|
Bhawana
Bhawana (also spelled as Bhowana) ( pa, , ur, ) is a city and capital of Bhawana Tehsil of Chiniot District in Punjab, Pakistan. It is located on the bank of the Chenab river, bounded by Faisalabad, Jhang, and Chiniot, three other cities in Punjab. History Bhawana is one of the ancient cities of Pakistan. The Mughal Emperor Zahir-ud-din Babur mentions the area in his book the ''Tuzk-e-Babari'' for its fine architecture and finely handcrafted jharoka windows of many of the old ''havelis'' (manors) and other buildings of the old/medieval town. Geography and climate Bhawana is located by the side of Jhang Chiniot road and on the left bank of the Chenab river. Recently, with a budget of 250 million rupees, a bridge from Bhawana to Kalri has been constructed over the Chenab river. Leaders of opposition political parties specially Imran Khan and Billawal Bhutto have criticised the Chief Minister Punjab Shabaz Sharif for spending such a huge amount on a bridge to benefit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bhawana Tehsil
Bhawana (also spelled as Bhowana) (Punjabi Punjabi, or Panjabi, most often refers to: * Something of, from, or related to Punjab, a region in India and Pakistan * Punjabi language * Punjabi people * Punjabi dialects and languages Punjabi may also refer to: * Punjabi (horse), a British Th ..., ur, ) is a sub-division ( tehsil) of Chiniot District in Punjab, Pakistan. Before February 2009 it was a part of Jhang district as a sub-division (sub-tehsil) of Chiniot Tehsil. References {{Tehsils of Punjab (Pakistan) Chiniot District Populated places in Chiniot District Tehsils of Punjab, Pakistan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiniot
Chiniot (Urdu and pa, ) is a city and the administrative headquarter of Chiniot District in the province of Punjab, Pakistan. Located on the bank of the river Chenab, it is the 28th largest city of Pakistan. It is also known for its intricate wooden furniture, architecture, and mosques, and is home to the Omar Hayat Mahal. History Early The origins of Chiniot are obscure, and historical records accurately detailing its founding are unavailable. According to some accounts, the city was founded by an ancient king's daughter named Chandan, who while on a hunting expedition, was charmed by the surrounding area, and ordered the construction of the settlement of ''Chandaniot,'' alternatively spelt ''Chandniot,'' which was named in her honour. The name Chiniot, a contracted version of the original name, eventually gained favour, though the older name had been used up until at least the 1860s. Mughal During Mughal rule, Chiniot was governed as part of the ''subah,'' or pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economy Of Faisalabad
Faisalabad (; Punjabi language, Punjabi/ ur, , ; ), formerly known as Lyallpur (Punjabi language, Punjabi, Urdu: لائل پور), named after James Broadwood Lyall, the founder of the city, but was renamed in 1977 in honour of late Faisal of Saudi Arabia, King Faisal of Saudi Arabia. It is the List of cities in Pakistan by population, 3rd largest city of Pakistan after Karachi and Lahore respectively, and the List of cities in Punjab, Pakistan by population, 2nd largest city of Punjab, Pakistan, Punjab after Lahore. Faisalabad is one of Pakistan's wealthiest cities, the largest industrial hub and 2nd largest city of wider Punjab, Punjab region. Historically one of the first planned cities within British India, it has long since developed into a cosmopolitan metropolis. Faisalabad was restructured into City Districts of Pakistan, city district status; a devolution promulgated by the 2001 Local government in Pakistan, local government ordinance (LGO). The total area of Faisala ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faisalabad
Faisalabad (; Punjabi/ ur, , ; ), formerly known as Lyallpur (Punjabi, Urdu: لائل پور), named after the founder of the city, but was renamed in 1977 in honour of late King Faisal of Saudi Arabia. It is the 3rd largest city of Pakistan after Karachi and Lahore respectively, and the 2nd largest city of Punjab after Lahore. Faisalabad is one of Pakistan's wealthiest cities, the largest industrial hub and 2nd largest city of wider Punjab region. Historically one of the first planned cities within British India, it has long since developed into a cosmopolitan metropolis. Faisalabad was restructured into city district status; a devolution promulgated by the 2001 local government ordinance (LGO). The total area of Faisalabad District is while the area controlled by the Faisalabad Development Authority (FDA) is . Faisalabad has grown to become a major industrial and distribution centre because of its central location in the region and connecting roads, rails, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
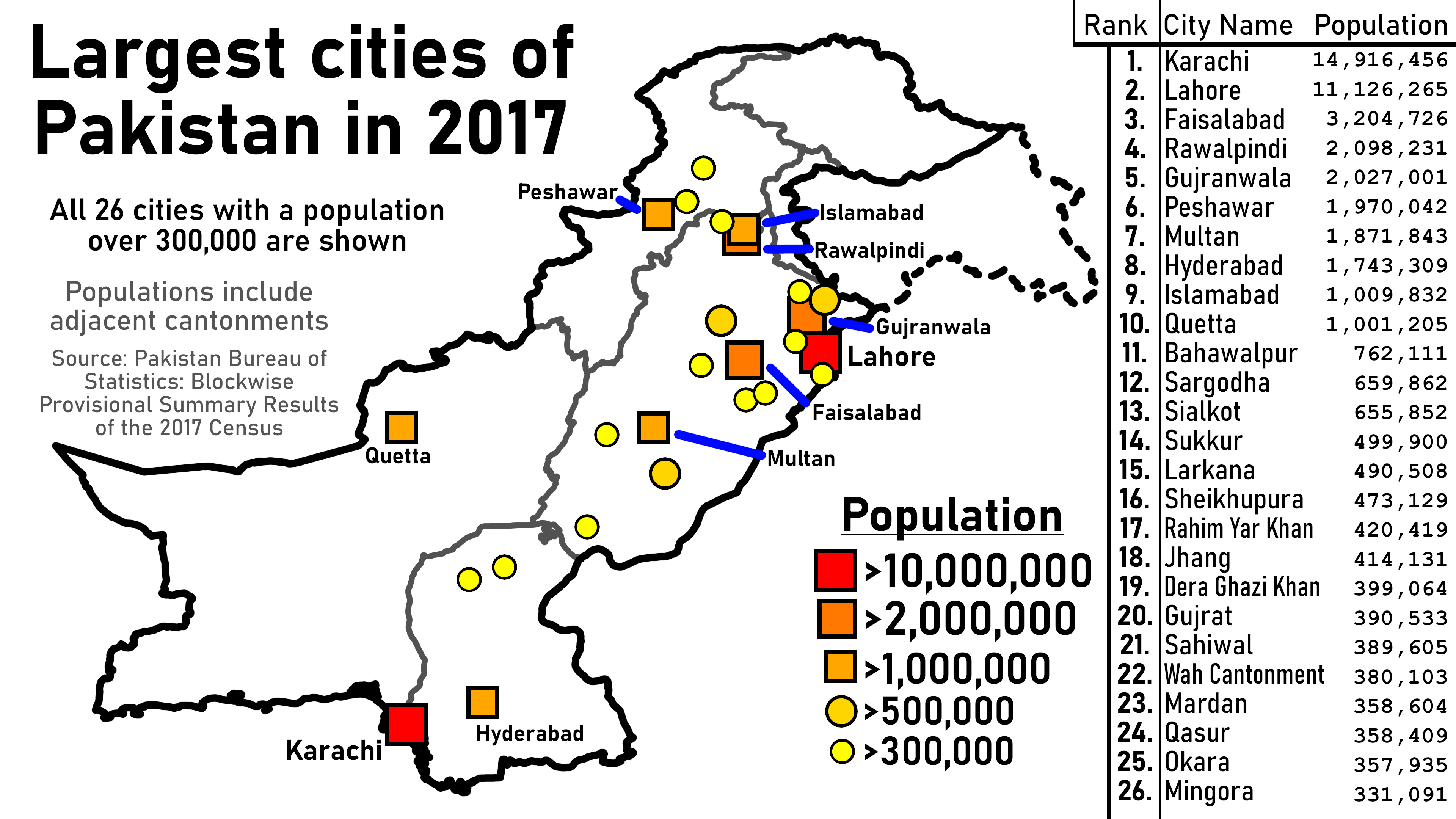
Cities Of Pakistan
This is a list showing the 100 most populous cities in Pakistan as of the 2017 Census of Pakistan. City populations found in this list only refer to the population found within the city's defined limits and any adjacent cantonment, if exists (except for Gujranwala and Okara). The census totals below come from the Pakistan Bureau of Statistics for the four provinces of Pakistan and the Islamabad Capital Territory, and from the Azad Jammu and Kashmir Planning & Development Department (PND AJK) for cities inside Azad Kashmir. As of the 2017 Census, there are two megacities, ten million-plus cities, and 100 cities having a population of 100,000 or more. Of these 100 cities, 58 are located in the country's most populous province, Punjab, 22 in Sindh, 11 in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, six in Balochistan, two in Azad Kashmir, and one in Islamabad Capital Territory. It is unknown whether Gilgit-Baltistan has any city with over 100,000 people or not, as Gilgit-Baltistan has not yet publicly rele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialling Codes In Pakistan
Fixed telephony The area codes in Pakistan consists of two to five digits; generally smaller the city, longer the prefix. All large cities have two-digit codes. The smaller towns might have six digital whereas big cities have seven digit numbers. Azad Kashmir telephone lines contain five digits. On 1 July 2009, telephone numbers in Karachi and Lahore were changed from seven digits to eight digits. This was accomplished by adding 9 to the beginning of all phone numbers that started with a 9 i.e. government and semi-government lines and adding 3 to all other lines. The following is the list of dialling codes for various cities and districts in Pakistan. See also * Telephone numbers in Pakistan References ITU allocations list External links PTCL - Official site {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Dialing Codes Of Pakistan Pakistan Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Schools In Pakistan
The following is a list of schools in Pakistan, categorized by province/territory and by district. Azad Jammu & Kashmir Mirpur * Balseri Government Girls' Middle School * Bahriatown School System * Batengi Primary School * Behdi Girls' Primary School * Unique High School * Joined Forces School * Fauji Foundation Model School * Roots School System * Dar-e-Arqam Schools * The Sepal Schools International, Mirpur campus * The City School Bhimber * Army Public School and College * Dar-e-Arqam Schools * READ Foundation College Rawalakot * Dar-e-Arqam Schools * The Educators Gilgit–Baltistan Gilgit * Public Schools and Colleges Jutial, Gilgit Skardu * Army Public School and College * Cadet College Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Abbottabad * Abbottabad Public School (APS) * Army Burn Hall College (ABHC) * Pakistan International Public School and College (PIPS) Battagram * Al Syed Garden Public School & College, Battagram * Sir Syed Institute of Learning & Motivation, Battagram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saqlain Anwar Sipra
Muhammad Saqlain Anwar Sipra is a Pakistani politician who had been a Member of the Provincial Assembly of the Punjab, from 2002 to May 2018. Early life and education He was born on 14 August 1977 in Jhang. He graduated in 1997 from Government College, Lahore and has the degree of Bachelor of Arts. Political career He was elected to the Provincial Assembly of the Punjab as an independent candidate from Constituency PP-75 (Jhang-III) in 2002 Pakistani general election. He received 21,708 votes and defeated Mehr Muhammad Nawaz Bharwana, a candidate of the National Alliance. He was re-elected to the Provincial Assembly of the Punjab as a candidate of Pakistan Muslim League (Q) from Constituency PP-75 (Jhang-III) in 2008 Pakistani general election 8 (eight) is the natural number following 7 and preceding 9. In mathematics 8 is: * a composite number, its proper divisors being , , and . It is twice 4 or four times 2. * a power of two, being 2 (two cubed), and is the fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sargodha
Sargodha (Punjabi and ur, ) is a city and capital of Sargodha Division, located in Punjab province, Pakistan. It is Pakistan's 12th largest city by population and one of the fastest-growing cities of the country. Sargodha is also known as the ''City of Eagles''. It is one of the few planned cities of Pakistan (others include Faisalabad, Islamabad & Gwadar). History Sargodha was established by the British as a canal-colony in 1903, and was initially spelled Sargoda. Sargodha was badly affected by an outbreak of the bubonic plague in 1903, and experienced a milder outbreak in 1904. Although it was a small town in the beginning, the British Royal Air Force built an airport here due to its strategic location. The term "Sargodha" has its origin in the words "Sar" (from "sarowar") meaning "pond" and "Godha" meaning " Sadhu", which means "Pond of Godha". This city was founded by Lady Trooper by the supervision of Sir Charles Montgomery Rivaz KCSI (1845 – 7 October 1926), a co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. The history of agriculture began thousands of years ago. After gathering wild grains beginning at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers began to plant them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs and cattle were domesticated over 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. Industrial agriculture based on large-scale monoculture in the twentieth century came to dominate agricultural output, though about 2 billion people still depended on subsistence agriculture. The major agricultural products can be broadly grouped into foods, fibers, fuels, and raw materials (such as rubber). Food classes include cereals ( grains), vegetables, fruits, cooking oils, m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jharoka
The Jharokha is a stone window projecting from the wall face of a building, in an upper story, overlooking a street, market, court or any other open space. A common feature in classical Indian architecture, most prominent in Rajasthan. It is supported on two or more brackets or corbelling, has two pillars or pilasters, balustrade and a cupola or pyramidal roof; technically closed by ''jali'' but generally partly open for the inmates to peep out to see passing processions. The ''jharokha'' is more formal and ornamental than English or French oriel window, and is one of the most distinctive characteristics of the façade in medieval Indian architecture until the 19th century. ''Jharokha Darshan'' The ''jharokha darshan'' of rulers was a structure for displaying the ruler to his court or people rather than allowing inhabitants of the palace to look out unseen. It was therefore more open, and not necessarily built projecting out from its wall. See also *Matroneum A trifo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |