|
Bellagio (Italian Region)
Bellagio (; ) is a ''comune'' (municipality) in the Province of Como in the Lombardy region of Italy. It is situated on Lake Como, known also by its Latin name ''Lario'', where the lake's two southern arms branch, creating the ''Triangolo lariano''. Bellagio's location at the tip of this promontory, looking out across the lake's northern arm towards the Alps, has long been noted for its scenic beauty. Bellagio is part of the ''Triangolo Lariano, Comunità montana del Triangolo lariano'', headquartered in Canzo. History Early history Traces of human presence around Bellagio date back to the Paleolithic period, approximately 30,000 years ago. Around the 7th to 5th centuries BC, a ''castellum'' (fortified hilltop settlement) may have existed on the promontory, potentially serving as a place of worship and trade for the scattered villages around the lake. From around 400 BC, the Insubres, a Celtic tribe, are identified as the first inhabitants of the Bellagio area. They occup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lombardy
The Lombardy Region (; ) is an administrative regions of Italy, region of Italy that covers ; it is located in northern Italy and has a population of about 10 million people, constituting more than one-sixth of Italy's population. Lombardy is located between the Alps mountain range and tributaries of the river Po (river), Po, and includes Milan, its capital, the largest metropolitan area in the country, and among the largest in the EU. Its territory is divided into 1,502 ''comuni'' (the region with the largest number of ''comuni'' in the entire national territory), distributed among twelve administrative subdivisions (eleven Provinces of Italy, provinces plus the Metropolitan City of Milan). The region ranks first in Italy in terms of population, population density, and number of local authorities, while it is fourth in terms of surface area, after Sicily, Piedmont, and Sardinia. It is the second-most populous Region (Europe), region of the European Union (EU), and the List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauls
The Gauls (; , ''Galátai'') were a group of Celts, Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age Europe, Iron Age and the Roman Gaul, Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They spoke Gaulish, a continental Celtic language. The Gauls emerged around the 5th century BC as bearers of La Tène culture north and west of the Alps. By the 4th century BC, they were spread over much of what is now France, Belgium, Switzerland, Southern Germany, Austria, and the Czech Republic, by virtue of controlling the trade routes along the river systems of the Rhône, Seine, Rhine, and Danube. They reached the peak of their power in the 3rd century BC. During the 4th and 3rd centuries BC, the Gauls expanded into Northern Italy (Cisalpine Gaul), leading to the Roman–Gallic wars, and Gallic invasion of the Balkans, into the Balkans, leading to Battle of Thermopylae (279 BC), war with the Greeks. These latter Gauls eventually settle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of The Teutoburg Forest
The Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, also called the Varus Disaster or Varian Disaster () by Ancient Rome, Roman historians, was a major battle fought between an alliance of Germanic peoples and the Roman Empire between September 8 and 11, 9 AD, near modern Kalkriese. Fighting began with an ambush by the Germanic alliance on three Roman legions being led by Publius Quinctilius Varus and their auxiliaries; the alliance was led by Arminius, a Germanic chieftain and officer of Varus's auxilia. Arminius had received Roman citizenship and a Roman Military education and training, military education, thus allowing him to deceive the Romans methodically and anticipate their tactical responses. Teutoburg Forest is considered one of the most important defeats in Roman history, bringing the triumphant period of expansion under Augustus to an abrupt end. It dissuaded the Romans from pursuing the conquest of Germania, and so can be considered one of the most important events in European ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Quinctilius Varus
Publius Quinctilius Varus (46 BC or before – September AD 9) was a Roman general and politician. Serving under Augustus, who founded the Roman Empire, he is generally remembered for having lost three Roman legions in the Battle of the Teutoburg Forest, during which he committed suicide to avoid Prisoner of war, capture (and inevitable Human sacrifice, execution) and Dignitas (Roman concept), shameful reproach. Varus' defeat to the Germanic tribes led by Arminius is considered to be one of the most important events in European history, as it dissuaded the Romans from further expanding into Germania and thus prevented the Romanization (cultural), Romanization of the Germanic peoples to the east of the Rhine. Early life and family Although he was a Patrician (ancient Rome), patrician by birth, his family, the Quinctilii Vari, had long been impoverished and was unimportant; Ronald Syme notes, "The sole and last consul of that family", Sextus Quinctilius, "had been two years antec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
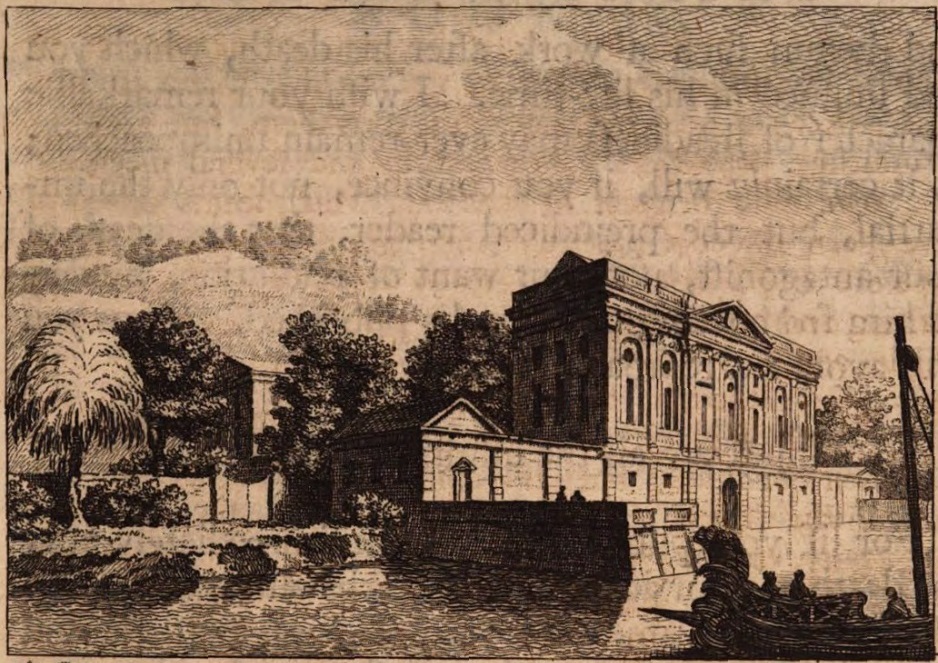
Pliny's Comedy And Tragedy Villas
Pliny's Comedy and Tragedy villas were two of the several villas owned by Pliny the Younger during the 1st century in the area surrounding Lake Como in northern Italy. In one of Pliny's letters to his boyhood friend Voconius Romanus (Book 9, Epistle 7), he named them as his favourites. In his letter, Pliny wrote that the Tragedy villa was atop a ridge above the lake, but the Comedy villa was right on the water's edge and that "each of them has particular beauties; a diversity which renders them to their master as still more agreeable."Orrery, John Boyle, 5th Earl of (1751)''The letters of Pliny the Younger: with observations on each letter'' p. 245. Bettenham According to the letter, Pliny had derived the villas' names from their geographical positions and the conventions of Roman theatre. He saw the Tragedy villa as rising from its setting like an actor wearing the tragedian's high platform boots ('), while the Comedy villa down by the lake wore the lowly comedian's slippers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pliny The Younger
Gaius Plinius Caecilius Secundus (born Gaius Caecilius or Gaius Caecilius Cilo; 61 – ), better known in English as Pliny the Younger ( ), was a lawyer, author, and magistrate of Ancient Rome. Pliny's uncle, Pliny the Elder, helped raise and educate him. Pliny the Younger wrote hundreds of letters, of which 247 survived, and which are of some historical value. These include 121 official memoranda addressed to Emperor Trajan (reigned 98-117). Some are addressed to reigning emperors or to notables such as the historian Tacitus. Pliny served as an imperial magistrate under Trajan, and his letters to Trajan provide one of the few surviving records of the relationship between the imperial office and provincial governors. Pliny rose through a series of civil and military offices, the ''cursus honorum''. He was a friend of the historian Tacitus and might have employed the biographer Suetonius on his staff. Pliny also came into contact with other well-known men of the period, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virgil
Publius Vergilius Maro (; 15 October 70 BC21 September 19 BC), usually called Virgil or Vergil ( ) in English, was an ancient Rome, ancient Roman poet of the Augustan literature (ancient Rome), Augustan period. He composed three of the most famous poems in Latin literature: the ''Eclogues'' (or ''Bucolics''), the ''Georgics'', and the Epic poetry, epic ''Aeneid''. A number of minor poems, collected in the ''Appendix Vergiliana'', were attributed to him in ancient times, but modern scholars generally regard these works as spurious, with the possible exception of a few short pieces. Already acclaimed in his own lifetime as a classic author, Virgil rapidly replaced Ennius and other earlier authors as a standard school text, and stood as the most popular Latin poet through late antiquity, the Middle Ages, and early modernity, exerting inestimable influence on all subsequent Western literature. Geoffrey Chaucer assigned Virgil a uniquely prominent position among all the celebrities ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (12 or 13 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC) was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in Caesar's civil war, a civil war. He subsequently became Roman dictator, dictator from 49 BC until Assassination of Julius Caesar, his assassination in 44 BC. Caesar played a critical role in Crisis of the Roman Republic, the events that led to the demise of the Roman Republic and the rise of the Roman Empire. In 60 BC, Caesar, Marcus Licinius Crassus, Crassus, and Pompey formed the First Triumvirate, an informal political alliance that dominated Roman politics for several years. Their attempts to amass political power were opposed by many in the Roman Senate, Senate, among them Cato the Younger with the private support of Cicero. Caesar rose to become one of the most powerful politicians in the Roman Republic through a string of military victories in the G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus (consul 83 BC)
Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus (fl. 82 BC; also called Scipio Asiagenes) was a great-grandson of Lucius Cornelius Scipio Asiaticus, consul in 190 BC, who was victor of the Battle of Magnesia (189 BC). Scipio Asiaticus, also known as Scipio Asiagenes, was co-consul with Gaius Norbanus in 83 BC. This Scipio is first mentioned in 100 BC, when he took up arms with the other members of the senate against Lucius Appuleius Saturninus. In the Social War he was stationed with Lucius Acilius in the town of Aesernia, escaping in the dress of slaves during the approach of Vettius Scato. He belonged to the party of Marius and Carbo during Sulla's civil war. In 83 BC he was appointed consul with Gaius Norbanus. In this year Lucius Cornelius Sulla returned to the Italian Peninsula, and advanced against the consuls. He defeated Norbanus in Italy, and convinced the troops of Scipio to desert their general. He was taken prisoner in his camp along with his son Lucius, but was dismissed by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Splügen Pass
The Splügen Pass (; ; ) is an Alpine mountain pass of the Lepontine Alps. It connects the Swiss, Grisonian Splügen to the north below the pass with the Italian Chiavenna to the south at the end of the Valle San Giacomo below the pass. Geography The pass road connects the Swiss Hinterrhein valley and Splügen in the canton of Graubünden with the Valle San Giacomo and Chiavenna in the Italian province of Sondrio, the road continuing to Lake Como. The pass is the water divide between the drainage basins of the Rhine, which flows into the North Sea, and the Po, which flows into the Adriatic. The pass is overlooked by Pizzo Tambo and the Surettahorn, on its western and eastern side, respectively. On the Italian side of the pass is Montespluga, a small three street village that is cut off from both Italy and Switzerland during the winter. Since the opening of the San Bernardino road tunnel in 1967, the pass has lost its former importance; it is not kept open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raetia
Raetia or Rhaetia ( , ) was a province of the Roman Empire named after the Rhaetian people. It bordered on the west with the country of the Helvetii, on the east with Noricum, on the north with Vindelicia, on the south-west with Transalpine Gaul and on the south with Venetia et Histria, a region of Roman Italy. It thus comprised the districts occupied in modern times by eastern and central Switzerland (containing the Upper Rhine and Lake Constance), southern Germany (Bavaria and most of Baden-Württemberg), Vorarlberg and the greater part of Tyrol in Austria, and part of northern Lombardy in Italy. The region of Vindelicia (today eastern Württemberg and western Bavaria) was annexed to the province at a later date than the others. The northern border of Raetia during the reigns of emperors Augustus and Tiberius was the River Danube. Later the Limes Germanicus marked the northern boundary, stretching for 166 km north of the Danube. Raetia was connected to Italy across t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |