|
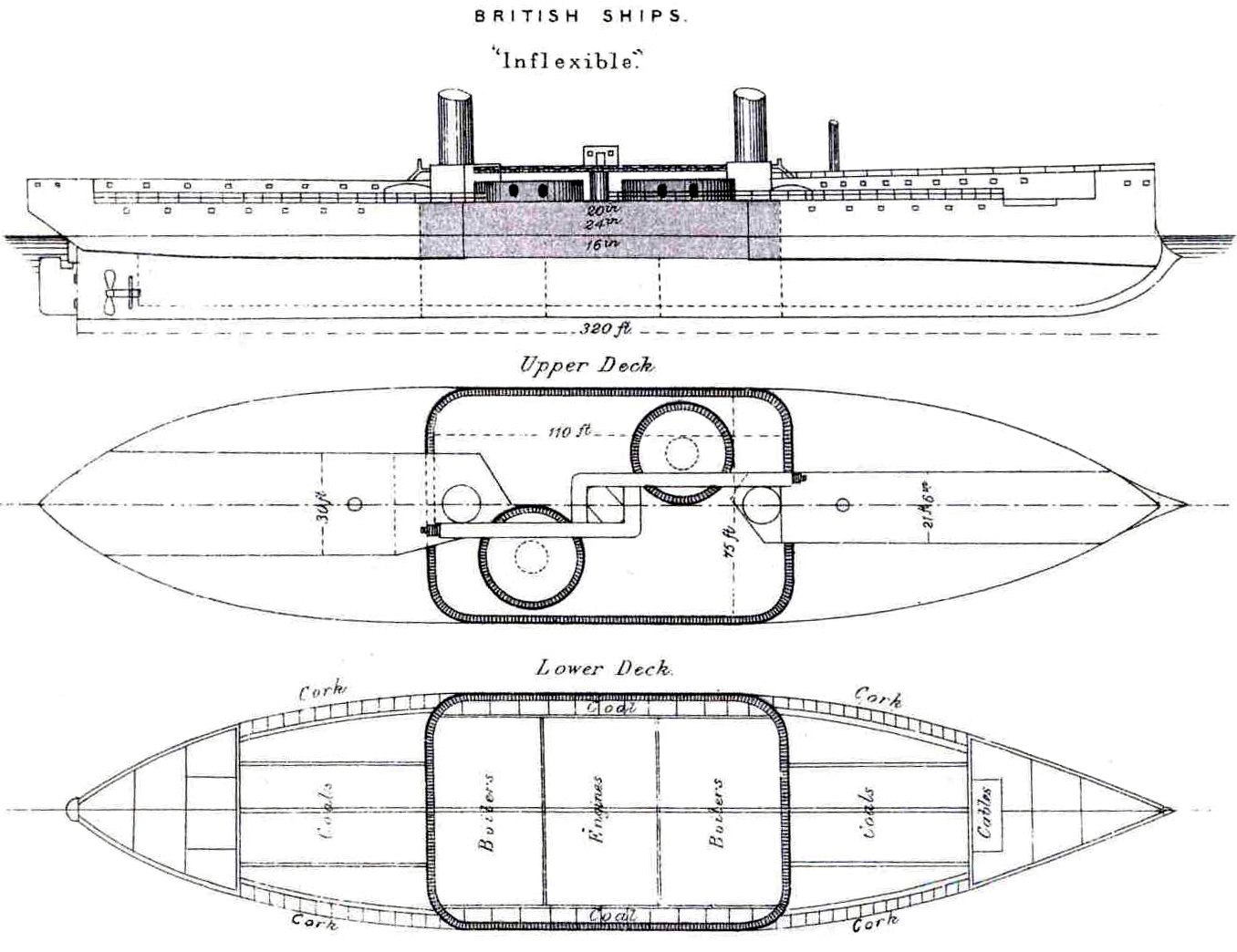
Belt Armor
Belt armor is a layer of heavy metal armor plated onto or within the outer hulls of warships, typically on battleships, battlecruisers and cruisers, and aircraft carriers. The belt armor is designed to prevent projectiles from penetrating to the heart of a warship. When struck by an artillery shell or underwater torpedo, the belt armor either absorbs the impact and explosion with its sheer thickness and strength, or else uses sloping to redirect the projectile and its blast downwards. Typically, the main armor belt covers the warship from its main deck down to some distance below the waterline. If, instead of forming the outer hull, the armor belt is built inside the hull, it is installed at a sloped angle for improved protection, as described above. The torpedo bulkhead Frequently, the main belt's armor plates were supplemented with a torpedo bulkhead spaced several meters behind the main belt, designed to maintain the ship's watertight integrity even if the main belt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WWI Style Ship Armor
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Bulkhead
A torpedo bulkhead is a type of naval armor common on the more heavily armored warships, especially battleships and battlecruisers of the early 20th century. It is designed to keep the ship afloat even if the hull is struck underneath the belt armor by a shell or by a torpedo. History As early torpedoes had demonstrated their effectiveness at seriously damaging ships below the waterline by the 1880s, naval designers began developing methods to better protect ships against the new weapons. The earliest protection scheme was devised by Sir Edward Reed in 1884; he proposed a double bottom that included an armored inner hull lining that connected to the bottom edges of the belt armor. It was not adopted, as it imposed serious limitations on internal space and reduced the thickness of the belt. Subsequent, early attempts relied primarily on the coal bunkers, on the assumption that the ship's coal would absorb the blast effects, which would be contained by the interior longitudin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protected Cruiser
Protected cruisers, a type of cruiser of the late 19th century, took their name from the armored deck, which protected vital machine-spaces from fragments released by explosive shells. Protected cruisers notably lacked a belt of armour along the sides, in contrast to armored cruisers which carried both deck and belt armour. Outside of a handful of very large designs in the major navies (which preceded the revival of armored cruisers), the majority of protected cruisers were of 'second-' or 'third-class' types, lighter in displacement and mounting fewer and/or lighter guns than armored cruisers. By the early 20th-century, with the advent of increasingly lighter yet stronger armour, even smaller vessels could afford some level of both belt and deck armour. In the place of protected cruisers, these new ' light armored cruisers' would evolve into light cruisers and heavy cruisers, the former especially taking on many of the roles originally envisioned for protected cruisers. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Torpedo Belt
The torpedo belt was part of the armoring scheme in some warships between the 1920s and 1940s. It consisted of a series of lightly armored compartments, extending laterally along a narrow belt that intersected the ship's waterline. In theory this belt would absorb the explosions from torpedoes, or any naval artillery shells that struck below the waterline, and thus minimize internal damage to the ship itself. Torpedo belts are also known as Side Protection Systems or SPS, or Torpedo Defense System or TDS. Background: insufficiency of belt armor Armored warships (pre-dreadnought battleships, armored cruisers, dreadnought battleships, battlecruisers, and later light and heavy cruisers) of the early 20th century carried their main protective armor above the waterline – the " main belt" – which was intended to stop flat-trajectory gunfire from piercing the hull. Below the belt, the armor generally tapered away, to reduce overall weight. This, however, makes a ship v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armored Flight Deck
An armoured flight deck is an aircraft carrier flight deck that incorporates substantial armour in its design. Comparison is often made between the carrier designs of the Royal Navy (RN) and the United States Navy (USN). The two navies followed differing philosophies in the use of armour on carrier flight decks, starting with the design of the RN's and ending with the design of the , when the USN also adopted armoured flight decks. The two classes most easily compared are the RN's ''Illustrious'' class and and their nearest USN contemporaries, the and es. The ''Illustrious'' class followed the ''Yorktown'' but preceded the ''Essex'', while the ''Implacable''-class design predated the ''Essex'' but these ships were completed after the lead ships of the ''Essex'' class. The development of armoured flight deck carriers proceeded during World War II, and before the end of World War II both the USN, with , and the Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN), with and would also commission armour ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sister Ship
A sister ship is a ship of the same Ship class, class or of virtually identical design to another ship. Such vessels share a nearly identical hull and superstructure layout, similar size, and roughly comparable features and equipment. They often share a common naming theme, either being named after the same type of thing or person (places, constellations, heads of state) or with some kind of alliteration. Typically the ship class is named for the first ship of that class. Often, sisters become more differentiated during their service as their equipment (in the case of naval vessels, their armament) are separately altered. For instance, the U.S. warships , , , and are all sister ships, each being an . Perhaps the most famous sister ships were the White Star Line's s trio, consisting of , and . As with some other liners, the sisters worked as running mates. Of the three sister ships, ''Titanic'' and ''Britannic'' would both sink within a year of being launched, while RMS ''O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
All Or Nothing (armor)
All or nothing is a method of naval warship armor, best known for its employment on dreadnought battleships. The concept involves heavily armoring the areas most important to a ship while the rest of the ship receives no armor. The "all or nothing" concept avoided light or moderate thicknesses of armor: armor was used in the greatest practicable thickness or not at all, thereby providing "either total or negligible protection". Compared to previous armoring systems, "all or nothing" ships had thicker armor covering a smaller proportion of the hull. The ironclad battleship launched in 1876 had featured a heavily armored central citadel, with relatively unarmored ends; however, by the era of , battleships were armored over the length of the ship with varying zones of heavy, moderate or light armor. The U.S. Navy adopted what was formally called "all or nothing" armor in the Standard-type battleships, starting with the laid down in 1912. The Imperial Japanese Navy soon impleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Buoyancy
Buoyancy (), or upthrust, is the force exerted by a fluid opposing the weight of a partially or fully immersed object (which may be also be a parcel of fluid). In a column of fluid, pressure increases with depth as a result of the weight of the overlying fluid. Thus, the pressure at the bottom of a column of fluid is greater than at the top of the column. Similarly, the pressure at the bottom of an object submerged in a fluid is greater than at the top of the object. The pressure difference results in a net upward force on the object. The magnitude of the force is proportional to the pressure difference, and (as explained by Archimedes' principle) is equivalent to the weight of the fluid that would otherwise occupy the submerged volume of the object, i.e. the Displacement (fluid), displaced fluid. For this reason, an object with average density greater than the surrounding fluid tends to sink because its weight is greater than the weight of the fluid it displaces. If the objec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armor-piercing Shell
Armour-piercing ammunition (AP) is a type of projectile designed to penetrate armour protection, most often including naval armour, body armour, and vehicle armour. The first, major application of armour-piercing projectiles was to defeat the thick armour carried on many warships and cause damage to their lightly armoured interiors. From the 1920s onwards, armour-piercing weapons were required for anti-tank warfare. AP rounds smaller than 20 mm are intended for lightly armoured targets such as body armour, bulletproof glass, and lightly armoured vehicles. As tank armour improved during World War II, anti-vehicle rounds began to use a smaller but dense penetrating body within a larger shell, firing at a very-high muzzle velocity. Modern penetrators are long rods of dense material like tungsten or depleted uranium (DU) that further improve the terminal ballistics. Penetration In the context of weaponry, ''penetration'' is the ability of a weapon or projectile to pierc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Naval Artillery
Naval artillery is artillery mounted on a warship, originally used only for naval warfare and then subsequently used for more specialized roles in surface warfare such as naval gunfire support (NGFS) and anti-aircraft warfare (AAW) engagements. The term generally refers to powder-launched projectile-firing weapons and excludes self-propelled projectiles such as torpedoes, rockets, and missiles and those simply dropped overboard such as depth charges and naval mines. Origins The idea of ship-borne artillery dates back to the classical era. Julius Caesar wrote about the Roman navy's usage of ship-borne catapults against Celtic Britons ashore in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico''. The dromons of the Byzantine Empire carried catapults and Greek fire. From the Middle Ages onwards, warships began to carry cannons of various calibres. In the Battle of Tangdao in 1161, the Southern Song general Li Bao used huopao (a type of gunpowder weapons, possibly cannons) and fire arro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King George V-class Battleship (1939)
The ''King George V''-class battleships were the most modern British battleships in commission during the World War II, Second World War. Five ships of this class were built: HMS King George V (41), HMS ''King George V'' (commissioned 1940), HMS Prince of Wales (53), HMS ''Prince of Wales'' (1941), HMS Duke of York (17), HMS ''Duke of York'' (1941), HMS Anson (79), HMS ''Anson'' (1942) and HMS Howe (32), HMS ''Howe'' (1942). The names honoured King George V, and his sons, Edward VIII, who had been Prince of Wales, and George VI who was Duke of York before ascending to the throne; the final two ships of the class were named after prominent 18th century admirals of the Royal Navy. The Washington Naval Treaty of 1922 limited all of the number, displacement (ship), displacement, and armament of warships built following its ratification, and this was extended by the First London Naval Treaty but these treaties were due to expire in 1936. With increased tensio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
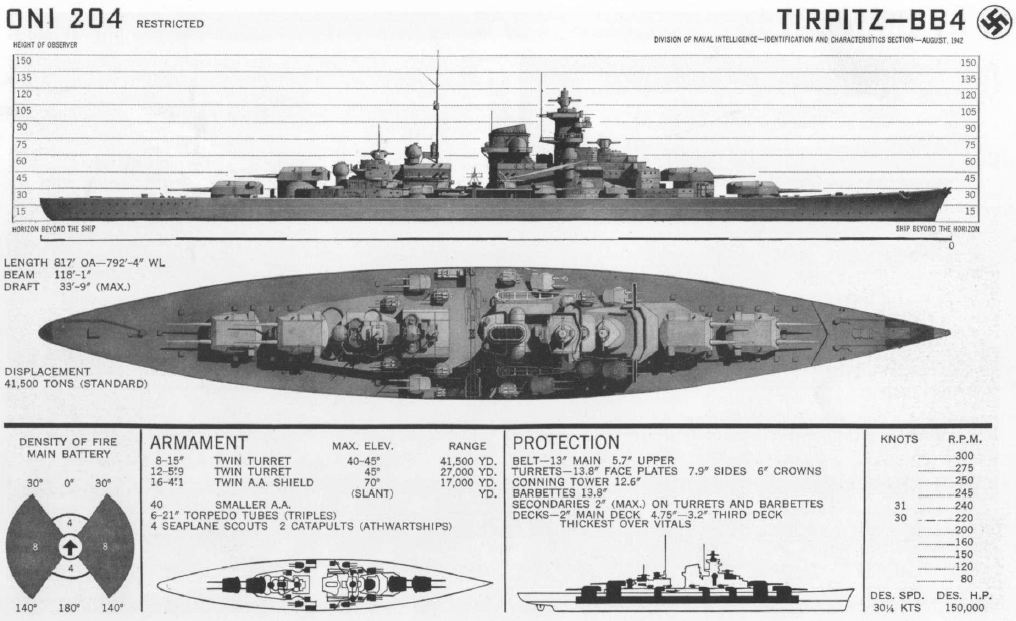
German Battleship Tirpitz
() was the second of two s built for Nazi Germany's (navy) prior to and during the Second World War. Named after Grand Admiral Alfred von Tirpitz, the architect of the (Imperial Navy), the ship was laid down at the in Wilhelmshaven in November 1936 and her Hull (watercraft), hull was launched two and a half years later. Work was completed in February 1941, when she was commissioned into the German fleet. Like her sister ship, , was armed with a main battery of eight 38 cm SK C/34 naval gun, guns in four twin Gun turret, turrets. After a series of wartime modifications she was 2000 tonnes heavier than , making her the heaviest battleship ever built by a European navy. After completing sea trials in early 1941, briefly served as the centrepiece of the Baltic Fleet, which was intended to prevent a possible break-out attempt by the Soviet Baltic Fleet#Great Patriotic War, Soviet Baltic Fleet. In early 1942, the ship sailed to Norway to act as a deterrent against an Allied in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |