|
Berliet VXB-170
The Berliet VXB-170 is a four-wheel armoured vehicle used primarily as an internal security vehicle. Developed and initially produced by Berliet until Berliet was merged with Saviem to form Renault Trucks (now Arquus), it lost to the Saviem VAB the competition to equip the French Army, even though it was cheaper than its competitor. Production stopped after fewer than 200 vehicles had been produced. History In 1967, the BL-12 was presented as a concept for the French military for transportation. It was selected in 1972 by the French Gendarmerie, but it lost out to the Saviem VAB the competition for equipment of the French Army. Following the merger of Berliet and Saviem under the Renault brand in 1974, became redundant in the brand product offering so production was stopped soon after the Gendarmerie order was complete. The VXB-170 was known as ''Véhicule blindé à roues de la Gendarmerie'' ("Gendarmerie wheeled armoured vehicle") or VBRG. Design The VXB-170 has a V8 170 h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
French Gendarmerie
The National Gendarmerie ( ) is one of two national law enforcement forces of France, along with the National Police. The Gendarmerie is a branch of the French Armed Forces placed under the jurisdiction of the Ministry of the Interior, with additional duties from the Ministry of Armed Forces. Its responsibilities include policing smaller towns, suburbs and rural areas, crowd and riot control, and criminal investigation, including cybercrime. By contrast, the National Police is a civilian law enforcement agency that is in charge of policing cities and larger towns. Because of its military status, the Gendarmerie also fulfills a range of military and defence missions. The Gendarmerie has a strength of around 102,269 people (as of 2018). The Gendarmerie is the heir of the , the oldest police force in France, dating back to the Middle Ages. The Gendarmerie has influenced the culture and traditions of gendarmerie forces around the world, especially in independent countries from th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
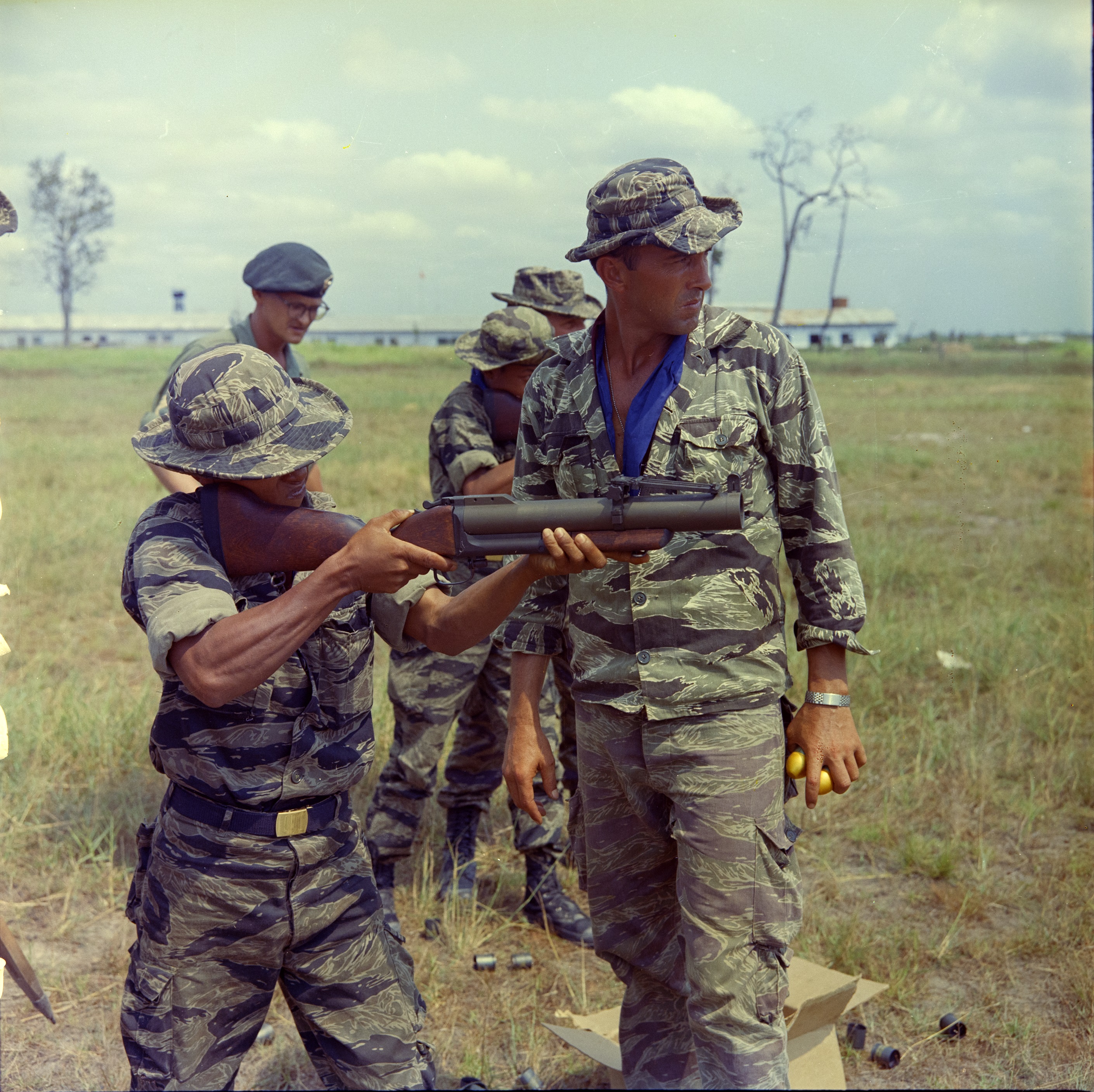
Grenade Launcher
A grenade launcher is a weapon that fires a specially designed, large caliber projectile, often with an explosive, Smoke screen, smoke, or tear gas, gas warhead. Today, the term generally refers to a class of dedicated firearms firing unitary grenade Cartridge (firearms), cartridges. The most common type are man-portable, shoulder-fired weapons issued to individuals, although larger crew-served launchers are issued at higher levels of organization by military forces. Grenade launchers are produced in the form of standalone weapons (either Single-shot, single shot or Repeating firearm, repeating) or as attachments mounted to a parent firearm, usually a rifle. Larger crew-served automatic grenade launchers such as the Mk 19 grenade launcher, Mk 19 are mounted on Weapon mount, tripods or vehicles. Some armored fighting vehicles also mount fixed arrays of short-range, single-shot grenade launchers as a means of defense. History Early precursors The earliest devices that could ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Vehicles Introduced In The 1970s
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. Militaries are typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with their members identifiable by a distinct military uniform. They may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of a military is usually defined as defence of their state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms "armed forces" and "military" are often synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include other paramilitary forces such as armed police. Beyond warfare, the military may be employed in additional sanctioned and non-sanctioned functions within the state, including internal security threats, crowd control, promotion of political agendas, emergency services and reconstruction, pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Internal Security Vehicles
An internal security vehicle (ISV), also known as an armored security vehicle (ASV), is an armored car or armored personnel carrier used for supporting contingency operations. Design Internal security vehicles are typically armed with a turreted heavy machine gun and auxiliary medium machine gun. The vehicle is designed to minimize firepower dead space and the vehicle's weapons can be depressed to a maximum of 12°. Less-lethal water cannons and tear gas cannons can provide suppressive fire in lieu of unnecessary deadly fire. The vehicle must be protected against weapons typical of riots. Protection from incendiary devices is achieved through coverage of the air intake and exhaust ports as well as a strong locking mechanism on the fuel opening. Turret and door locks prevent access to the interior of the vehicle by rioters. Vision blocks, ballistic glass and window shutters and outside surveillance cameras allow protected observation from within the vehicle. Wheeled 4×4 and 6 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wheeled Amphibious Armoured Fighting Vehicles
A wheel is a rotating component (typically circular in shape) that is intended to turn on an axle bearing. The wheel is one of the key components of the wheel and axle which is one of the six simple machines. Wheels, in conjunction with axles, allow heavy objects to be moved easily facilitating movement or transportation while supporting a load, or performing labor in machines. Wheels are also used for other purposes, such as a ship's wheel, steering wheel, potter's wheel, and flywheel. Common examples can be found in transport applications. A wheel reduces friction by facilitating motion by rolling together with the use of axles. In order for a wheel to rotate, a moment must be applied to the wheel about its axis, either by gravity or by the application of another external force or torque. Terminology The English word ''wheel'' comes from the Old English word , from Proto-Germanic , from Proto-Indo-European , an extended form of the root . Cognates within Indo-Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armoured Personnel Carriers Of France
Armour (Commonwealth English) or armor (American English; see spelling differences) is a covering used to protect an object, individual, or vehicle from physical injury or damage, especially direct contact weapons or projectiles during combat, or from a potentially dangerous environment or activity (e.g. cycling, construction sites, etc.). Personal armour is used to protect soldiers and war animals. Vehicle armour is used on warships, armoured fighting vehicles, and some combat aircraft, mostly ground attack aircraft. A second use of the term ''armour'' describes armoured forces, armoured weapons, and their role in combat. After the development of armoured warfare, tanks and mechanised infantry and their combat formations came to be referred to collectively as "armour". Etymology The word "armour" began to appear in the Middle Ages as a derivative of Old French. It is dated from 1297 as a "mail, defensive covering worn in combat". The word originates from the Old Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ratel IFV
The Ratel is a South African infantry fighting vehicle. It was the first wheeled infantry fighting vehicle to enter service worldwide and was built on a modified MAN Truck & Bus, MAN truck chassis. The Ratel was designed in response to a South African Army specification for a light armoured vehicle suited to the demands of rapid offensives, providing maximum firepower and strategic mobility to mechanised infantry units intended to operate across the vast distances of Southern Africa. Primarily envisaged in SADF doctrine as a vehicle that could deliver mechanised infantry and supporting fire to tanks in conventional warfare, it was also anticipated that the Ratel could form the centrepiece for semi-independent battlegroups where logistics or politics precluded the use of tanks. The Ratel was a simple, economical design which helped reduce the significant logistical commitment necessary to keep heavier combat vehicles operational in undeveloped regions. It was generally regarded as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
International Institute For Strategic Studies
The International Institute for Strategic Studies (IISS) is an international research institute or think tank focusing on defence and security issues. Since 1997, its headquarters have been at Arundel House in London. It has offices on four continents, producing data and research on questions of defence, security and global affairs, publishing publications and online analysis, and convening major security summits. ''The Guardian'' newspaper has described the IISS as ‘one of the world’s leading security think tanks.’ The current Director-General and Chief Executive is Bastian Giegerich while Sir John Chipman is the Executive Chairman. The 2017 Global Go To Think Tank Index ranked IISS as the tenth-best think tank worldwide and the second-best Defence and National Security think tank globally, while Transparify ranked it third-largest UK think tank by expenditure, but gave it its lowest rating, describing it as deceptive, on funding transparency. Research The institu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
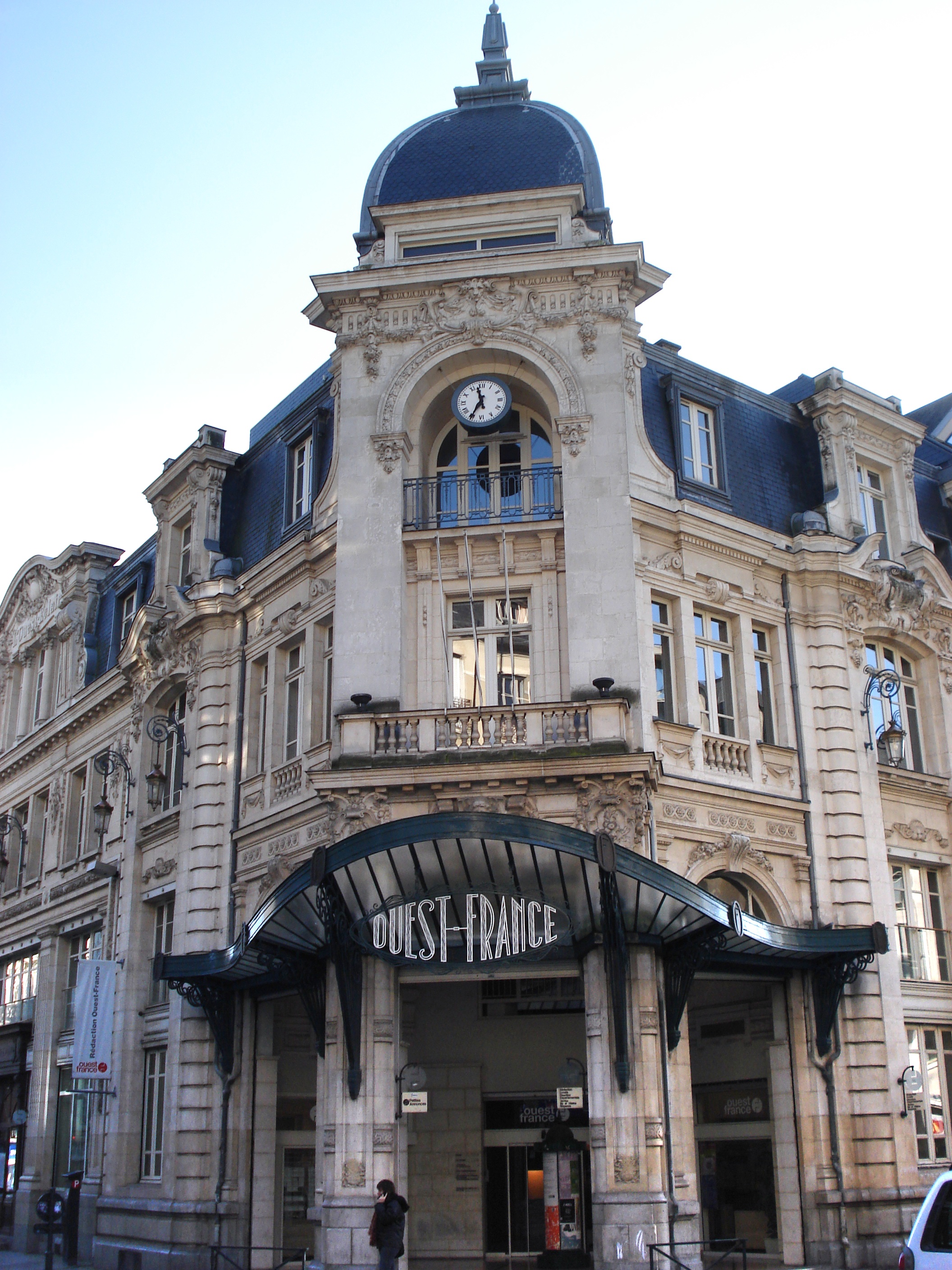
Ouest France
''Ouest-France'' ( ; French for "West-France") is a daily French newspaper known for its emphasis on both local and national news. The paper is produced in 47 different editions covering events in different French départements within the régions of Brittany, Lower Normandy and Pays de la Loire. Its readership has been unaffected by the decline of newspaper reading in France, unlike most other dailies. With 2.5 million daily readers (and a circulation of almost 800 000 units), it is by far the most read francophone newspaper in the world, ahead of French national newspapers ''Le Figaro'' and ''Le Monde''. History ''Ouest-France'' was founded in 1944 by Adolphe Le Goaziou and others following the closure of '' Ouest-Éclair'', which was banned by Liberation forces for collaborationism during the war.Jean-Loup Avril, ''Mille Bretons, dictionnaire biographique'', Les Portes du Large, Saint-Jacques-de-la-Lande, 2003, () It is based in Rennes and Nantes and has a circulation ab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metropolitan France
Metropolitan France ( or ), also known as European France (), is the area of France which is geographically in Europe and chiefly comprises #Hexagon, the mainland, popularly known as "the Hexagon" ( or ), and Corsica. This collective name for the European regions of France is used in everyday life in France but has no administrative meaning, with the exception that only Metropolitan France is part of the Schengen Area. Indeed, the overseas departments and regions of France, overseas regions have exactly the same administrative divisions of France, administrative status as the metropolitan regions. Metropolitan France comprises mainland France and Corsica, as well as nearby List_of_islands_of_France#Islands_of_metropolitan_France, French islands in the Atlantic Ocean, the English Channel and the Mediterranean Sea waters. Its borders have undergone significant territorial evolution of France, changes over the centuries, particularly in the east, but have remained unaltered since 1947 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overseas France
Overseas France (, also ) consists of 13 France, French territories outside Europe, mostly the remnants of the French colonial empire that remained a part of the French state under various statuses after decolonisation. Most are part of the European Union. "Overseas France" is a collective name; while used in everyday life in France, it is not an administrative designation in its own right. Instead, the five Overseas departments and regions of France, overseas regions have exactly the same Administrative divisions of France, administrative status as the thirteen Metropolitan France, metropolitan regions; the five Overseas collectivity, overseas collectivities are semi-autonomous; and New Caledonia is an autonomous territory. Overseas France includes island territories in the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pacific and Indian Ocean, Indian oceans, French Guiana on the South American continent, and several list of Antarctic and Subantarctic islands, peri-Antarctic islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |