|
Bengali Group Of Languages
The Bengali Group of languages also known as, Gauda-Banga languages or Gaudic languages, are a linguistic grouping or continuum of dialects spoken in the greater Bengal region and it's divided from Bengali-Assamese language branch of Eastern Indo-Aryan languages. It's comprising Bengali and those languages and dialects closer to it. Most of them are descended from Gaudi Prakrit. The languages in this group are Bengali, Bishnupriya, Chakma, Chittagonian, Kharia Thar, Kurmukar, Mal Paharia, Noakhali, Rohingya, Sylheti,"Along the linguistic continuum of eastern Indic languages, Sylheti occupies an ambiguous position, where it is considered a distinct language by many and also as a dialect of Bengali or Bangla by some others." "At the geographical extremes, Chittagonian, Sylheti, Mal Paharia, and Rohingya are so unintelligible to speakers of other dialects that they are almost universally considered by linguists to be separate languages on their own." Tangchangya, Goal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh
Bangladesh, officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by population, eighth-most populous country in the world and among the List of countries and dependencies by population density, most densely populated with a population of over 171 million within an area of . Bangladesh shares land borders with India to the north, west, and east, and Myanmar to the southeast. It has a coastline along the Bay of Bengal to its south and is separated from Bhutan and Nepal by the Siliguri Corridor, and from China by the List of Indian states, Indian state of Sikkim to its north. Dhaka, the capital and list of cities and towns in Bangladesh, largest city, is the nation's political, financial, and cultural centre. Chittagong is the second-largest city and the busiest port of the country. The territory of modern Bangladesh was a stronghold of many List of Buddhist kingdoms and empires, Buddhist and List of Hindu empir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kharia Thar Language
Kharia Thar is an Indic language spoken by the Hill Kharia culture of India. References External linksKharia.in Eastern Indo-Aryan languages Languages of India {{IndoAryan-lang-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of The Bengali Language
Bengali, also known by its endonym Bangla (, , ), is an Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Indo-Iranian branch of the Indo-European language family. It is native to the Bengal region (Bangladesh, India's West Bengal and Tripura) of South Asia. With over 242 million native speakers and another 43 million as second language speakers as of 2025, Bengali is the sixth most spoken native language and the seventh most spoken language by the total number of speakers in the world. Bengali is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh, with 98% of Bangladeshis using Bengali as their first language. It is the second-most widely spoken language in India. It is the official language of the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and the Barak Valley region of the state of Assam. It is also the second official language of the Indian state of Jharkhand since September 2011. It is the most widely spoken language in the Andaman and Nicobar Islands in the Bay of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
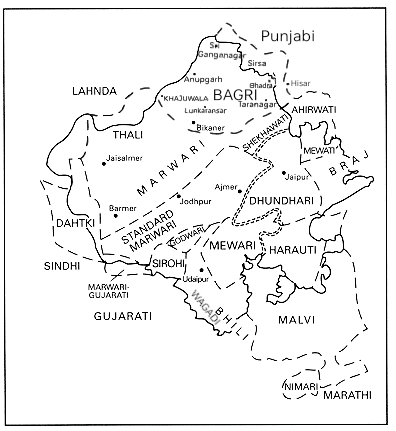
Rajasthani Languages
The Rajasthani languages are a group of Western Indo-Aryan languages, primarily spoken in Rajasthan and Malwa, and adjacent areas of Haryana, Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh in India and South Punjab and the adjacent areas of Sindh in Pakistan. They have also reached different corners of India, especially eastern and southern parts of India, due to the migrations of people of the Marwari community who use them for internal communication. Rajasthani languages are also spoken to a lesser extent in Nepal, where they are spoken by 25,394 people according to the 2011 Census of Nepal. The term Rajasthani is also used to refer to a literary language mostly based on Marwari.. Geographical distribution Most of the Rajasthani languages are chiefly spoken in the state of Rajasthan but are also spoken in Gujarat, Western Madhya Pradesh i.e. Malwa and Nimar, Haryana and Punjab. Rajasthani languages are also spoken in the Bahawalpur and Multan sectors of the Pakistani provinces of Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindhi Languages
The Sindhi languages or Sindhic include Sindhi and its dialects as well as Indo-Aryan languages closely related to it. Lasi and Sindhi Bhil are sometimes added, but are commonly considered dialects of Sindhi proper. It is not clear if Jandavra is Sindhi or Gujarati. Though Dhatki is a Rajasthani language, it is heavily influenced by Sindhi and Kutchi. Khetrani shares grammatical features with both Sindhi and Saraiki but is not mutually intelligible with either. See also * Sindhi language * Gujarati languages * Punjabi dialects The Punjabi dialects and languages or Greater Panjabic are a series of dialects and Indo-Aryan languages spoken around the Punjab region of Pakistan and India with varying degrees of official recognition. They have sometimes been referred to ... Notes References {{Indo-Aryan languages Sindhi language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gujarati Languages
The Gujarati languages are a Western Indo-Aryan language family, comprising Gujarati and those Indic languages closest to it. They are ultimately descended from Shauraseni Prakrit. It is the official language of Gujarat Gujarat () is a States of India, state along the Western India, western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the List of states and union territories ... state as well as Diu, Daman and Dadra and Nagar Haveli. It is the sixth most spoken language in India with more than 55 million speakers. Numerous Gujarati languages are transitional between Gujarati and Sindhi. The precise relationship, if any exists, between Vaghri, the Bhil languages, Wagdi, Rajasthani, and Bagri, has not been presently elucidated. Notes References {{IndoAryan-lang-stub * Western Indo-Aryan languages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surjapuri Language
Surjapuri is an Indo-Aryan language of the Bengali-Assamese branch, spoken in Eastern India including some eastern parts of Purnia division of Bihar, parts of Uttar Dinajpur district in West Bengal and Goalpara Division of Assam in India, as well as Jhapa district in Nepal and Thakurgaon district in Bangladesh. Among speakers in some regions, it is known as 'Deshi Bhasa'. It possesses similarities with Kamatapuri, Assamese, Bengali, and Maithili. Geographical distribution Surjapuri is mainly spoken in some parts of Purnia division ( Kishanganj, Katihar, Purnia, and Araria districts) of Bihar. It is also spoken in West Bengal (some parts of Islampur subdivision of Uttar Dinajpur district and Jalpaiguri division in northern Bengal region), Bangladesh ( Thakurgaon District) as well as in parts of eastern Nepal Nepal, officially the Federal Democratic Republic of Nepal, is a landlocked country in South Asia. It is mainly situated in the Himalayas, but also i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Goalpariya Dialects
Goalpariya is a group of Indo-Aryan dialects spoken in the Goalpara region of Assam, India. Along with Kamrupi, they form the western group of Assamese dialects. The North Bengali dialect is situated to its west, amidst a number of Tibeto-Burman speech communities. The basic characteristic of the Goalpariya is that it is a composite one into which words of different concerns and regions have been amalgamated. Deshi people speak this language and there are around 20 lakhs people. History The Eastern Magadhi Prakrit gave rise to four historical dialects—Radhi, Varendri, Kamarupi and Vanga. The Kamarupi dialect gave rise to Indo-Aryan speeches of Brahmaputra valley, including Goalpariya, and the KRNB lects spoken outside Assam. Dialects There are three identified dialects in this group: (1) Eastern, (2) Western and (3) Intermediate. Scholars from Assam associate these dialects with the Assamese language, Chatterji (1926) classifies Western Goalpariya with the North Benga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangchangya Language
The Tanchangya language is one of the eleven indigenous languages spoken in the Chittagong Hill Tracts, Mizoram, Tripura, and Rakhine State. Despite the common belief that it is a Tibeto-Burman language, it is categorized as a Indo-Aryan language. It is closely related to Chakma and Chittagonian. It is primarily spoken by the Tanchangyas people. Vocabulary Tanchangya has many words from Indo-Aryan languages The Indo-Aryan languages, or sometimes Indic languages, are a branch of the Indo-Iranian languages in the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family. As of 2024, there are more than 1.5 billion speakers, primarily concentrated east .... It also maintains some Burmanised words, particularly in Buddhist terminologies. Ancient Tanchangya The original words of Tanchangya are believed to be from ancient Tanchangya.Roti Kanta Tanchangya (2000): 62-65 Tibeto-Burman Tanchangay belongs to the Tibeto-Burman language family; hence, many Buddhist terms can be fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sylheti Language
Sylheti (Sylheti Nagri: , ''síloṭi'', ; , ''sileṭi'', ) is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language spoken by an estimated 11 million people, primarily in the Sylhet Division of Bangladesh, Barak Valley of Assam, and northern parts of Tripura in India."Sylheti is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by about 11 million people in India and Bangladesh (Hammarström et al., 2017). Sylheti is an Eastern Indo-Aryan language, primarily spoken in the Sylhet division of Bangladesh, and in Barak valley, in Assam of the India and in the northern parts of the state of Tripura in India." Besides, there are substantial numbers of Sylheti speakers in the Indian states of Meghalaya, Manipur, and Nagaland as well as diaspora communities in the United Kingdom, the United States, Canada and the Middle East. It is variously perceived as either a Bengali dialects, dialect of Bengali or a language in its own right. While most linguists consider it an independent language,"Along the linguistic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rohingya Language
Rohingya (; Hanifi Rohingya: , ,, ) is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by the Rohingya people living in Rakhine State, Myanmar and Chittagong Division of Bangladesh. It is an Eastern Indo-Aryan language belonging to the Bengali–Assamese branch, and is closely related to the Chittagonian language spoken in neighbouring Bangladesh. The Rohingya and Chittagonian languages have a high degree of mutual intelligibility. Phonology Consonants Rohingya has primarily the following 25 native consonant phonemes. There are some other consonant phonemes which are from foreign languages such as Arabic, Bengali, Burmese and Urdu. * A dental fricative may also be heard in words of Arabic origin. * is only used in words of foreign origin. * is heard as when preceding . * Allophones of can be heard as . Vowels * Short allophones of are heard as , . Allophones of are heard as . There are six vowels and several diphthongs in the Rohingya language. They contrast between " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noakhali Language
Noakhali or Noakhalian, endonym ''Noakhailla'' (), is an Indo-Aryan language spoken by an estimated 7 million people, primarily in the Greater Noakhali region of Bangladesh, as well as in southern parts of Tripura in India. Outside of these regions, there are substantial numbers of Noakhali speakers in other parts of Bangladesh and a diaspora population in the Middle East, Europe and the United States. Noakhali has no presence in formal settings, neither in Bangladesh nor India, though its standardisation has been proposed. Etymology Noakhailla is eponymously named after the district of Noakhali. It is in the transformed Vangiya form of the archaic Noakhaliya (), where "''-iya''" is a suffix, commonly used in Bengali as a demonym, having gone through a linguistic process called Apinihiti (), a form of epenthesis, to become Noakhailla (). It may also be known in English as Noakhalian, a relatively recent term which has gained prominence as a locative demonym since at the least th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |