|
Bet-Zamani
Bit-Zamani is an ancient Aramean state in northern Mesopotamia, located within the mountainous region of Tur Abdin. In Bit-Zamani was the city of Amida (Amedu, modern Diyarbakır). It was one of the four Aramean states that bordered Assyria. The others were Bit-Halupe, Bit Bahiani and Laqe. By the ninth century BC all of them lost to Assyria. History The first time Bit-Zamani named was in Assyrian texts from the beginning of the 13th century BC, originating in the city of Shibaniba (modern Tell Billa), in which Ashur-kashid, governor of Bit-Zamani was mentioned. Then Bit-Zamani appears only in Assyrian sources from the beginning of the ninth century BC, from the reign of Assyrian king Tukulti-Ninurta II (890–884 BC). The king was victorious over Ammi-Ba'al, the king of Bit-Zamani, and then entered into a treaty with him, as a result of which Bit-Zamani became an ally, and in fact a vassal of Assyria. Ammi-Ba'al remained in power, but from that moment on, he had to support ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aramean
The Arameans ( oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; syc, ܐܪ̈ܡܝܐ, Ārāmāyē) were an ancient Semitic-speaking people in the Near East, first recorded in historical sources from the late 12th century BCE. The Aramean homeland was known as the land of Aram and encompassed central regions of modern Syria. At the beginning of the 1st millennium BCE, a number of Aramean states were established throughout the western regions of the ancient Near East. The most notable was the Kingdom of Aram-Damascus, which reached its height in the second half of the 9th century BCE during the reign of king Hazael. A distinctive Aramaic alphabet was developed and used to write the Old Aramaic language. During the 8th century BCE, local Aramean kingdoms were gradually conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire. The policy of population displacement and relocation that was applied throughout Assyrian domains also affected Arameans, many of whom were resettled by Assyrian auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neo-hittites Et Arameens
The states that are called Syro-Hittite, Neo-Hittite (in older literature), or Luwian-Aramean (in modern scholarly works), were Luwian and Aramean regional polities of the Iron Age, situated in southeastern parts of modern Turkey and northwestern parts of modern Syria, known in ancient times as lands of Hatti and Aram. They arose following the collapse of the Hittite New Kingdom in the 12th century BCE, and lasted until they were subdued by the Assyrian Empire in the 8th century BCE. They are grouped together by scholars, on the basis of several cultural criteria, that are recognized as similar and mutually shared between both societies, northern (Luwian) and southern (Aramean). Cultural exchange between those societies is seen as a specific regional phenomena, particularly in light of significant linguistic distinctions between two main regional languages, with Luwian belonging to the Anatolian group of Indo-European languages, and Aramaic belonging to the Northwest Semitic group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limmu
: Limmu was an Assyrian eponym. At the beginning of the reign of an Assyrian king, the limmu, an appointed royal official, would preside over the New Year festival at the capital. Each year a new limmu would be chosen. Although picked by lot, there was most likely a limited group, such as the men of the most prominent families or perhaps members of the city assembly. The Assyrians used the name of the limmu for that year to designate the year on official documents. Lists of limmus have been found accounting for every year between 892 BC and 648 BC. During the Old Assyrian period, the king himself was never the ''limmum'', as it was called in their language. In the Middle Assyrian and Neo-Assyrian periods, however, the king could take this office. References See also *Eponym list The Eponym dating system was a calendar system for Assyria, for a period of over one thousand years. Every year was associated with the name, an eponym, of the Limmu, the official who led that yea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tushhan
Tushhan (also Tushan, or Tušhan) is a Kurdish village known as ( ku, Behramki) or ( ku, Tepe-i Barava) by residents. It was an ancient city in Mesopotamia and was a provincial capital in the upper Tigris river valley, on the south bank and inhabited since the Mitanni period, and mainly during the Neo-Assyrian period during the Iron Age. It is now believed to be located at the site of the modern Ziyaret Tepe ( ku, Tepa Barava), Diyarbakır Province, Turkey. History The site of Ziyaret Tepe was occupied as early as the Early Bronze Age. Most of the urban development uncovered to date is from the Middle Iron Age, when the city was rebuilt after its collapse at the end of the Middle Assyrian period. In late Assyrian times it was known as Tushhan, until circa 612 BC to 605 BC, when that empire fell. The site was also occupied in a much smaller scale in the Hellenistic, Roman, Medieval and Ottoman periods. The site is expected to be inundated by the Ilısu Dam around 2014. Archaeolog ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rabshakeh
Rabshakeh (Akkadian: 𒃲𒁉𒈜𒈨𒌍 ''rab šāqê'' AL.BI.LUL.MEŠ ; grc, Ραψακης ''Rapsakēs''; la, Rabsaces; aii, ܪܲܒ݂ܫܵܩܹ̈ܐ; alternative spellings include Rab-shakeh, Rabsaces, or Rab shaqe) is a title meaning "chief of the princes/cup-bearers" in the Semitic Akkadian and Aramaic languages. The title was given to the chief cup-bearer or the vizier of the Akkadian, Assyrian and Babylonian royal courts in ancient Mesopotamia, and revived by the Assyrians as a military rank during World War I. Biblical accounts The Hebrew Bible mentions it for one of Sennacherib's messengers to Hezekiah, who was sent to Jerusalem along with the Tartan and the Rabsaris. The speech he delivered, in the Hebrew language, in the hearing of all the people, as he stood near the wall on the north side of the city, is quoted in 2 Kings and in Isaiah Isaiah ( or ; he, , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "God is Salvation"), also known as Isaias, was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
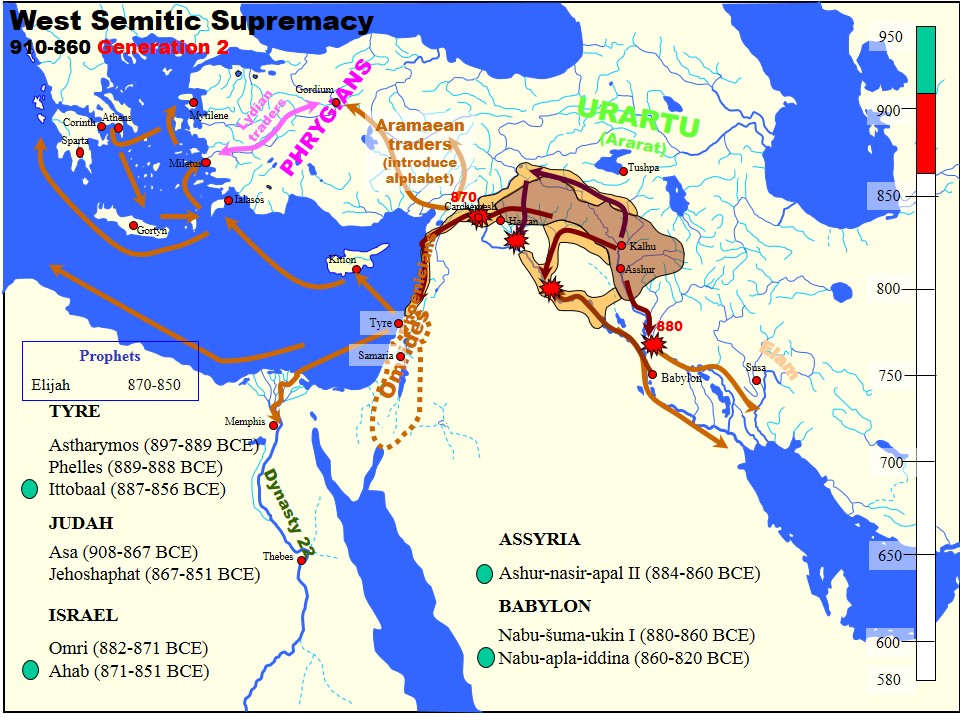
Shalmaneser III
Shalmaneser III (''Šulmānu-ašarēdu'', "the god Shulmanu is pre-eminent") was king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Ashurnasirpal II in 859 BC to his own death in 824 BC. His long reign was a constant series of campaigns against the eastern tribes, the Babylonians, the nations of Mesopotamia and Syria, as well as Kizzuwadna and Urartu. His armies penetrated to Lake Van and the Taurus Mountains; the Neo-Hittites of Carchemish were compelled to pay tribute, and the kingdoms of Hamath and Aram Damascus were subdued. It is in the annals of Shalmaneser III from the 850s BC that the Arab people, Arabs and Chaldeans first appear in recorded history. Reign Campaigns Shalmaneser began a campaign against the Urartu, Urartian Kingdom and reported that in 858 BC he destroyed the city of Sugunia and then in 853 BC also Araškun. Both cities are assumed to have been capitals of the Kingdom before Tushpa became a center for the Urartians. In 853 BC, a coalition was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ashurnasirpal II
Ashur-nasir-pal II ( transliteration: ''Aššur-nāṣir-apli'', meaning "Ashur is guardian of the heir") was king of Assyria from 883 to 859 BC. Ashurnasirpal II succeeded his father, Tukulti-Ninurta II, in 883 BC. During his reign he embarked on a vast program of expansion, first conquering the peoples to the north in Asia Minor as far as Nairi and exacting tribute from Phrygia, then invading Aram (modern Syria) conquering the Aramaeans and Neo-Hittites between the Khabur and the Euphrates Rivers. His harshness prompted a revolt that he crushed decisively in a pitched, two-day battle. According to his monument inscription, while recalling this massacre he says: Following this victory, he advanced without opposition as far as the Mediterranean and exacted tribute from Phoenicia. On his return home, he moved his capital to the city of Kalhu ( Nimrud). Family Ashurnasirpal II's father was Tukulti-Ninurta II. His son and successor was Shalmaneser III. His queen was M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nairi
Nairi ( classical hy, Նայիրի, ''Nayiri'', reformed: Նաիրի, ''Nairi''; , also ''Na-'i-ru'') was the Akkadian name for a region inhabited by a particular group (possibly a confederation or league) of tribal principalities in the Armenian Highlands, approximately spanning the area between modern Diyabakır and Lake Van and the region west of Lake Urmia. Nairi has sometimes been equated with Nihriya, known from Mesopotamian, Hittite, and Urartian sources. However, its co-occurrence with Nihriya within a single text may argue against this. Prior to the Bronze Age collapse, the Nairi tribes were considered a force strong enough to contend with both Assyria and Hatti. If Nairi and Nihriya are to be identified, then the region was the site of the Battle of Nihriya (c. 1230 BCE), the culminating point of the hostilities between Hittites and Assyrians for control over the remnants of the former kingdom of Mitanni. The first kings of Urartu referred to their kingdom as ''Na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |