Brahmi should refer to the left-to-right 'Indo-Pali' script of the Aśokan pillar inscriptions, and Kharosthi to the right-to-left 'Bactro-Pali' script of the rock inscriptions from the northwest." that appeared as a fully developed script ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buddhist
Buddhism, also known as Buddhadharma and Dharmavinaya, is an Indian religion and List of philosophies, philosophical tradition based on Pre-sectarian Buddhism, teachings attributed to the Buddha, a wandering teacher who lived in the 6th or 5th century Before the Common Era, BCE. It is the Major religious groups, world's fourth-largest religion, with about 500 million followers, known as Buddhists, who comprise four percent of the global population. It arose in the eastern Gangetic plain as a movement in the 5th century BCE, and gradually spread throughout much of Asia. Buddhism has subsequently played a major role in Asian culture and spirituality, eventually spreading to Western world, the West in the 20th century. According to tradition, the Buddha instructed his followers in a path of bhavana, development which leads to Enlightenment in Buddhism, awakening and moksha, full liberation from ''Duḥkha, dukkha'' (). He regarded this path as a Middle Way between extremes su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |