|
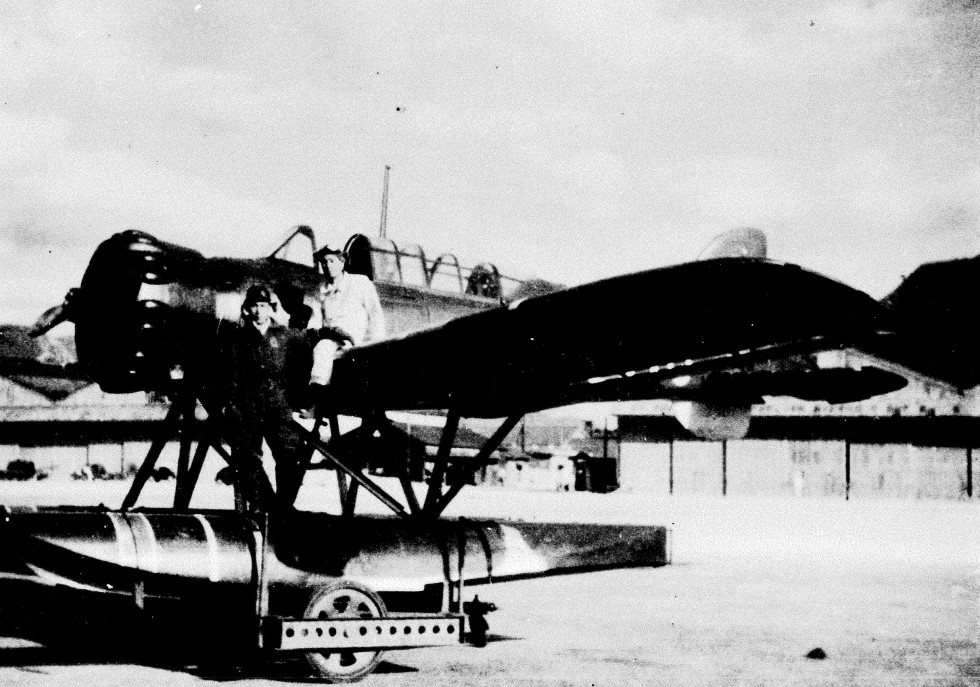
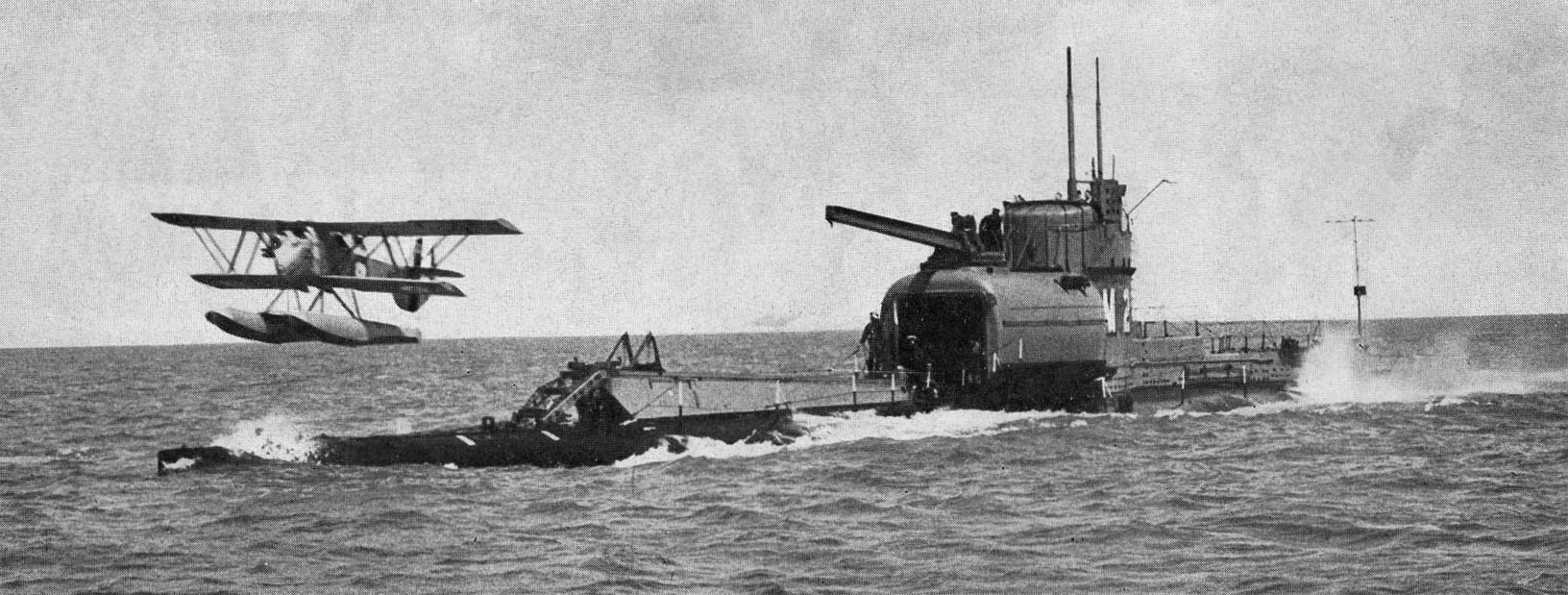
Besson MB.411
The Besson MB.411 was a French two-seat spotter and observation floatplane, designed by Besson. Development In 1932, Besson created the MB.410 by replacing the twin floats of the MB.35 with a single main float and two outrigger floats just inboard of the wingtips. The engine was cowled and fuselage streamlining was improved. The prototype was destroyed in a fatal accident during testing. The French Navy required a spotter aircraft for its new submarine '' Surcouf'', and ordered a production version, designated ''MB.411''. It was specifically designed for housing in a cylindrical hangar in the back of ''Surcoufs conning tower. The Besson MB.411 could be assembled to put on the wings in about 4 minutes (at open sea up to 20 minutes) after it was removed from its hangar, then lowered to the water and retrieved by a crane. MB.411 was a low-wing monoplane with a large single central float and under the wing two small stabilizing floats. The Besson MB.411 was constructed with a mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within Wikimedia project, sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by ''Smithsonian Magazine, Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organization ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luftwaffe
The ''Luftwaffe'' () was the aerial-warfare branch of the German '' Wehrmacht'' before and during World War II. Germany's military air arms during World War I, the '' Luftstreitkräfte'' of the Imperial Army and the '' Marine-Fliegerabteilung'' of the Imperial Navy, had been disbanded in May 1920 in accordance with the terms of the 1919 Treaty of Versailles which banned Germany from having any air force. During the interwar period, German pilots were trained secretly in violation of the treaty at Lipetsk Air Base in the Soviet Union. With the rise of the Nazi Party and the repudiation of the Versailles Treaty, the ''Luftwaffe''s existence was publicly acknowledged on 26 February 1935, just over two weeks before open defiance of the Versailles Treaty through German rearmament and conscription would be announced on 16 March. The Condor Legion, a ''Luftwaffe'' detachment sent to aid Nationalist forces in the Spanish Civil War, provided the force with a valuable testing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Aircraft Of World War II
A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of America * SC Germania List, German rugby union club Other uses * Angle of list, the leaning to either port or starboard of a ship * List (information), an ordered collection of pieces of information ** List (abstract data type), a method to organize data in computer science * List on Sylt, previously called List, the northernmost village in Germany, on the island of Sylt * ''List'', an alternative term for ''roll'' in flight dynamics * To ''list'' a building, etc., in the UK it means to designate it a listed building that may not be altered without permission * Lists (jousting), the barriers used to designate the tournament area where medieval knights jousted * ''The Book of Lists'', an American series of books with unusual lists See also * The List (other) * Listing (di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yokosuka E14Y
The Yokosuka E14Y ( Allied reporting name Glen) was an Imperial Japanese Navy reconnaissance seaplane transported aboard and launched from Japanese submarine aircraft carriers such as the during World War II. The Japanese Navy designation was "Type 0 Small Reconnaissance Seaplane" (零式小型水上偵察機). Design and development Operational history The E14Y was used for several Japanese reconnaissance missions during the Pacific War. On 26 February 1942 the Japanese submarine ''I-25'', under the command of Captain Akiji Tagami, was off the northern tip of King Island in Bass Strait off the coast of Victoria, Australia, when an E14Y was launched on a reconnaissance flight over the Port of Melbourne. The pilot and observer/gunner were in the air for three hours, during which time they successfully flew over Port Phillip Bay and observed the ships at anchor off Melbourne before returning to land on its floats beside the submarine, where it was winched aboard and disas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parnall Peto
The Parnall Peto was a small seaplane designed to the British Air Ministry's specification 16/24 in the early 1920s for use as a submarine-carried reconnaissance aircraft. Design and development Two examples were designed and built by George Parnall and Company and were given serial numbers N181 and N182. The first prototype, N181, crashed at Gibraltar and was rebuilt as N255 before being lost with the submarine HMS ''M2'' when her hangar flooded. The Peto was one of the most challenging design projects that the Parnall company undertook, because of the very small hangar in which the aircraft had to fit. Of mixed wood, fabric, aluminium and steel construction, it had unequal span, Warren-braced folding rectangular wings. The first aircraft, ''N181'', was powered by a 128 hp Bristol Lucifer engine and had mahogany plywood "Consuta" type floats. Performance was generally satisfactory but following crash damage, improvements were made and the machine was rebuilt with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loening XSL-1
A submarine aircraft carrier is a submarine equipped with aircraft for observation or attack missions. These submarines saw their most extensive use during World War II, although their operational significance remained rather small. The most famous of them were the Japanese s and the , although small numbers of similar craft were built for other nations' navies as well. Most operational submarine aircraft carriers, with the exception of the ''I-400'' and AM classes, used their aircraft for reconnaissance and observation. This is in contrast to the typical surface aircraft carrier, whose main function is serving as a base for offensive aircraft. Early history (World War I) Germany was the first nation to experiment with submarine aircraft carriers, initiated by the Imperial German Naval Air Service commander Oberleutnant zur See Friedrich von Arnauld de la Perière who commanded a unit of two Friedrichshafen FF.29 reconnaissance seaplanes in Zeebrugge. One of the first U-bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chyetverikov SPL
The SPL (''Samolyet dlya Podvodnikh Lodok'' – aeroplane for submarine boats) (a.k.a. OSGA-101, and Gidro-1) was a submarine borne flying boat designed and built in the USSR from 1931. Development After successful trials by the Royal Navy, with submarine borne aircraft, using the Parnall Peto and the M-class submarines, the V-MF (''Voenno-morskoj flot'' – Naval Fleet") wanted to deploy aircraft from cruiser submarines for open sea reconnaissance. In 1931 Chyetverikov had given a proposal for a submarine-launched folding flying boat to the head of TsKB (''Tsentrahl'noye Konstrooktorskoye byuro'' – central construction bureau) but nothing was heard for two years until the NII (''Naoochno-Issledovatel'skiy Institoot '' – scientific test institute) placed an order for two prototypes of the SPL. To prove the design, aerodynamically and hydrodynamically, Chyetverikov designed and built a non-folding version of the SPL with manually retracting landing gear designated OSGA- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aichi M6A
The is a submarine-launched attack floatplane designed for the Imperial Japanese Navy during World War II. It was intended to operate from I-400 class submarines whose original mission was to conduct aerial attacks against the United States. Design and development From the late 1920s, the Imperial Japanese Navy had developed a doctrine of operating floatplanes from submarines to search for targets.Layman and McLaughlin 1991, p. 176. In December 1941, Commander-in-Chief of the Japanese Combined Fleet, Admiral Isoroku Yamamoto, proposed constructing a large fleet of submarine aircraft carriers (also designated STo or ''sen-toku'' — special submarine) whose purpose was to mount aerial attacks against American coastal cities. The submarines would surface to launch their aircraft by catapult, submerge to avoid detection, then surface again to retrieve the aircrews who would ditch their planes nearby. By June 1942, the plan was to build a fleet of eighteen such submarines. This ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmson 9Nd
Between 1920 and 1951 the Société des Moteurs Salmson in France developed and built a series of widely used air-cooled aircraft engines.Gunston 1986, p. 158. Design and development After their successful water-cooled radial engines, developed from 1908 to 1918, Salmson changed their focus to air-cooling to reduce weight and increase specific power (power per unit weight). The majority of the engines produced by Salmson were of radial type with a few other arrangements such as the Salmson T6.E. In common with other engines produced by this manufacturer, the air-cooled radial engines featured the unorthodox Canton-Unné internal arrangement that dispensed with a master rod in favour of a cage of epicyclic gears driving the crankpin. Production ended in 1951 with the liquidation of the manufacturing company. British Salmson The 3,7 and 9 cylinder Salmsons were license-built in Great Britain, during the 1920s and 1930s, by the British Salmson engine company as the British Sal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salmson 9Nc
Between 1920 and 1951 the Société des Moteurs Salmson in France developed and built a series of widely used air-cooled aircraft engines.Gunston 1986, p. 158. Design and development After their successful water-cooled radial engines, developed from 1908 to 1918, Salmson changed their focus to air-cooling to reduce weight and increase specific power (power per unit weight). The majority of the engines produced by Salmson were of radial type with a few other arrangements such as the Salmson T6.E. In common with other engines produced by this manufacturer, the air-cooled radial engines featured the unorthodox Canton-Unné internal arrangement that dispensed with a master rod in favour of a cage of epicyclic gears driving the crankpin. Production ended in 1951 with the liquidation of the manufacturing company. British Salmson The 3,7 and 9 cylinder Salmsons were license-built in Great Britain, during the 1920s and 1930s, by the British Salmson engine company as the British S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Military Administration In Occupied France During World War II
The Military Administration in France (german: Militärverwaltung in Frankreich; french: Occupation de la France par l'Allemagne) was an interim occupation authority established by Nazi Germany during World War II to administer the occupied zone in areas of northern and western France. This so-called ' was established in June 1940, and renamed ' ("north zone") in November 1942, when the previously unoccupied zone in the south known as ' ("free zone") was also occupied and renamed ' ("south zone"). Its role in France was partly governed by the conditions set by the Second Armistice at after the success of the leading to the Fall of France; at the time both French and Germans thought the occupation would be temporary and last only until Britain came to terms, which was believed to be imminent. For instance, France agreed that its soldiers would remain prisoners of war until the cessation of all hostilities. The "French State" (') replaced the French Third Republic that had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |