|
Bezlotoxumab
Bezlotoxumab, sold under the brand name Zinplava, is a human monoclonal antibody designed for the prevention of recurrence of ''Clostridioides difficile'' infections. This drug, along with actoxumab, was developed through Phase II efficacy trials by a partnership between Medarex Inc and MassBiologics of the University of Massachusetts Medical School. The project was then licensed to Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp for further development and commercialization. Actoxumab and bezlotoxumab are fully human monoclonal antibodies which bind ''C. difficile'' toxins A and B, respectively. A Phase III trial only showed a benefit from bezlotoxumab; the combination of actoxumab and bezlotoxumab worked no better to prevent recurrence of ''C. difficile'' associated diarrhea than bezlotoxumab alone. Progress towards FDA approval On June 9, 2016, the U.S. FDA's Antimicrobial Drugs Advisory Committee (formerly known as the Anti-Infective Drugs Advisory Committee) met to discuss bezlotoxumab. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridioides Difficile Toxin B
Clostridium difficile toxin B is a cytotoxin produced by the bacteria ''Clostridioides difficile (bacteria), Clostridioides difficile'', formerly known as ''Clostridium difficile''. It is one of two major kinds of toxins produced by ''C. difficile'', the other being an related enterotoxin (Clostridium difficile toxin A, Toxin A). Both are very potent and lethal. Structure Toxin B (TcdB) is a cytotoxin that has a molecular weight of 270 kDa and an isoelectric point, pl, of 4.1. Toxin B has four different structural domains: catalytic, cysteine protease, protein translocation, translocation, and receptor binding. The N-terminal glucosyltransferase catalytic domain includes amino acid residues 1–544 while the cysteine protease domain includes residues 545–801. Additionally, the translocation region incorporates amino acid residues from 802 to 1664 while the receptor binding region is part of the C-terminal region and includes amino acid residues from 1665 to 2366. The gl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridium Difficile (bacteria)
''Clostridioides difficile'' (syn. ''Clostridium difficile'') is a bacterium that is well known for causing serious diarrheal infections, and may also cause colon cancer. Also known as ''C. difficile'', or ''C. diff'' (), is Gram-positive species of spore-forming bacteria. ''Clostridioides'' spp. are anaerobic, motile bacteria, ubiquitous in nature and especially prevalent in soil. Its vegetative cells are rod-shaped, pleomorphic, and occur in pairs or short chains. Under the microscope, they appear as long, irregular (often drumstick- or spindle-shaped) cells with a bulge at their terminal ends (forms subterminal spores). Under Gram staining, ''C. difficile'' cells are Gram-positive and show optimum growth on blood agar at human body temperatures in the absence of oxygen. ''C. difficile'' is catalase- and superoxide dismutase-negative, and produces up to three types of toxins: enterotoxin A, cytotoxin B and Clostridioides difficile transferase (CDT). Under stress conditi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intravenous Infusion
Intravenous therapy (abbreviated as IV therapy) is a medical technique that administers fluids, medications and nutrients directly into a person's vein. The intravenous route of administration is commonly used for rehydration or to provide nutrients for those who cannot, or will not—due to reduced mental states or otherwise—consume food or water by mouth. It may also be used to administer medications or other medical therapy such as blood products or electrolytes to correct electrolyte imbalances. Attempts at providing intravenous therapy have been recorded as early as the 1400s, but the practice did not become widespread until the 1900s after the development of techniques for safe, effective use. The intravenous route is the fastest way to deliver medications and fluid replacement throughout the body as they are introduced directly into the circulatory system and thus quickly distributed. For this reason, the intravenous route of administration is also used for the consum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monoclonal Antibody
A monoclonal antibody (mAb, more rarely called moAb) is an antibody produced from a cell Lineage made by cloning a unique white blood cell. All subsequent antibodies derived this way trace back to a unique parent cell. Monoclonal antibodies can have monovalent affinity, binding only to the same epitope (the part of an antigen that is recognized by the antibody). In contrast, polyclonal antibodies bind to multiple epitopes and are usually made by several different antibody-secreting plasma cell lineages. Bispecific monoclonal antibodies can also be engineered, by increasing the therapeutic targets of one monoclonal antibody to two epitopes. It is possible to produce monoclonal antibodies that specifically bind to virtually any suitable substance; they can then serve to detect or purify it. This capability has become an investigative tool in biochemistry, molecular biology, and medicine. Monoclonal antibodies are being used on a clinical level for both the diagnosis and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clostridioides Difficile Infection
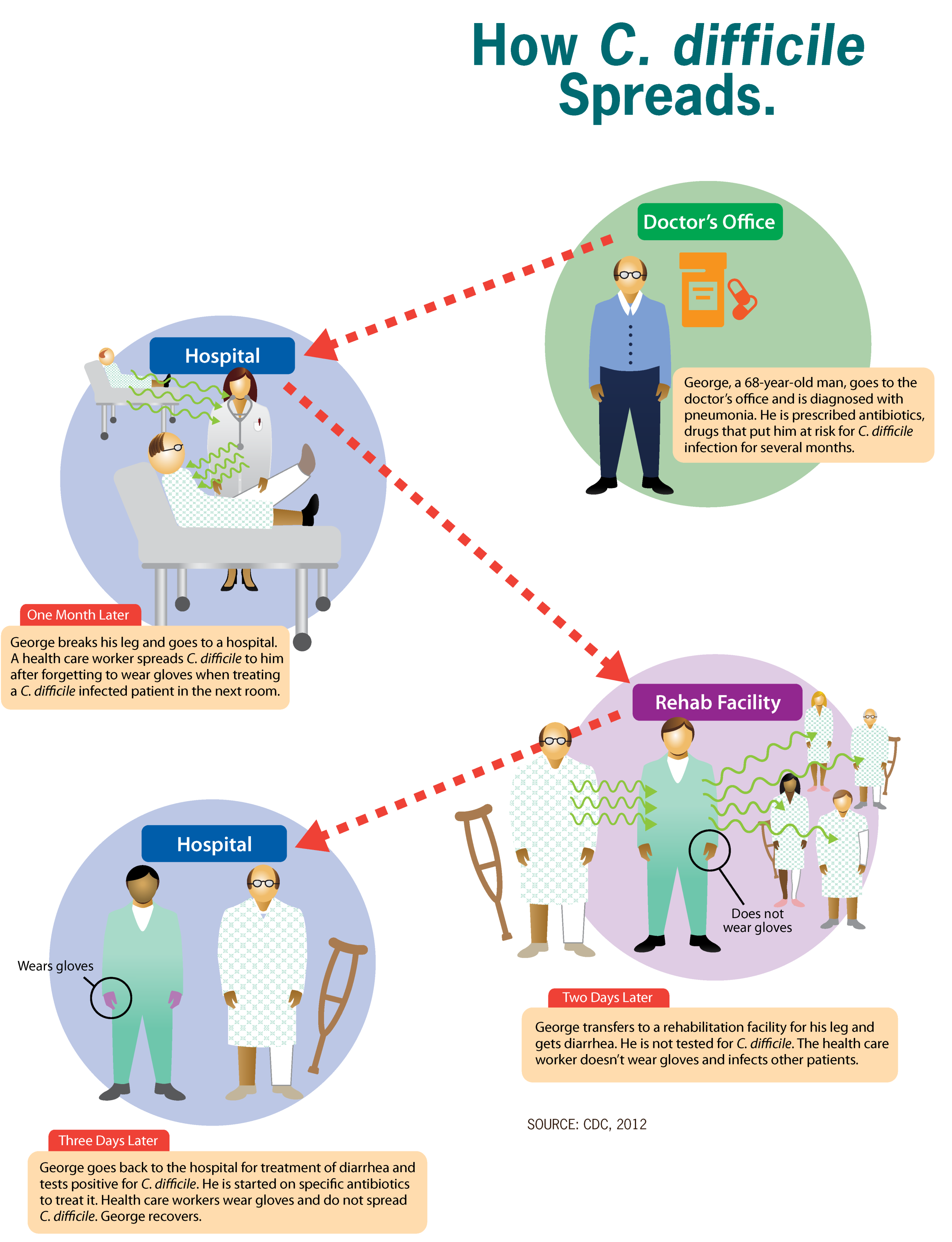
''Clostridioides difficile'' infection (CDI or C-diff), also known as ''Clostridium difficile'' infection, is a symptomatic infection due to the spore-forming bacterium ''Clostridioides difficile''. Symptoms include watery diarrhea, fever, nausea, and abdominal pain. It makes up about 20% of cases of antibiotic-associated diarrhea. Antibiotics can contribute to detrimental changes in gut microbiota; specifically, they decrease short-chain fatty acid absorption which results in osmotic, or watery, diarrhea. Complications may include pseudomembranous colitis, toxic megacolon, perforation of the colon, and sepsis. ''Clostridioides difficile'' infection is spread by bacterial spores found within feces. Surfaces may become contaminated with the spores with further spread occurring via the hands of healthcare workers. Risk factors for infection include antibiotic or proton pump inhibitor use, hospitalization, other health problems, and older age. Diagnosis is by stool culture or t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
American Medical Association
The American Medical Association (AMA) is a professional association and lobbying group of physicians and medical students. Founded in 1847, it is headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. Membership was approximately 240,000 in 2016. The AMA's stated mission is "to promote the art and science of medicine and the betterment of public health." The Association also publishes the '' Journal of the American Medical Association'' (JAMA). The AMA also publishes a list of Physician Specialty Codes which are the standard method in the U.S. for identifying physician and practice specialties. The American Medical Association is governed by a House of Delegates as well as a board of trustees in addition to executive management. The organization maintains the AMA Code of Medical Ethics, and the AMA Physician Masterfile containing data on United States Physicians. The ''Current Procedural Terminology'' coding system was first published in 1966 and is maintained by the Association. It has also p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Actoxumab
Actoxumab is a human monoclonal antibody designed for the prevention of recurrence of '' Clostridium difficile'' infection. This drug, along with bezlotoxumab, was developed through Phase II efficacy trials by a partnership between Medarex Inc and MassBiologics of the University of Massachusetts Medical School The University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School is a public medical school in Worcester, Massachusetts. It is part of the University of Massachusetts system. It is home to three schools: the T.H. Chan School of Medicine, the Morningside Grad .... The project was then licensed to Merck & Co., Inc. for further development and commercialization. A study compared it with bezlotoxumab (that targets CD toxin-B) and found Actoxumab less effective. References Monoclonal antibodies Experimental drugs {{monoclonal-antibody-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Massachusetts Medical School
The University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School is a public medical school in Worcester, Massachusetts. It is part of the University of Massachusetts system. It is home to three schools: the T.H. Chan School of Medicine, the Morningside Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences, and the Tan Chingfen Graduate School of Nursing, as well as a biomedical research enterprise and a range of public-service initiatives throughout the state. History UMMS was established by the 162nd Massachusetts General Court in 1962 to provide residents of the commonwealth an opportunity to study medicine at an affordable cost and to increase the number of primary-care physicians practicing in the commonwealth's under-served areas. The School of Medicine accepted its first class of 16 students in 1970. Six years later a 371-bed hospital opened on campus; the Graduate School of Biomedical Sciences opened in 1979, and the Graduate School of Nursing opened in 1986. In 1998 the UMMS system of hospitals a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merck & Co
Merck & Co., Inc. is an American multinational pharmaceutical company headquartered in Rahway, New Jersey, and is named for Merck Group, founded in Germany in 1668, of whom it was once the American arm. The company does business as Merck Sharp & Dohme or MSD outside the United States and Canada. Merck & Co. was originally established as the American affiliate of Merck Group in 1891. Merck develops and produces medicines, vaccines, biologic therapies and animal health products. It has multiple blockbuster drugs or products each with 2020 revenues including cancer immunotherapy, anti-diabetic medication and vaccines against HPV and chickenpox. The company is ranked 71st on the 2022 ''Fortune'' 500 and 87th on the 2022 ''Forbes'' Global 2000, both based on 2021 revenues. Products The company develops medicines, vaccines, biologic therapies and animal health products. In 2020, the company had 6 blockbuster drugs or products, each with over $1 billion in revenue: ''Keytrud ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Food And Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food safety, tobacco products, caffeine products, dietary supplements, prescription and over-the-counter pharmaceutical drugs (medications), vaccines, biopharmaceuticals, blood transfusions, medical devices, electromagnetic radiation emitting devices (ERED), cosmetics, animal foods & feed and veterinary products. The FDA's primary focus is enforcement of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act (FD&C), but the agency also enforces other laws, notably Section 361 of the Public Health Service Act, as well as associated regulations. Much of this regulatory-enforcement work is not directly related to food or drugs, but involves such things as regulating lasers, cellular phones, and condoms, as well as control of disease in contexts v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prescription Drug User Fee Act
The ''Prescription Drug User Fee Act'' (PDUFA) was a law passed by the United States Congress in 1992 which allowed the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) to collect fees from drug manufacturers to fund the new drug approval process. The Act provided that the FDA was entitled to collect a substantial application fee from drug manufacturers at the time a New Drug Application (NDA) or Biologics License Application (BLA) was submitted, with those funds designated for use only in Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER) or Center for Biologics Evaluation and Research (CBER) drug approval activities. In order to continue collecting such fees, the FDA is required to meet certain performance benchmarks, primarily related to the speed of certain activities within the NDA review process. History The move towards imposing user fees to pay for the regulatory review of new medicines was the result of dissatisfaction among consumers, industry, and the FDA. All three groups felt that dr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysteine Protease
Cysteine proteases, also known as thiol proteases, are hydrolase enzymes that degrade proteins. These proteases share a common catalytic mechanism that involves a nucleophilic cysteine thiol in a catalytic triad or dyad. Discovered by Gopal Chunder Roy in 1873, the first cysteine protease to be isolated and characterized was papain, obtained from ''Carica papaya''. Cysteine proteases are commonly encountered in fruits including the papaya, pineapple, fig and kiwifruit. The proportion of protease tends to be higher when the fruit is unripe. In fact, the latex of dozens of different plant families are known to contain cysteine proteases. Cysteine proteases are used as an ingredient in meat tenderizers. Classification The MEROPS protease classification system counts 14 superfamilies plus several currently unassigned families (as of 2013) each containing many families. Each superfamily uses the catalytic triad or dyad in a different protein fold and so represent co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)