|
Betazole
Betazole (also known as ametazole) is a histamine H2 receptor agonist. Betazole hydrochloride is known as gastramine and histalog. It has been used as a gastric stimulant to test for maximal production of gastric secretion activity. The test can be used in diagnosis of diseases such as Zollinger-Ellison syndrome where there is excess acid production, in this case driven by over production of gastrin. The volume of acid secretion is measured following administration of betazole, diagnosis being secretion greater than 60% of the maximal acid secretion following betazole stimulation. This procedure can lead to complications and should be avoided in subjects with coronary artery disease. It is also used in diagnosis of gastritis in association with a test for secretin activity. Betazole is used as a stimulant in preference to histamine because of its specificity for the H2 receptor and its advantage of not generating the undesirable side effects that histamine would induce. It t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Histamine H2 Receptor
H2 receptors are a type of histamine receptor found in many parts of the anatomy of humans and other animals. They are positively coupled to adenylate cyclase via Gs alpha subunit. It is a potent stimulant of cAMP production, which leads to activation of protein kinase A. PKA functions to phosphorylate certain proteins, affecting their activity. The drug betazole is an example of a histamine H2 receptor agonist. Function Histamine is a ubiquitous messenger molecule released from mast cells, enterochromaffin-like cells, and neurons. Its various actions are mediated by histamine receptors H1, H2, H3 and H4. The histamine receptor H2 belongs to the rhodopsin-like family of G protein-coupled receptors. It is an integral membrane protein and stimulates gastric acid secretion. It also regulates gastrointestinal motility and intestinal secretion and is thought to be involved in regulating cell growth and differentiation. Histamine may play a role in penile erection. Tissue distri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Betaxolol
Betaxolol is a beta blocker used in the treatment of hypertension and angina. It acts as a selective β1-adrenergic receptor antagonist. The drug was patented in 1975 and approved for medical use in 1983. Medical uses Hypertension Betaxolol is most commonly ingested orally alone or with other medications for the management of essential hypertension. It is a cardioselective beta blocker, targeting beta-1 adrenergic receptors found in the cardiac muscle. Blood pressure is decreased by the mechanism of blood vessels relaxing and improving the flow of blood. Glaucoma Ophthalmic betaxolol is an available treatment for primary open angle glaucoma (POAG) and optical hypertension. Betaxolol effectively prevents the increase of intracellular calcium, which leads to increased production of the aqueous humor. In the context of open angle glaucoma, increased aqueous humor produced by ciliary bodies increases intraocular pressure, causing degeneration of retinal ganglion cells and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastric Secretion
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the upper gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The Ancient Greek name for the stomach is ''gaster'' which is used as ''gastric'' in medical terms related to the stomach. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach is involved in the gastric phase of digestion, following the cephalic phase in which the sight and smell of food and the act of chewing are stimuli. In the stomach a chemical breakdown of food takes place by means of secreted digestive enzymes and gastric acid. It also plays a role in regulating gut microbiota, influencing digestion and overall health. The stomach is located between the esophagus and the small intestine. The pyloric sphincter controls the passage of partially digested food (chyme) from the stomach into the duodenum, the first and shortest part of the small intestine, where peristalsis takes over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastrin
Gastrin is a peptide hormone that stimulates secretion of gastric acid (HCl) by the parietal cells of the stomach and aids in gastric motility. It is released by G cells in the pyloric antrum of the stomach, duodenum, and the pancreas. Gastrin binds to cholecystokinin B receptors to stimulate the release of histamines in enterochromaffin-like cells, and it induces the insertion of K+/H+ ATPase pumps into the apical membrane of parietal cells (which in turn increases H+ release into the stomach cavity). Its release is stimulated by peptides in the lumen of the stomach. Physiology Genetics In humans, the ''GAS'' gene is located on the long arm of the seventeenth chromosome (17q21). Synthesis Gastrin is a linear peptide hormone produced by G cells of the duodenum and in the pyloric antrum of the stomach. It is secreted into the bloodstream. The encoded polypeptide is preprogastrin, which is cleaved by enzymes in posttranslational modification to produce progastri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
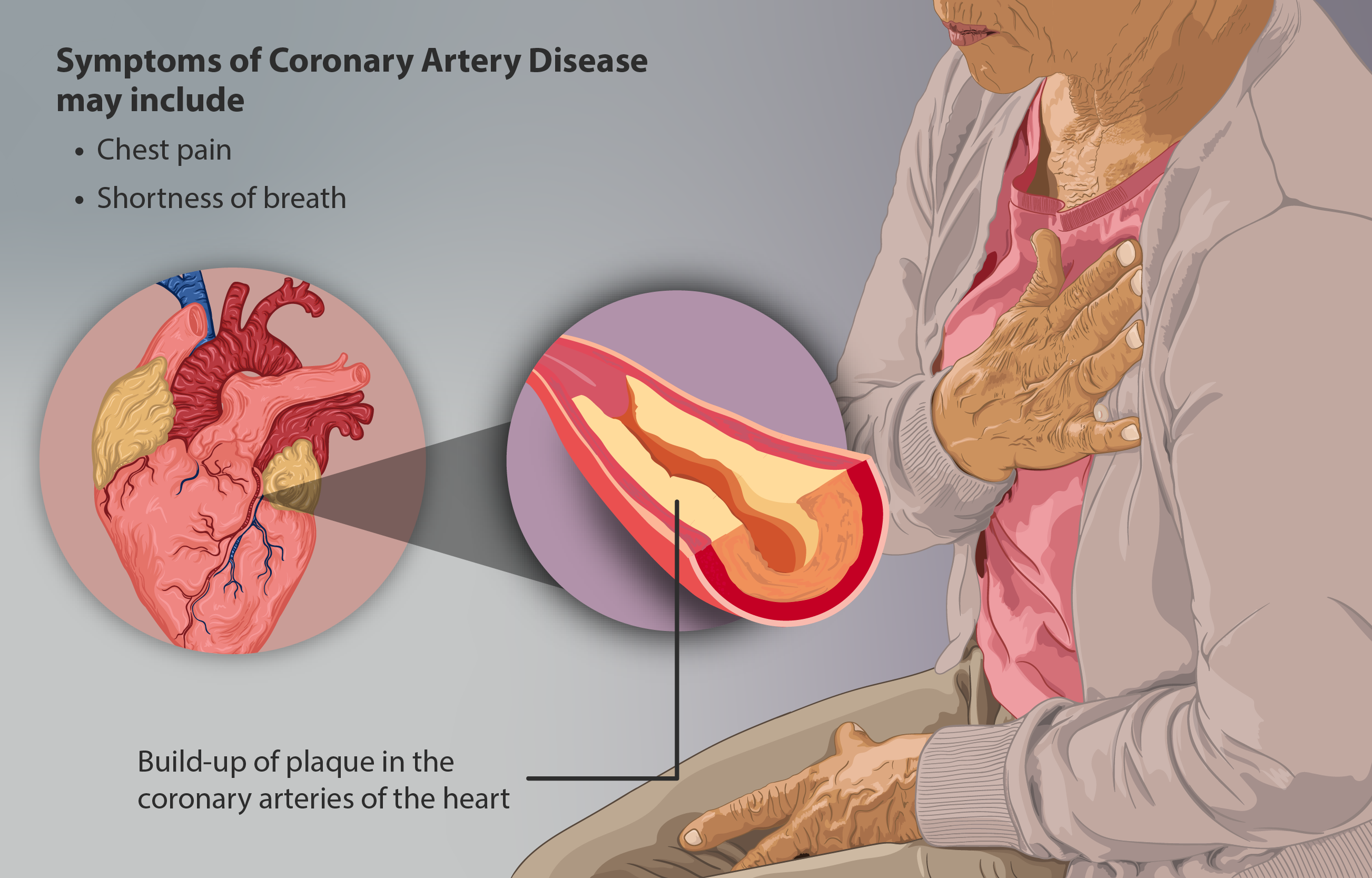
Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease (CAD), also called coronary heart disease (CHD), or ischemic heart disease (IHD), is a type of cardiovascular disease, heart disease involving Ischemia, the reduction of blood flow to the cardiac muscle due to a build-up of atheromatous plaque in the Coronary arteries, arteries of the heart. It is the most common of the cardiovascular diseases. CAD can cause stable angina, unstable angina, myocardial ischemia, and myocardial infarction. A common symptom is angina, which is chest pain or discomfort that may travel into the shoulder, arm, back, neck, or jaw. Occasionally it may feel like heartburn. In stable angina, symptoms occur with exercise or emotional Psychological stress, stress, last less than a few minutes, and improve with rest. Shortness of breath may also occur and sometimes no symptoms are present. In many cases, the first sign is a Myocardial infarction, heart attack. Other complications include heart failure or an Heart arrhythmia, abnormal h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gastritis
Gastritis is the inflammation of the lining of the stomach. It may occur as a short episode or may be of a long duration. There may be no symptoms but, when symptoms are present, the most common is upper abdominal pain (see dyspepsia). Other possible symptoms include nausea and vomiting, bloating, loss of appetite and heartburn. Complications may include stomach bleeding, stomach ulcers, and stomach tumors. When due to autoimmune problems, low red blood cells due to not enough vitamin B12 may occur, a condition known as pernicious anemia. Common causes include infection with '' Helicobacter pylori'' and use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs ( NSAIDs). When caused by ''H. pylori'' this is now termed ''Helicobacter pylori'' induced gastritis, and included as a listed disease in ICD11. Less common causes include alcohol, smoking, cocaine, severe illness, autoimmune problems, radiation therapy and Crohn's disease. Endoscopy, a type of X-ray known as an upper gast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Secretin
Secretin is a hormone that regulates water homeostasis throughout the body and influences the environment of the duodenum by regulating secretions in the stomach, pancreas, and liver. It is a peptide hormone produced in the S cells of the duodenum, which are located in the intestinal glands. In humans, the secretin peptide is encoded by the ''SCT'' gene. Secretin helps regulate the pH of the duodenum by inhibiting the secretion of gastric acid from the parietal cells of the stomach and stimulating the production of bicarbonate from the ductal cells of the pancreas. It also stimulates the secretion of bicarbonate and water by cholangiocytes in the bile duct, protecting it from bile acids by controlling the pH and promoting the flow in the duct. Meanwhile, in concert with secretin's actions, the other main hormone simultaneously issued by the duodenum, cholecystokinin (CCK), stimulates the gallbladder to contract, delivering its stored bile. Prosecretin is a precursor to secreti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nizatidine
Nizatidine is a histamine H2 receptor antagonist that inhibits stomach acid production, and is commonly used in the treatment of peptic ulcer disease and gastroesophageal reflux disease. It was patented in 1980 and approved for medical use in 1988. It was developed by Eli Lilly. Medical use Nizatidine is used to treat duodenal ulcers, gastric ulcers, and gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD/GORD), and to prevent stress ulcers. Adverse effects Side effects are uncommon, usually minor, and include diarrhea, constipation, fatigue, drowsiness, headache, and muscle aches. History and development Nizatidine was developed by Eli Lilly, and was first marketed in 1988. It is considered to be equipotent with ranitidine Ranitidine, previously sold under the brand name Zantac among others, is a medication used to decrease stomach acid production. It was commonly used in treatment of peptic ulcer disease, gastroesophageal reflux disease, and Zollinger–Ellis ... and differs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |