|
Bert R. Bulkin
Bertram Raoul Bulkin (July 20, 1929 – March 10, 2012) was an American aeronautical engineer who participated in the first United States photo-reconnaissance satellite programs and is best known for his role in building the Hubble Space Telescope. Biography Early life and education Bulkin was born in Brooklyn, New York, the son of David Bulkin and Anne Clara Strauss, both immigrants. He was named after Berel Reven Bulkin, a paternal uncle from the Kiev area of Ukraine. After residing briefly in Springfield, Massachusetts, he and his family returned to Brooklyn, where he attended P.S. 197, an elementary school. Bulkin was graduated from John Marshall High School (Los Angeles, California) in 1946 at age 16. He then attended the University of California, Los Angeles, where he received a Bachelor of Science degree in aeronautical engineering. During his time at UCLA, he took a summer job with what was then called Lockheed's Advanced Development Projects facility, also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeronautical Engineering
Aerospace engineering is the primary field of engineering concerned with the development of aircraft and spacecraft. It has two major and overlapping branches: aeronautical engineering and astronautical engineering. Avionics engineering is similar, but deals with the electronics side of aerospace engineering. "Aeronautical engineering" was the original term for the field. As flight technology advanced to include vehicles operating in outer space, the broader term "aerospace engineering" has come into use. Aerospace engineering, particularly the astronautics branch, is often colloquially referred to as "rocket science". Overview Flight vehicles are subjected to demanding conditions such as those caused by changes in atmospheric pressure and temperature, with structural loads applied upon vehicle components. Consequently, they are usually the products of various technological and engineering disciplines including aerodynamics, Air propulsion, avionics, materials science, struc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lockheed L-188 Electra
The Lockheed L-188 Electra is an American turboprop airliner built by Lockheed. First flown in 1957, it was the first large turboprop airliner built in the United States. Initial sales were good, but after two fatal crashes that led to expensive modifications to fix a design defect, no more were ordered. With its unique high power-to-weight ratio, huge propellers and very short wings (resulting in the majority of the wingspan being enveloped in propwash), large Fowler flaps which significantly increased effective wing area when extended, and four-engined design, the airplane had airfield performance capabilities unmatched by many jet transport aircraft even today—particularly on short runways and high field elevations. Jet airliners soon supplanted turboprops for many purposes, and many Electras were modified as freighters. Some Electras are still being used in various roles into the 21st century. The airframe was also used as the basis for the Lockheed P-3 Orion maritime p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
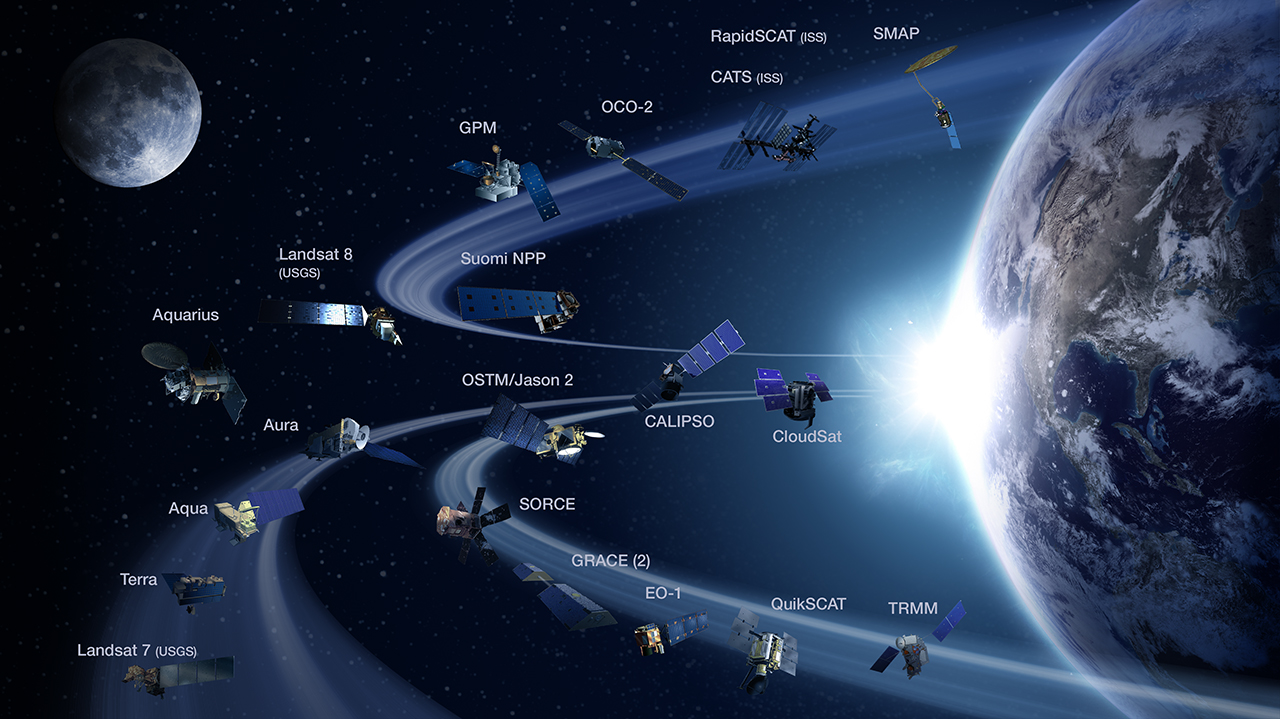
NASA Earth Science
NASA Earth Science, formerly called NASA Earth Science Enterprise (ESE) and Mission To Planet Earth (MTPE), is a NASA research program "to develop a scientific understanding of the Earth system and its response to natural and human-induced changes to enable improved prediction of climate, weather, and natural hazards for present and future generations". Its director was Michael Freilich (2006–2019). NASA supports research in the Earth Sciences and, as part of its Earth Observing System (EOS), launches and maintains Earth observing satellites to monitor the state of the climate, atmospheric chemistry, ocean and land ecosystems. It was a NASA scientist, Dr. James Hansen, who first alerted the world to the dangers of global warming due to greenhouse gases emitted by human burning of fossil fuels. Earth Science research also provides the foundations of understanding for the search for extraterrestrial life through the NASA Astrobiology Institute The NASA Astrobiology Institut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Probe Plus
The Parker Solar Probe (PSP; previously Solar Probe, Solar Probe Plus or Solar Probe+) is a NASA space probe launched in 2018 with the mission of making observations of the outer corona of the Sun. It will approach to within 9.86 solar radii (6.9 million km or 4.3 million miles) from the center of the Sun, and by 2025 will travel, at closest approach, as fast as , or 0.064% the speed of light. It is the fastest object ever built. The project was announced in the fiscal 2009 budget year. The cost of the project is US$1.5 billion. Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory designed and built the spacecraft, which was launched on 12 August 2018. It became the first NASA spacecraft named after a living person, honoring wikt:nonagenarian, nonagenarian physicist Eugene Parker, Eugene Newman Parker, professor emeritus at the University of Chicago. A memory card containing the names of over 1.1 million people was mounted on a plaque and installed below the spacecraft's hig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gravity Probe B
Gravity Probe B (GP-B) was a satellite-based experiment to test two unverified predictions of general relativity: the geodetic effect and frame-dragging. This was to be accomplished by measuring, very precisely, tiny changes in the direction of spin of four gyroscopes contained in an Earth-orbiting satellite at of altitude, crossing directly over the poles. The satellite was launched on 20 April 2004 on a Delta II rocket. The spaceflight phase lasted until 2005; Its aim was to measure spacetime curvature near Earth, and thereby the stress–energy tensor (which is related to the distribution and the motion of matter in space) in and near Earth. This provided a test of general relativity, gravitomagnetism and related models. The principal investigator was Francis Everitt. Initial results confirmed the expected geodetic effect to an accuracy of about 1%. The expected frame-dragging effect was similar in magnitude to the current noise level (the noise being dominated by initi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spitzer Space Telescope
The Spitzer Space Telescope, formerly the Space Infrared Telescope Facility (SIRTF), was an infrared space telescope launched in 2003. Operations ended on 30 January 2020. Spitzer was the third space telescope dedicated to infrared astronomy, following IRAS (1983) and ISO (1995–1998). It was the first spacecraft to use an Earth-trailing orbit, later used by the Kepler planet-finder. The planned mission period was to be 2.5 years with a pre-launch expectation that the mission could extend to five or slightly more years until the onboard liquid helium supply was exhausted. This occurred on 15 May 2009. Without liquid helium to cool the telescope to the very low temperatures needed to operate, most of the instruments were no longer usable. However, the two shortest-wavelength modules of the IRAC camera continued to operate with the same sensitivity as before the helium was exhausted, and continued to be used into early 2020 in the Spitzer Warm Mission. During the warm missio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Perkin Elmer
PerkinElmer, Inc., previously styled Perkin-Elmer, is an American global corporation focused in the business areas of diagnostics, life science research, food, environmental and industrial testing. Its capabilities include detection, imaging, informatics, and service. PerkinElmer produces analytical instruments, genetic testing and diagnostic tools, medical imaging components, software, instruments, and consumables for multiple end markets. PerkinElmer is part of the S&P 500 Index and operates in 190 countries. History Founding Richard Perkin was attending the Pratt Institute in Brooklyn to study chemical engineering, but left after a year to try his hand on Wall Street. Still interested in the sciences, he gave public lectures on various topics. Charles Elmer ran a firm that supplied court reporters and was nearing retirement when he attended one of Perkin's lectures on astronomy being held at the Brooklyn Institute of Arts and Sciences. The two struck up a friendship o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Space Shuttle Challenger Disaster
On January 28, 1986, the broke apart 73 seconds into its flight, killing all seven crew members aboard. The spacecraft disintegrated above the Atlantic Ocean, off the coast of Cape Canaveral, Florida, at 11:39a.m. EST (16:39 UTC). It was the first fatal accident involving an American spacecraft in flight. The mission, designated STS-51-L, was the tenth flight for the orbiter and the twenty-fifth flight of the Space Shuttle fleet. The crew was scheduled to deploy a communications satellite and study Halley's Comet while they were in orbit, in addition to taking school teacher Christa McAuliffe into space. The latter resulted in a higher than usual media interest and coverage of the mission; the launch and subsequent disaster were seen live in many schools across the United States. The cause of the disaster was the failure of the two O-ring seals in a joint in the shuttle's right solid rocket booster (SRB). The record-low temperatures of the launch had stiffened the rubb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fort Wayne, Indiana
Fort Wayne is a city in and the county seat of Allen County, Indiana, United States. Located in northeastern Indiana, the city is west of the Ohio border and south of the Michigan border. The city's population was 263,886 as of the 2020 Census, making it the second-most populous city in Indiana after Indianapolis, and the 76th-most populous city in the United States. It is the principal city of the Fort Wayne metropolitan area, consisting of Allen and Whitley counties which had an estimated population of 423,038 as of 2021. Fort Wayne is the cultural and economic center of northeastern Indiana. In addition to the two core counties, the combined statistical area (CSA) includes Adams, DeKalb, Huntington, Noble, Steuben, and Wells counties, with an estimated population of 649,105 in 2021. Fort Wayne was built in 1794 by the United States Army under the direction of American Revolutionary War general Anthony Wayne, the last in a series of forts built near the Miami villag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ITT Corporation
ITT Inc., formerly ITT Corporation, is an American worldwide manufacturing company based in Stamford, Connecticut. The company produces specialty components for the aerospace, transportation, energy and industrial markets. ITT's three businesses include Industrial Process, Motion Technologies, and Connect and Control Technologies. ITT has approximately 10,000 employees in more than 35 countries and serves customers in well over 100 countries. The company's long-standing brands include Goulds Pumps, Cannon connectors, KONI shock absorbers and Enidine energy absorption components. The company was founded in 1920 as International Telephone & Telegraph. During the 1960s and 1970s, under the leadership of CEO Harold Geneen, the company rose to prominence as the archetypal conglomerate, deriving its growth from hundreds of acquisitions in diversified industries. ITT divested its telecommunications assets in 1986. In 1995, the company sold off its hospitality portfolio, including ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
KH-9 Hexagon
KH-9 (BYEMAN codename HEXAGON), commonly known as Big Bird or KeyHole-9, p.32 Big Bird was a series of photographic reconnaissance satellites launched by the United States between 1971 and 1986. Of twenty launch attempts by the National Reconnaissance Office, all but one were successful. Photographic film aboard the KH-9 was sent back to Earth in recoverable film return capsules for processing and interpretation. The highest ground resolution achieved by the main cameras of the satellite was . Another source says "images in the "better-than-one-foot" category" for the last "Gambit" missions. They are also officially known as the Broad Coverage Photo Reconnaissance satellites (Code 467), built by Lockheed Corporation for the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO). The satellites were an important factor in determining Soviet military capabilities and in the acquisition of accurate intelligence for the formulation of U.S. national policy decisions as well as deployment of U.S. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Clara University
Santa Clara University is a private Jesuit university in Santa Clara, California. Established in 1851, Santa Clara University is the oldest operating institution of higher learning in California. The university's campus surrounds the historic Mission Santa Clara de Asís which traces its founding to 1777. The campus mirrors the Mission's architectural style and is one of the finest groupings of Mission Revival architecture and other Spanish Colonial Revival styles. The university is classified as a "Doctoral/Professional" university. The university offers bachelor's degrees, master's degrees, and doctoral degrees through its six colleges, the College of Arts and Sciences, School of Education and Counseling Psychology, Leavey School of Business, School of Engineering, Jesuit School of Theology, and School of Law. It enrolls about 5,400 undergraduate students and about 3,300 postgraduate students. Among Santa Clara's alumni are governors, congressmen, mayors, senators, pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)




.jpg)