|
Berthoud Pass
Berthoud Pass ( ; elevation ) is a high mountain pass in central Colorado, in the Front Range of the Rocky Mountains of the western United States. The pass is located west of Denver, and provides a high route between upper Clear Creek Canyon to the upper valley of the Fraser River in Middle Park to the north. It traverses the continental divide at the Front Range, on the border between Clear Creek County and Grand County. The pass is named for Edward L. Berthoud, the chief surveyor of the Colorado Central Railroad during the 1870s. Accompanied by Jim Bridger, Berthoud discovered the pass in July 1861 while surveying a possible route for the railroad. Berthoud concluded that the pass was suitable as a wagon road, but not as a railroad, and was then hired by the Central Overland California and Pikes Peak Express Company to survey a route over the pass to Salt Lake. The route of U.S. Highway 40 currently traverses the pass north of its junction with Interstate 70 in Clear C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clear Creek County, Colorado
Clear Creek County is a county located in the U.S. state of Colorado. As of the 2020 census, the population was 9,397. The county seat is Georgetown. History Clear Creek County was one of the original 17 counties created by the Colorado legislature on November 1, 1861, and is one of only two counties (along with Gilpin) to have persisted with its original boundaries unchanged. It was named after Clear Creek, which runs down from the continental divide through the county. Idaho Springs was originally designated the county seat, but the county government was moved to Georgetown in 1867. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the county has a total area of , of which is land and (0.3%) is water. Adjacent counties * Jefferson - east * Gilpin - northeast * Park - south * Summit - west * Grand - northwest Major highways * Interstate 70 * U.S. Highway 6 * U.S. Highway 40 * State Highway 5 * State Highway 103 * Central City Parkway National protected a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Overland California And Pikes Peak Express Company
The Central Overland California and Pike's Peak Express Company was a stagecoach line that operated in the American West in the early 1860s, but it is most well known as the parent company of the Pony Express. It was formed as a subsidiary of the freighting company Russell, Majors, and Waddell, after the latter two partners bought out Russell's stage line, the Leavenworth and Pikes Peak Express Company. The stage line had made its first journey from Westport, Missouri, to Denver on March 9, 1859. Its stage lines ran from St. Joseph, Missouri, to Denver and Salt Lake City and it succeeded the George Chorpenning contract for mail service from Utah to California in May 1860. In an attempt to win a more lucrative contract with the United States government, it started an express mail service between St. Joseph and San Francisco on April 3, 1860, known as the Pony Express. Maintenance of frequent stage service and heavy losses from the Pony Express brought embarrassment to the C. O. C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada Lynx
The Canada lynx (''Lynx canadensis'') or Canadian lynx is one of the four living species in the genus ''Lynx''. It is a medium-sized wild cat characterized by long, dense fur, triangular ears with black tufts at the tips, and broad, snowshoe-like paws. Its hindlimbs are longer than the forelimbs, so its back slopes downward to the front. The Canada lynx stands tall at the shoulder and weighs between . It is a good swimmer and an agile climber. The Canada lynx was first scientific description, described by Robert Kerr (writer), Robert Kerr in 1792. Three subspecies have been proposed, but their valid name (zoology), validity is doubted; it is mostly considered a monotypic species. It ranges across Alaska, Canada and northern areas of the contiguous United States, where it predominantly inhabits dense Taiga, boreal forests. It is a Specialist and generalist species, specialist predator and depends heavily on the snowshoe hare (''Lepus americanus'') for food. This leads to a Lot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alpine Climate
Alpine climate is the typical climate for elevations above the tree line, where trees fail to grow due to cold. This climate is also referred to as a mountain climate or highland climate. Definition There are multiple definitions of alpine climate. In the Köppen climate classification, the alpine and mountain climates are part of group ''E'', along with the polar climate, where no month has a mean temperature higher than . According to the Holdridge life zone system, there are two mountain climates which prevent tree growth : a) the alpine climate, which occurs when the mean biotemperature of a location is between . The alpine climate in Holdridge system is roughly equivalent to the warmest tundra climates (ET) in the Köppen system. b) the alvar climate, the coldest mountain climate since the biotemperature is between 0 °C and 1.5 °C (biotemperature can never be below 0 °C). It corresponds more or less to the coldest tundra climates and to the ice cap cli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subarctic Climate
The subarctic climate (also called subpolar climate, or boreal climate) is a continental climate with long, cold (often very cold) winters, and short, warm to cool summers. It is found on large landmasses, often away from the moderating effects of an ocean, generally at latitudes from 50°N to 70°N, poleward of the humid continental climates. Like other Class D climates, they are rare in the Southern Hemisphere, only found at some isolated highland elevations. Subarctic or boreal climates are the source regions for the cold air that affects temperate latitudes to the south in winter. These climates represent Köppen climate classification ''Dfc'', ''Dwc'', ''Dsc'', ''Dfd'', ''Dwd'' and ''Dsd''. Description This type of climate offers some of the most extreme seasonal temperature variations found on the planet: in winter, temperatures can drop to below and in summer, the temperature may exceed . However, the summers are short; no more than three months of the year (but at least on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
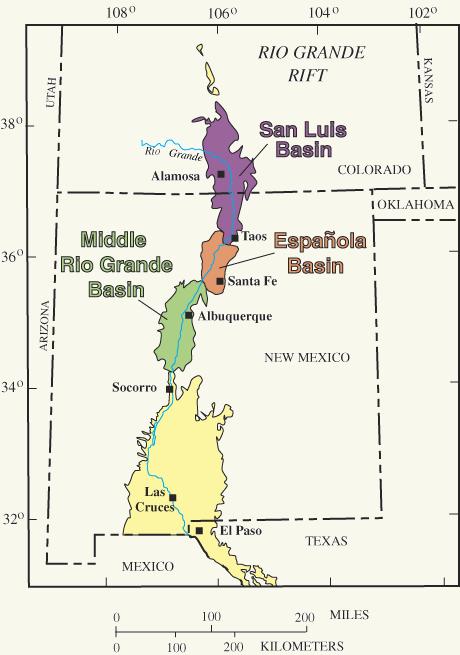
Geology Of New Mexico
The geology of New Mexico includes bedrock exposures of four physiographic provinces, with ages ranging from almost 1800 million years (Ma (unit), Ma) to nearly the present day. Here the Great Plains, southern Rocky Mountains, Colorado Plateau, and Basin and Range Province, Basin and Range Provinces meet, giving the state great geologic diversity. The geologic history of the state began with its assembly during the Yavapai orogeny, Yavapai and Mazatzal orogeny, Mazatzal orogeny, orogenies 1750 to 1650 million years ago (Mya (unit), Mya). This was followed by 200 million years of tectonic quiescence that ended in the Picuris orogeny. This event transformed the New Mexico crust into mature continental crust. Over a thousand million years of tectonic quiescence followed, ending with the rise of the Ancestral Rocky Mountains in Pennsylvanian (geology), Pennsylvanian time, 300 Mya. The Permian and most of the Mesozoic were another interval of relative tectonic quiescence, where gradua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metasedimentary Rock
In geology, metasedimentary rock is a type of metamorphic rock. Such a rock was first formed through the deposition and solidification of sediment Sediment is a solid material that is transported to a new location where it is deposited. It occurs naturally and, through the processes of weathering and erosion, is broken down and subsequently sediment transport, transported by the action of .... Then, the rock was buried underneath subsequent rock and was subjected to high pressures and temperatures, causing the rock to recrystallize. The overall composition of a metasedimentary rock can be used to identify the original sedimentary rock, even where they have been subject to high-grade metamorphism and intense deformation. Types of metasedimentary rocks See also * References Metamorphic petrology {{Rock-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colorado Department Of Transportation
The Colorado Department of Transportation (CDOT, pronounced See Dot) is the principal department of the government of Colorado, Colorado state government that administers state government responsibility for Transportation in Colorado, transportation in the state of Colorado. CDOT is responsible for maintaining Colorado's 9,144 mile highway system, including 3,429 bridges with over 28 billion vehicle miles of travel per year. CDOT's stated Mission is "To provide the best multi-modal transportation system for Colorado that most effectively moves people, goods, and information." It is governed by the Transportation Commission of Colorado. Motor Carriers over 10,000 lbs are regulated by the state and are required to obtain a federal United States Department of Transportation (USDOT) safety tracking number used to monitor carriers' safety management practices and controls. History The Colorado Department of Transportation has its roots in 1909, when the first highway bill was pass ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hairpin Turn
A hairpin turn (also hairpin bend or hairpin corner) is a bend in a road with a very acute inner angle, making it necessary for an oncoming vehicle to turn about 180° to continue on the road. It is named for its resemblance to a bent metal hairpin. Such turns in ramps and trails may be called switchbacks in American English, by analogy with switchback railways. Description Hairpin turns are often built when a route climbs up or down a steep slope, so that it can travel mostly across the slope with only moderate steepness, and are often arrayed in a zigzag pattern. Highways with repeating hairpin turns allow easier, safer ascents and descents of mountainous terrain than a direct, steep climb and descent, at the price of greater distances of travel and usually lower speed limits, due to the sharpness of the turn. Highways of this style are also generally less costly to build and maintain than highways with tunnels. On occasion, the road may loop completely, using a tunnel or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grade (slope)
The grade (US) or gradient (UK) (also called stepth, slope, incline, mainfall, pitch or rise) of a physical feature, landform or constructed line is either the elevation angle of that surface to the horizontal plane, horizontal or its tangent. It is a special case of the slope, where zero indicates horizontal plane, horizontality. A larger number indicates higher or steeper degree of "tilt". Often slope is calculated as a ratio of "rise" to "run", or as a fraction ("rise over run") in which ''run'' is the horizontal distance (not the distance along the slope) and ''rise'' is the vertical distance. Slopes of existing physical features such as canyons and hillsides, bank (geography), stream and river banks, and stream bed, beds are often described as grades, but typically the word "grade" is used for human-made surfaces such as roads, landscape grading, roof pitches, rail tracks, railroads, aqueduct (watercourse), aqueducts, and pedestrian or bicycle routes. The grade may refer to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |