|
Benjamin Pierce (1841–1853)
Franklin Pierce (November 23, 1804October 8, 1869) was the 14th president of the United States, serving from 1853 to 1857. A northern Democrat who believed that the abolitionist movement was a fundamental threat to the nation's unity, he alienated anti-slavery groups by signing the Kansas–Nebraska Act and enforcing the Fugitive Slave Act. Conflict between North and South continued after Pierce's presidency, and, after Abraham Lincoln was elected president in 1860, the Southern states seceded, resulting in the American Civil War. Pierce was born in New Hampshire, the son of state governor Benjamin Pierce. He served in the House of Representatives from 1833 until his election to the Senate, where he served from 1837 until his resignation in 1842. His private law practice was a success, and he was appointed New Hampshire's U.S. attorney in 1845. Pierce took part in the Mexican–American War as a brigadier general in the United States Army. Democrats saw him as a compr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathew Brady
Mathew B. Brady ( – January 15, 1896) was an American photographer. Known as one of the earliest and most famous photographers in American history, he is best known for his scenes of the American Civil War, Civil War. He studied under inventor Samuel Morse, who pioneered the daguerreotype technique in America. Brady opened his own studio in New York City in 1844, and went on to photograph President of the United States, U.S. presidents John Quincy Adams, Abraham Lincoln, Millard Fillmore, Martin Van Buren, and other public figures. When the Civil War began, Brady's use of a mobile studio and darkroom enabled thousands of vivid War photography, battlefield photographs to bring home the reality of war to the public. He also photographed generals and politicians on both sides of the conflict, though most of these were taken by his assistants rather than by Brady himself. After the end of the Civil War, these pictures went out of fashion, and the government did not purchase the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benjamin Kendrick Pierce
Benjamin Kendrick Pierce (August 29, 1790 – April 1, 1850) was a career officer in the United States Army. He was a son of New Hampshire Governor Benjamin Pierce and brother of President Franklin Pierce. Benjamin K. Pierce was a veteran of the War of 1812, the Second Seminole War, and the Mexican–American War, and rose to the rank of lieutenant colonel in the Army and colonel in the Florida Militia. Early life The eldest son of Benjamin Pierce and Anna (Kendrick) Pierce, and a descendant of Thomas Pierce (1618–1683), who was born in Norwich, England and settled in the Massachusetts Bay Colony, Benjamin Kendrick Pierce was born in Hillsborough, New Hampshire, on August 29, 1790, and named for his maternal grandfather. His father was determined that his sons receive college educations, and Benjamin K. Pierce attended Phillips Exeter Academy in preparation for admission to a university. He studied at Dartmouth College from 1807 until 1810, when he was dismissed for carr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
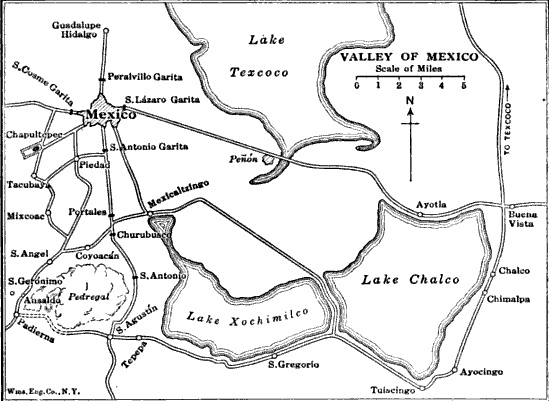
Battle Of Chapultepec
The Battle of Chapultepec took place between U.S. troops and Mexican forces holding the strategically located Chapultepec Castle on the outskirts of Mexico City on the 13th of September, 1847 during the Mexican–American War. The castle was built atop a hill in 1783, and in 1833 it was converted into a military academy and a gunpowder storage facility. The hill was surrounded by a wall 1,600 yards long. The battle was one of the most pivotal battles during the Mexican–American War as it paved the way to seize Mexico City and led to a decisive American victory. On the U.S. side the army was headed by General Winfield Scott, who led a force totaling 7,200 men. The Mexican side was led by General Antonio López de Santa Anna, commander of the Mexican army, had formed an army of approximately 25,000 men. Chapultepec Castle was defended by General Nicholas Bravo and his infantry of approximately 832 men, including military cadets of the Heroic Military Academy (Mexico), Military A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Molino Del Rey
The Battle of Molino del Rey (8 September 1847) was one of the bloodiest engagements of the Mexican–American War as part of the Battle for Mexico City. It was fought in September 1847 between Mexican forces under General Antonio León against an American force under Major General Winfield Scott at El Molino del Rey on the fringes of Mexico City. The Americans made little progress in this battle, but the Mexican forces were unable to hold them back long enough to prevent the capture of Mexico City one week later. Ulysses S. Grant served as a captain during this battle. Background The Americans were camped south of Mexico City, Scott and Worth's division at Tacubaya, Gideon Johnson Pillow's division at Mixcoac, David E. Twiggs division at San Ángel, and John A. Quitman's division at San Agustín. On 6 September 1847, Scott ended the armistice following the Battle of Churubusco as negotiations broke down, as it became clear that Antonio López de Santa Anna was prepa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Churubusco
The Battle of Churubusco took place on August 20, 1847, while Santa Anna's army was in retreat from the Battle of Contreras or Battle of Padierna during the Mexican–American War. It was the battle where the San Patricio Battalion, made up largely of US deserters, made their last stand against U.S. forces. The U.S. Army was victorious, outnumbering more than six-to-one the defending Mexican troops. After the battle, the U.S. Army was only 5 miles (8 km) away from Mexico City. 50 Saint Patrick's Battalion members were officially executed by the U.S. Army, all but two by hanging. Collectively, this was the largest mass execution in United States history. Background Following their defeats at Contreras, Antonio López de Santa Anna ordered Major General Nicolás Bravo Rueda with the Army of the Center, to retreat from San Antonio to Churubusco.Bauer, K.J., 1974, ''The Mexican War, 1846-1848'', New York:Macmillan, Santa Anna also ordered Major General Manuel Rincón t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Contreras
The Battle of Contreras, also known as the Battle of Padierna, took place on 19–20 August 1847, in one of the final encounters of the Mexican–American War, as invading U.S. forces under Winfield Scott approached the Mexican capital. American forces surprised and then routed the Mexican forces of General Gabriel Valencia, who had disobeyed General Antonio López de Santa Anna's orders for his forces' placement. Although the battle was an overwhelming victory for U.S. forces, there are few depictions of it in contemporary popular prints. The armies re-engaged the next day in the Battle of Churubusco. Background General Gabriel Valencia's army of the north was part of the forces that fought at the Battle of Buena Vista in February 1847, in which Santa Anna retreated before giving a crushing blow to the forces of Zachary Taylor. The Mexican forces were then divided in two, with one sent to Cerro Gordo and the other to San Luis Potosí. General Valencia was given the command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mexican–American War
The Mexican–American War (Spanish language, Spanish: ''guerra de Estados Unidos-México, guerra mexicano-estadounidense''), also known in the United States as the Mexican War, and in Mexico as the United States intervention in Mexico, (April 25, 1846 – February 2, 1848) was an invasion of Second Federal Republic of Mexico, Mexico by the United States Army. It followed the 1845 American annexation of Texas, which Mexico still considered its territory because it refused to recognize the Treaties of Velasco, signed by President Antonio López de Santa Anna after he was captured by the Texian Army during the 1836 Texas Revolution. The Republic of Texas was ''de facto'' an independent country, but most of its Anglo-American citizens who had moved from the United States to Texas after 1822 wanted to be annexed by the United States. Sectional politics over slavery in the United States had previously prevented annexation because Texas would have been admitted as a slave state ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier General (United States)
In the United States Armed Forces, a brigadier general is a one-star general officer in the United States Army, Marine Corps, Air Force, and Space Force. A brigadier general ranks above a colonel and below a Major general (United States), major general. The U.S. uniformed services pay grades, pay grade of brigadier general is O-7. It is equivalent to the rank of Rear admiral (United States)#Rear admiral (lower half), rear admiral (lower half) in the other United States Uniformed services of the United States, uniformed services which use Naval officer ranks, naval ranks. It is abbreviated as BG in the Army, BGen in the Marine Corps, and Brig Gen in the Air Force and Space Force. The Civil Air Patrol also uses this grade for its National Vice Commander and some past National commanders. History The rank of brigadier general has existed in the U.S. military since the inception of the Continental Army in June 1775. To prevent mistakes in recognizing officers, a general ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonel (United States)
A colonel () in the United States Army, United States Marine Corps, Marine Corps, United States Air Force, Air Force and United States Space Force, Space Force, is the most senior field officer, field-grade United States Military, military Officer (armed forces), officer military rank, rank, immediately above the rank of Lieutenant colonel (United States), lieutenant colonel and just below the rank of Brigadier general (United States), brigadier general. Colonel is equivalent to the naval rank of Captain (United States O-6), captain in the other Uniformed services of the United States, uniformed services. By law, an officer previously required at least 22 years of cumulative service and a minimum of three years as a lieutenant colonel before being promoted to colonel. With the signing of the National Defense Authorization Act of 2019 (NDAA 2019), military services now have the authorization to directly commission new officers up to the rank of colonel. The U.S. uniformed service ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the primary Land warfare, land service branch of the United States Department of Defense. It is designated as the Army of the United States in the United States Constitution.Article II, section 2, clause 1 of the United States Constitution (1789).See alsTitle 10, Subtitle B, Chapter 301, Section 3001 It operates under the authority, direction, and control of the United States Secretary of Defense, United States secretary of defense. It is one of the six armed forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. The Army is the most senior branch in order of precedence amongst the armed services. It has its roots in the Continental Army, formed on 14 June 1775 to fight against the British for independence during the American Revolutionary War (1775–1783). After the Revolutionary War, the Congress of the Confederation created the United States Army on 3 June 1784 to replace the disbanded Continental Army.Library of CongressJournals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Hampshire Militia
The New Hampshire Militia was a militia of what is now the U.S. state of New Hampshire. First organized in 1631, it was redesignated as the New Hampshire National Guard in 1879. History The Militia was first organized within the Province of New Hampshire, a colony of the Kingdom of England, in 1631. That instance of the militia lasted until 1641, when the area came under the jurisdiction of the Massachusetts Bay Colony. After New Hampshire became an separate colony again in 1679, Provincial Governor John Cutt reorganized the militia on March 16, 1680, with one foot-company apiece for the four major settlements in Portsmouth, Dover, Exeter, and Hampton, and an artillery and cavalry company in Portsmouth.Gabriele Esposito, ''Armies of Early Colonial North America'', 1607–1713 ''History, Organization and Uniforms'' (Pen & Sword Books, 2018) The King of England authorized the Provincial Governor to give commissions to persons who shall be best qualified for regulating and disc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northampton Law School
Northampton Law School, sometimes called the Howe and Mills Law School, was a school for legal education and was located in Northampton, Massachusetts. Though open for only a few years in the 1820s, it produced a few prominent alumni, including President Franklin Pierce. History In 1823 Judge Samuel Howe (1785–1828) opened a law school in Northampton which was modeled on his alma mater, the Litchfield Law School. Howe operated the school from his law offices with the assistance of his partner Elijah H. Mills. In addition, Howe also enlisted the aid of local lawyer John H. Ashmun (the son of United States Senator Eli Porter Ashmun and brother of Congressman George Ashmun). The school continued with Howe in the lead role until his death in 1828. When Mills decided to curtail his participation, Ashmun took on leadership of the school. In 1829 Ashmun was appointed to a professorship at Harvard Law School. As a result, he closed the Northampton Law School, with many of his st ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |