|
Beynac-et-Cazenac
Beynac-et-Cazenac (; ) is a village located in the Dordogne department in southwestern France. The medieval Château de Beynac is located in the commune. The village is classified as one of ''Les plus beaux villages de France'' (most beautiful villages of France). Geography The commune lies on the banks of the river Dordogne southwest of Sarlat-la-Canéda. History Historically the first mention of Beynac dates to 1115 when Maynard de Beynac made a gift to the sisters at Fontevrault Abbey. Simon de Montfort seized the château at the end of the 12th century, but the people of Beynac recovered their château thanks to the intervention of Philippe Auguste in 1217. The château stayed in possession of the family de Beynac until 1753 when the de Beynac family became extinct in male line with Pierre last marquis of Beynac who married in 1727 Anne-Marie Boucher and had two daughters: Julie de Beynac, married to the marquis de Castelnau, and Claude-Marie de Beynac, married in 17 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Château De Beynac
The Château de Beynac is a castle situated in the '' commune'' of Beynac-et-Cazenac, in the Dordogne ''département'' of France. The castle is one of the best-preserved and best known in the region. This Middle Ages construction, with its austere appearance, is perched on top of a limestone cliff, dominating the town and the north bank of the Dordogne. History The castle was built in the 12th century by the barons of Beynac (one of the four baronies of Périgord) to close the valley. The sheer cliff face being sufficient to discourage any assault from that side, the defences were built up on the plateau: double crenellated walls, double moats, one of which was a deepened natural ravine, double barbican. The oldest part of the castle is a large, square Romanesque keep with vertical sides and few openings, held together with attached watch towers and equipped with a narrow spiral staircase terminating on a crenellated terrace. To one side, a residence of the same period is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dordogne (river)
The Dordogne (; ) is a river in south-central and southwest France. It is long. The Dordogne and its watershed were designated Man and the Biosphere Programme, Biosphere Reserve by UNESCO on 11 July 2012. Geography The river rises on the flanks of the Puy de Sancy at above sea level in the mountains of Auvergne, from the confluence of two small torrents above the town of Le Mont-Dore (France), Le Mont-Dore: the ''Dore'' and the ''Dogne''. It flows generally west nearly through the Limousin (région), Limousin and Périgord regions before flowing into the Gironde estuary, Gironde, its common estuary with the Garonne, at the Bec d'Ambès ("Ambès beak"), north of the city of Bordeaux. Nature The Dordogne is one of the few rivers in the world that exhibit the phenomenon of a tidal bore, known as a ''mascaret''. The upper valley of the Dordogne is a series of deep gorges. The cliffs, steep banks, fast flowing water and high bridges attract both walkers and drivers. In severa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Les Plus Beaux Villages De France
(, ) is an independent association created in 1982 for the promotion of the tourist appeal of small rural villages with a rich cultural heritage. As of 2024, it numbers 176 member villages (independent Communes of France, ''communes'' or part of a ). It is affiliated to the international association The Most Beautiful Villages in the World. Membership requires meeting certain selection criteria and offers a strategy for development and promotion to tourists. The three initial selection criteria are the rural nature of the village (a population of less than 2,000 inhabitants), the presence of at least two national heritage sites (' or Monument historique, ''monuments historiques'') and local support in the form of a vote by the council. Each village must pay an annual fee to the association and the mayor must sign the association's Quality Charter. If the village fails to meet the requirements of the charter it may be excluded. The association claims membership can bring a rise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beynac Vu De Castelnaud
Beynac (; ) is a commune in the Haute-Vienne department in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region in central-western France. Inhabitants are known as ''Beynacois'' in French. See also *Communes of the Haute-Vienne department The following is a list of the 195 communes of the Haute-Vienne department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Communes of Haute-Vienne {{HauteVienne-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of The Dordogne Département
The following is a list of the 503 communes of the Dordogne department of France. The communes cooperate in the following intercommunalities (as of 2025):Périmètre des groupements en 2025 BANATIC. Accessed 28 May 2025. * Communauté d'agglomération Bergeracoise *Communauté d'agglomération Le Grand Périgueux * * Communauté de communes Castillon-Pujols (partly) * * * [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Communes Of France
A () is a level of administrative divisions of France, administrative division in the France, French Republic. French are analogous to civil townships and incorporated municipality, municipalities in Canada and the United States; ' in Germany; ' in Italy; ' in Spain; or civil parishes in the United Kingdom. are based on historical geographic communities or villages and are vested with significant powers to manage the populations and land of the geographic area covered. The are the fourth-level administrative divisions of France. vary widely in size and area, from large sprawling cities with millions of inhabitants like Paris, to small hamlet (place), hamlets with only a handful of inhabitants. typically are based on pre-existing villages and facilitate local governance. All have names, but not all named geographic areas or groups of people residing together are ( or ), the difference residing in the lack of administrative powers. Except for the Municipal arrondissem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; ) is a large rural departments of France, department in south west France, with its Prefectures in France, prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and the Pyrenees, it is named after the river Dordogne (river), Dordogne, which runs through it. It corresponds roughly to the ancient county of Périgord. In January 2023, Dordogne had a population of 412,807. History The county of Périgord dates back to when the area was inhabited by ancient celtic Gauls, Gaulish tribes. It was originally home to four tribes, and since "four tribes" in the Gaulish language is "Petrocore", the area eventually became known as the county of Le Périgord. Its inhabitants became known as the Périgordins (or Périgourdins), and there are four Périgords in the Dordogne. * Périgord Vert (Green Périgord), with its main town of Nontron, consists of verdant valleys in a region crossed by many rivers and streams ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Departments Of France
In the administrative divisions of France, the department (, ) is one of the three levels of government under the national level ("territorial collectivity, territorial collectivities"), between the Regions of France, administrative regions and the Communes of France, communes. There are a total of 101 departments, consisting of ninety-six departments in metropolitan France, and five Overseas department and region, overseas departments, which are also classified as overseas regions. Departments are further subdivided into 333 Arrondissements of France, arrondissements and 2,054 Cantons of France, cantons (as of 2023). These last two levels of government have no political autonomy, instead serving as the administrative basis for the local organisation of police, fire departments, and, in certain cases, elections. Each department is administered by an elected body called a departmental council (France), departmental council ( , ). From 1800 to April 2015, these were called gene ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
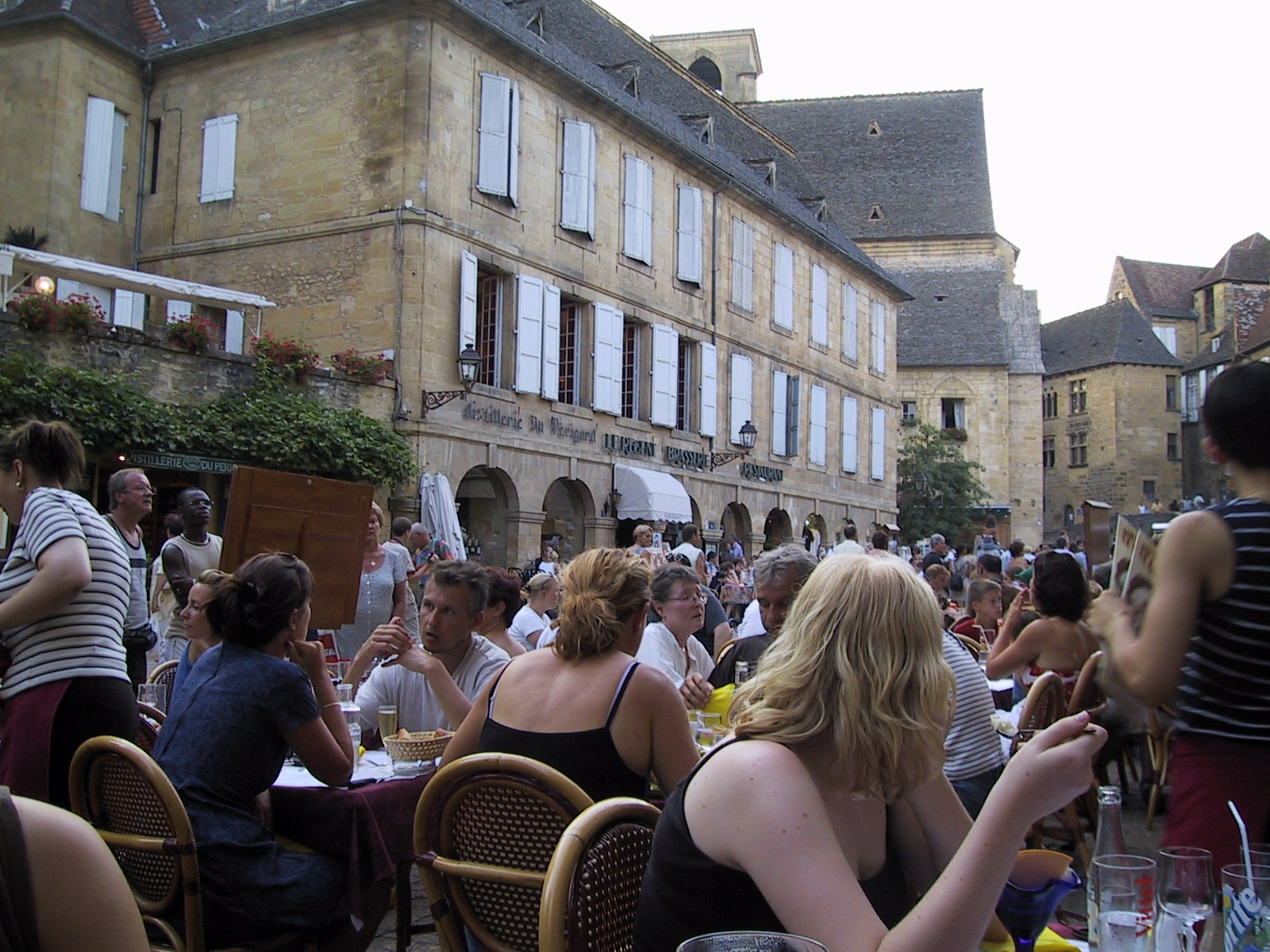
Sarlat-la-Canéda
Sarlat-la-Canéda (; ), commonly known as Sarlat, is a commune in the southwestern French department of Dordogne, a part of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. Sarlat and La Canéda were distinct towns until merged into one commune in March 1965. Geography The town of Sarlat is in a region known in France as Périgord Noir. It lies in the southeastern part of the Dordogne department, 7 km north of the river Dordogne. Sarlat railway station offers train services to Bergerac, Bordeaux and Périgueux. The commune is also served by Brive–Souillac Airport, Brive Vallée de la Dordogne airport (50 km), Bergerac Dordogne Périgord Airport, Bergerac Roumanière airport (70 km) and two bus lines. History Sarlat is a medieval town that developed around a large Benedictine abbey of Carolingian origin. The medieval Sarlat Cathedral is dedicated to Sacerdos of Limoges, Saint Sacerdos. This abbey appears in records as early as 1081 and was one of the few in the region that was not ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fontevrault Abbey
The Royal Abbey of Our Lady of Fontevraud or Fontevrault (in French: ''abbaye de Fontevraud'') was a monastery in the village of Fontevraud-l'Abbaye, near Chinon, in the former French Duchy of Anjou. It was founded in 1101 by the itinerant preacher Robert of Arbrissel. The foundation flourished and became the centre of a new monastic Order, the Order of Fontevraud. This order was composed of double monasteries, in which the community consisted of both men and women — in separate quarters of the abbey — all of whom were subject to the authority of the Abbess of Fontevraud. The Abbey of Fontevraud itself consisted of four separate communities, all managed by the same abbess. The first permanent structures were built between 1110 and 1119.Melot (1971) The area where the Abbey is located was then part of what is sometimes referred to as the Angevin Empire. The king of England, Henry II, his wife, Eleanor of Aquitaine, and their son, King Richard the Lionheart, were all buried he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Simon De Montfort, 5th Earl Of Leicester
Simon de Montfort, 5th Earl of Leicester ( – 25 June 1218), known as Simon IV (or V) de Montfort and as Simon de Montfort the Elder, was a French nobleman and knight of the early 13th century. He is widely regarded as one of the great military commanders of the Middle Ages. He took part in the Fourth Crusade and was one of the prominent figures of the Albigensian Crusade. Montfort is mostly noted for his campaigns in the latter, notably for his battle at Battle of Muret, Muret. He died at the Siege of Toulouse (1217–1218), Siege of Toulouse in 1218. He was Seigneur of Montfort, Lord of Montfort from 1188 to his death and Earl of Leicester in England from 1204. He was also Viscount of Albi, Béziers and Carcassonne from 1213, as well as Count of Toulouse from 1215. Early life He was the son of Simon de Montfort (died 1188), Simon de Montfort (d. 1188), lord of Montfort l'Amaury in France near Paris, and Amice (Countess), Amicia de Beaumont, daughter of Robert de Beaumont, 3rd ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippe Auguste
Philip II (21 August 1165 – 14 July 1223), also known as Philip Augustus (), was King of France from 1180 to 1223. His predecessors had been known as kings of the Franks (Latin: ''rex Francorum''), but from 1190 onward, Philip became the first French monarch to style himself "King of France" (''rex Francie''). The son of King Louis VII and his third wife, Adela of Champagne, he was originally nicknamed () because he was a first son and born late in his father's life. Philip was given the epithet "Augustus" by the chronicler Rigord for having extended the crown lands of France so remarkably. After decades of conflicts with the House of Plantagenet, Philip succeeded in putting an end to the Angevin Empire by defeating a coalition of his rivals at the Battle of Bouvines in 1214. This victory would have a lasting impact on western European politics: the authority of the French king became unchallenged, while John, King of England, was forced by his barons to assent to Magna Carta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |