|
Bharatas (tribe)
The Bharatas were an early Vedic that existed in the latter half of the second millennium B.C.E. The earliest mentioned location of the Bharatas was on the Sarasvatī River. Led by the tribal king Divodāsa, the Bharatas moved through the Hindu Kush mountains and defeated Śambara. Divodāsa's descendant, Sudās, won the Battle of the Ten Kings against a Pūru-led coalition, after which the initial compilation of hymns of the R̥gveda was carried out. After the battle, the Bharatas and other Pūru clans eventually formed the Kuru kingdom, which was the first attested state in Indian history. Etymology The name ''Bharata'' is of Indo-Aryan and Indo-Iranian origin, meaning "bearers" or "carriers". History Two Bharatas, Devaśravas Bhārata and Devavāta Bhārata, are mentioned as living near the Āpayā, Sarasvatī and Dr̥ṣadvatī rivers. Devavāta's son, Sṛñjaya Daivavāta, defeated the Turvaśas, and is mentioned alongside Abhyāvartin Cāyamāna who def ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-Aryan Peoples
Indo-Aryan peoples are a diverse collection of peoples predominantly found in South Asia, who (traditionally) speak Indo-Aryan languages. Historically, Aryans were the Indo-Iranian speaking pastoralists who migrated from Central Asia into South Asia and introduced the Proto-Indo-Aryan language. The early Indo-Aryan peoples were known to be closely related to the Indo-Iranian group that have resided north of the Indus River; an evident connection in cultural, linguistic, and historical ties. Today, Indo-Aryan speakers are found south of the Indus, across the modern-day regions of Bangladesh, Nepal, eastern-Pakistan, Sri Lanka, Maldives and northern-India. History Proto-Indo-Iranians The introduction of the Indo-Aryan languages in the Indian subcontinent was the outcome of a migration of Indo-Aryan people from Central Asia into the northern Indian subcontinent (modern-day Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka). These migrations started appr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
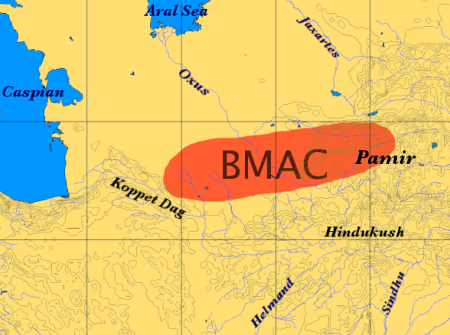
Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex
The Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex (BMAC) is the modern archaeological designation for a particular Middle Bronze Age civilisation of southern Central Asia, also known as the Oxus Civilization. The civilisation's urban phase or Integration Era was dated in 2010 by Sandro Salvatori to –1950 BC, but a different view is held by Nadezhda A. Dubova and Bertille Lyonnet, –1700 BC.Lyonnet, Bertille, and Nadezhda A. Dubova, (2020b)"Questioning the Oxus Civilization or Bactria- Margiana Archaeological Culture (BMAC): an overview" in Bertille Lyonnet and Nadezhda A. Dubova (eds.), ''The World of the Oxus Civilization'', Routledge, London and New York, p. 32.: "...Salvatori has often dated its beginning very early (ca. 2400 BC), to make it match with Shahdad where a large amount of material similar to that of the BMAC has been discovered. With the start of international cooperation and the multiplication of analyses, the dates now admitted by all place the Oxus Civilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vasiṣṭha
Vasishtha (, ) is one of the oldest and revered Vedic rishis or sages, and one of the Saptarishis (seven great Rishis). Vasishtha is credited as the chief author of Mandala 7 of the ''Rigveda''. Vasishtha and his family are mentioned in Rigvedic verse 10.167.4, other Rigvedic mandalas and in many Vedic texts. His ideas have been influential and he was called the first sage of the Vedanta school of Hindu philosophy by Adi Shankara. The ''Yoga Vasistha, Yoga Vasishtha'', ''Vasishtha Samhita'', as well as some versions of the ''Agni Purana'' and ''Vishnu Purana'' are attributed to him. He is the subject of many stories, such as him being in possession of the divine cow Kamadhenu and Nandini her child, who could grant anything to their owners. He is famous in Hindu stories for his legendary conflicts with sage Vishvamitra. In the Ramayana, he was the family priest of the Raghu dynasty and teacher of Rama and his brothers. Etymology Vasishtha is also spelled as ' and is Sanskrit fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutlej
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River. The combination of the Sutlej and Chenab rivers in the plains of Punjab forms the Panjnad, which finally flows into the Indus River at Mithankot. In India, the Bhakra Dam is built around the river Sutlej to provide irrigation and other facilities to the states of Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana. The waters of the Sutlej are allocated to India under the Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan, and are mostly diverted to irrigation canals in India like the Sirhind Canal, Bhakra Main Line and the Rajasthan canal. The mean annual flow is 14 million acre feet (MAF) (roughly 1.727 × 1013 L) upstream of Ropar barrage, downstream of the Bhakra dam. It has several major hydroelectric points, including t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sutudri
The Sutlej River or the Satluj River is a major river in Asia, flowing through China, India and Pakistan, and is the longest of the five major rivers of the Punjab region. It is also known as ''Satadru''; and is the easternmost tributary of the Indus River. The combination of the Sutlej and Chenab rivers in the plains of Punjab forms the Panjnad, which finally flows into the Indus River at Mithankot. In India, the Bhakra Dam is built around the river Sutlej to provide irrigation and other facilities to the states of Punjab, Rajasthan and Haryana. The waters of the Sutlej are allocated to India under the Indus Waters Treaty between India and Pakistan, and are mostly diverted to irrigation canals in India like the Sirhind Canal, Bhakra Main Line and the Rajasthan canal. The mean annual flow is 14 million acre feet (MAF) (roughly 1.727 × 1013 L) upstream of Ropar barrage, downstream of the Bhakra dam. It has several major hydroelectric points, including the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vishvamitra
Vishvamitra (, ) is one of the most venerated rishis or sages of ancient India. Vishvamitra is one of the seven Brahmarshi. According to Hindu tradition, he is stated to have written most of the Mandala 3 of the Rigveda, including the Gayatri Mantra (3.62.10). The Puranas mention that only 24 rishis since antiquity have understood the whole meaning of —and thus wielded the whole power of — the Gayatri Mantra. Vishvamitra is supposed to have been the first, and Yajnavalkya the last. Before renouncing his kingdom and royal status, Brahmarishi Vishvamitra was a king, and thus he retained the title of Rajarshi, or 'royal sage'. Textual background Historically, Viśvāmitra Gāthina was a Rigvedic rishi who was the chief author of Mandala 3 of the Rigveda. Viśvāmitra was taught by Jamadagni Bhārgava. He was the purohita of the Bharata tribal king Sudās, until he was replaced by Vasiṣṭha. He aided the Bharatas in crossing the Vipāśa and Śutudrī rivers (mod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Purohita
Purohita (), in the Hindu context, means '' chaplain'' or ''family priest'' within the Vedic priesthood. In Thailand and Cambodia, it refers to the royal chaplains. A ''tīrthapurohit'' is a priest/ritual performer (''purohit'') at a sacred site (''tīrtha''). Etymology The word ''purohita'' derives from the Sanskrit, ''puras'' meaning "front", and ''hita'', "placed". The word is also used synonymously with the word '' pandit'', which also means "priest". '' Tirtha purohita'' means the ''purohita'' who sit at the fords of the holy rivers or holy tanks and who have maintained the records of the forefathers of the Hindu family for thousands of years. ''Purohita'' can refer to a house priest. Another less-formal name for teerth purohits is ''panda'', which is derived from the word ''pandit'' (from the Sanskrit ''paṇḍita'', meaning "learned man"). Education In India, literate men from the Brahmin varna who desire to become ''purohitas'' receive special training both in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sudas
''For other uses, see Suda (other) and Souda (other) Sudās Paijavana was an Indo-Aryan tribal king of the Bharatas, during the main or middle Rigvedic period (c. 14th century BCE). He led his tribe to victory in the Battle of the Ten Kings near the Paruṣṇī (modern Ravi River) in Punjab, defeating an alliance of the powerful Puru tribe with other tribes, for which he was eulogized by his purohita Vashistha in a hymn of the Rigveda. His victory established the ascendency of the Bhārata clan, allowing them to move eastwards and settle in Kurukshetra, paving the way for the emergence of the Kuru "super-tribe" or tribal union, which dominated northern India in the subsequent period. Family Sudās' ancestors include Pijavana, Divodāsa Atithigva, and Devavant, although scholars disagree regarding the order of these ancestors chronologically. According to Witzel, Divodāsa was the father of Sudās, but he includes Pijavana on the grid of Bharata ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yadu
This is a list of ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes that are mentioned in the literature of Indian religions. From the second or first millennium BCE, ancient Indo-Aryan peoples and tribes turned into most of the population in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent – Indus Valley (roughly today's Pakistani Punjab and Sindh), Western India, Northern India, Central India, Eastern India and also in areas of the southern part like Sri Lanka and the Maldives through and after a complex process of migration, assimilation of other peoples and language shift. Ancestors * Proto-Indo-Iranians (common ancestors of the Iranian, Nuristani and Indo-Aryan peoples) ( Proto-Indo-Iranian speakers) ** Proto-Indo-Aryans ( Proto-Indo-Aryan speakers) Vedic tribes * Alina people (RV 7.18.7) * Anu (RV 1.108.8, RV 8.10.5) * Āyu * Bhageratha * Bhalanas * Bharatas- The Bharatas are a major Aryan clan, especially in Mandala 3 attributed to the Bharata sage Vishvamitra. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a physiographic region of Asia below the Himalayas which projects into the Indian Ocean between the Bay of Bengal to the east and the Arabian Sea to the west. It is now divided between Bangladesh, India, and Pakistan. (subscription required) Although the terms "Indian subcontinent" and "South Asia" are often also used interchangeably to denote a wider region which includes, in addition, Bhutan, the Maldives, Nepal and Sri Lanka, the "Indian subcontinent" is more of a geophysical term, whereas "South Asia" is more geopolitical. "South Asia" frequently also includes Afghanistan, which is not considered part of the subcontinent even in extended usage.Jim Norwine & Alfonso González, ''The Third World: states of mind and being'', pages 209, Taylor & Francis, 1988, Quote: ""The term "South Asia" also signifies the Indian Subcontinent""Raj S. Bhopal, ''Ethnicity, race, and health in multicultural societies'', pages 33, Oxford University Press, 2007, ; Q ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bharadvaja
Bharadvaja (, ; also spelled Bharadwaja) was one of the revered Vedic sages (maharishi) in Ancient India. He was a renowned scholar, economist, grammarian and a physician. He is one of the Saptarshis (seven great sages or Maharṣis). His contributions to ancient Indian literature, specifically the ''Rigveda'', provide significant insight into ancient Vedic society. He and his family of students were the authors of Mandala 6 in the ''Rigveda''. In the epic ''Mahabharata'', Bharadvaja was the father of Droṇācārya, the guru and instructor to the Pandava and Kaurava princes in the Mahabharata. Bharadvaja is also mentioned in ''Charaka Samhita'', an authoritative ancient Indian medical text. Etymology The word ''Bharadvaja'' is a compound Sanskrit from "''bhara(d)''" and "''vaja(m)''", which together mean "bringing about nourishment". The name lends itself to more than one yoga asana called Bharadvajasana ("nourishing pose") named after the eponymous sage. Description Hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |