|
Belarusian Patriotic Party
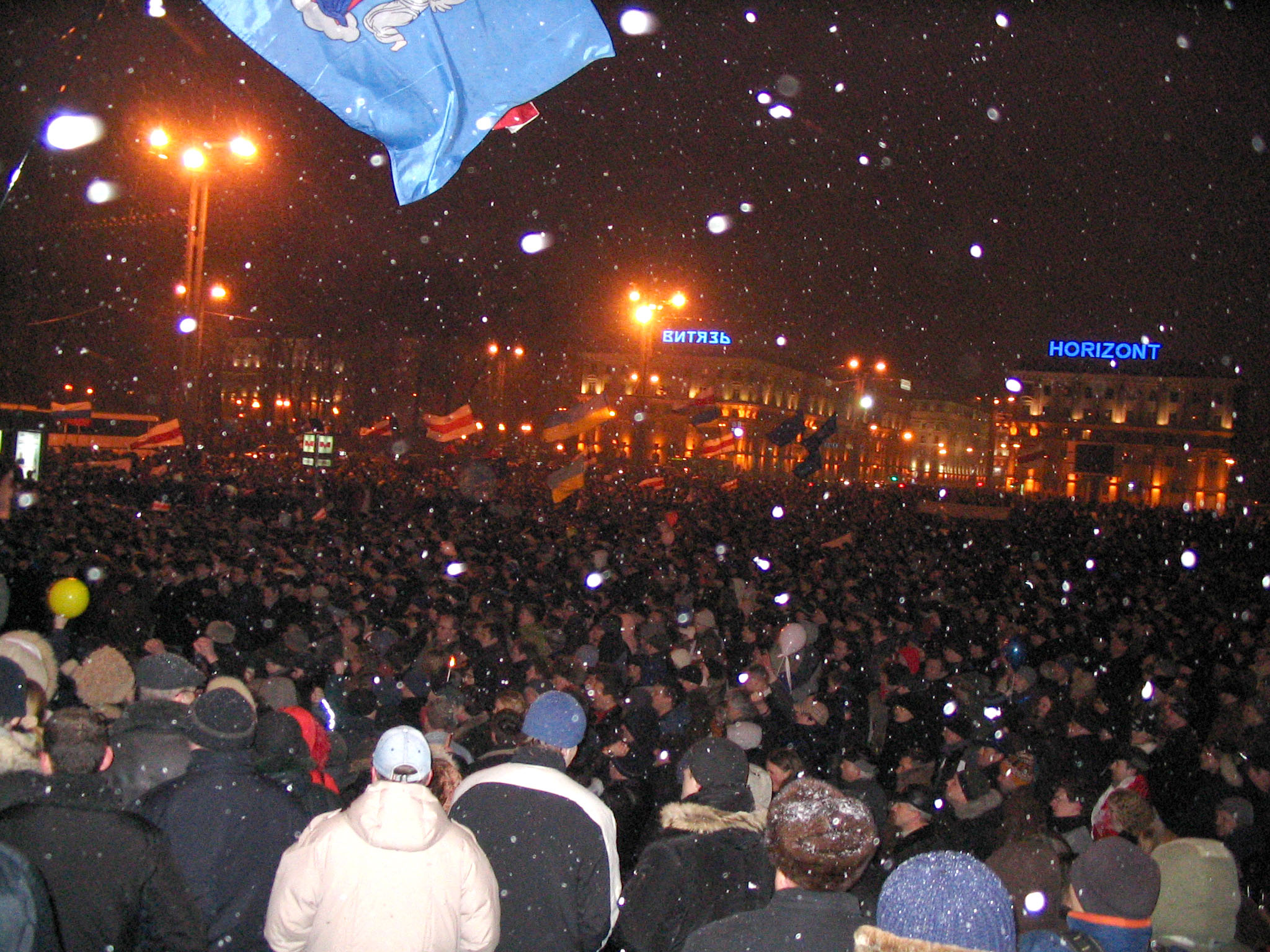
The Belarusian Patriotic Party ( be, Беларуская патрыятычная партыя, Bielaruskaja patryjatyčnaja partyja, BPP) is a political party in Belarus loyal to President Alexander Lukashenko. Nikolai Ulakhovich is party chairman. History The party was established in 1994,Vitali Silitski & Jan Zaprudnik (2010) ''The A to Z of Belarus'', Scarecrow Press, p237 and was initially named the Belarusian Patriotic Movement. The party was originally formed under presidential candidate Alexander Lukashenko. Major General, Honored Pilot of the Soviet Union, Deputy Chairman of the Union of Officers of Belarus Anatoly Barankevich became the leader of the party. BPM won one seat in the second round of voting in the 1995 parliamentary elections. It changed its name to the Belarusian Patriotic Party in 1996. On August 19, 2000, at a congress, the BPP nominated 16 candidates for the parliamentary elections When checking the Telegraph correspondent of the offices of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2000 Belarusian Parliamentary Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Belarus on 15 October 2000, with further rounds of voting on 29 October, 18 March and 1 April. The vast majority of successful candidates, 94 of 110, were independents.Nohlen & Stöver, p261 Voter turnout was reported to be 61.08% in the first round. A total of 566 candidates contested the election, only around fifty of which were opponents of President Alexander Lukashenko. Opposition parties called for a boycott, criticising the government's control of the state media. In response, the Department of Justice stated that anyone calling for a boycott could receive a jail sentence of up to two years, and several activists were detained.Belarus: Elections held in 2000 Inter-Parliamentary Union Although a Russian delegation claimed the elections were free and fair, other international ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2006 Belarusian Presidential Election
Presidential elections were held in Belarus on 19 March 2006. The result was a victory for incumbent, President Alexander Lukashenko, who received 84.4% of the vote. However, Western observers deemed the elections rigged. The Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe (OSCE) declared that the election "failed to meet OSCE commitments for democratic elections". In contrast, election observers from the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) described the vote as open and transparent. Candidates On 17 February 2006, the Central Election Commission approved the following list of candidates: *Alexander Lukashenko: incumbent, in office since 1994, not associated with any party. *Alaksandar Milinkievič: challenger, candidate from an opposition union, United Democratic Forces of Belarus. *Sergei Gaidukevich: Liberal Democratic Party. *Alyaksandr Kazulin: Belarusian Social Democratic Party. Former candidates *Zianon Pazniak: withdrew on 26 January * Valeri Frolov: withdr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2001 Belarusian Presidential Election
Presidential elections were held in Belarus on 9 September 2001. The election should have been held in 1999, but a revised constitution adopted in 1996 extended incumbent Alexander Lukashenko's term for another two years. Lukashenko was re-elected with 77.4% of the vote over two minor candidates. Voter turnout was 84%. A senior official for the Organization for Security and Co-operation in Europe noted that the pre-election environment was "not democratic" and would not describe it as "free and fair". BBC News, 10 September 2001 Results References {{Belarusian elections Presidential elections in Belarus |
1994 Belarusian Presidential Election
Presidential elections were held in Belarus on 23 June 1994, with a second round on 10 July. They were the first national elections held in Belarus since the country seceded from the Soviet Union The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ... three years earlier. The result was a victory for Alexander Lukashenko, who received 80.6% of the vote in the second round. Voter turnout was 79.0% in the first round and 70.6% in the second. In 1995, a year after taking office, Lukashenko won a 1995 Belarusian referendum, referendum that gave him the power to dissolve the legislature. In 1996, he won 1996 Belarusian referendum, another referendum that dramatically increased his power, and also extended his original five-year term to 2001 Belarusian presidential election, 2001. As a res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kastrychnitski District
Kastrychnitski District ( be, Кастрычніцкі раён, Kastryčnicki rajon; russian: Октябрьский район, translit=Oktyabr'skiy rayon) is an administrative subdivision of the city of Minsk, Belarus. It was named after the October Revolution. , Minsk administration website Geography The district is situated in central and south-western area of the city and borders with Leninsky and Maskowski districts.Transport The main railway station[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
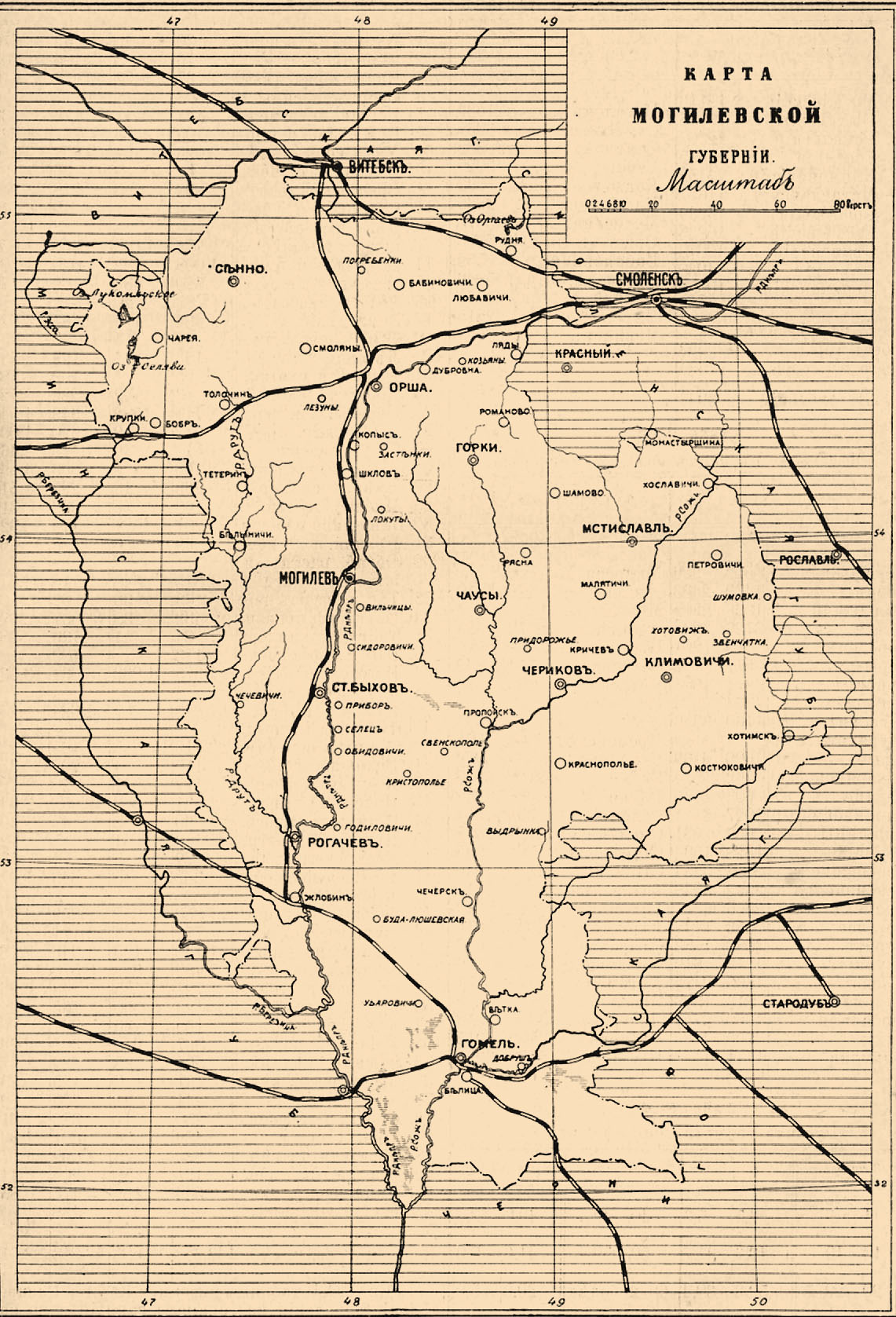
Mogilev
Mogilev (russian: Могилёв, Mogilyov, ; yi, מאָלעוו, Molev, ) or Mahilyow ( be, Магілёў, Mahilioŭ, ) is a city in eastern Belarus, on the Dnieper River, about from the border with Russia's Smolensk Oblast and from the border with Russia's Bryansk Oblast. , its population was 360,918, up from an estimated 106,000 in 1956. It is the administrative centre of Mogilev Region and the third-largest city in Belarus. History The city was first mentioned in historical records in 1267. From the 14th century, it was part of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and since the Union of Lublin (1569), part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, where it became known as ''Mohylew''. In the 16th-17th centuries, the city flourished as one of the main nodes of the east–west and north–south trading routes. In 1577, Polish King Stefan Batory granted it city rights under Magdeburg law. In 1654, the townsmen negotiated a treaty of surrender to the Russians peacefully ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitebsk
Vitebsk or Viciebsk (russian: Витебск, ; be, Ві́цебск, ; , ''Vitebsk'', lt, Vitebskas, pl, Witebsk), is a city in Belarus. The capital of the Vitebsk Region, it has 366,299 inhabitants, making it the country's fourth-largest city. It is served by Vitebsk Vostochny Airport and Vitebsk Air Base. History Before 1945 Vitebsk developed from a river harbor where the Vićba River (Віцьба, from which it derives its name) flows into the larger Western Dvina, which is spanned in the city by the Kirov Bridge. Archaeological research indicates that Baltic tribes had settlements at the mouth of Vitba. In the 9th century, Slavic settlements of the tribal union of the Krivichs replaced them. According to the ''Chronicle of Michael Brigandine'' (1760), Princess Olga of Kiev founded Vitebsk (also recorded as Dbesk, Vidbesk, Videbsk, Vitepesk, or Vicibesk) in 974. Other versions give 947 or 914. Academician Boris Rybakov and historian Leonid Alekseyev have come to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brest, Belarus
Brest ( be, Брэст / Берасьце, Bieraście, ; russian: Брест, ; uk, Берестя, Berestia; lt, Brasta; pl, Brześć; yi, בריסק, Brisk), formerly Brest-Litovsk (russian: Брест-Литовск, lit=Lithuanian Brest; be, links=no, translit=Berastze Litouski (Berastze), Берасце Літоўскі (Берасце); lt, links=no, Lietuvos Brasta; pl, links=no, Brześć Litewski, ), Brest-on-the-Bug ( pl, links=no, Brześć nad Bugiem), is a city (population 350,616 in 2019) in Belarus at the border with Poland opposite the Polish city of Terespol, where the Bug and Mukhavets rivers meet, making it a border town. It is the capital city of the Brest Region. Brest is a historical site for many cultures, as it hosted important historical events, such as the Union of Brest and Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. Furthermore, the Brest Fortress was recognized by the Soviet Union as a Hero Fortress in honour of the defense of Brest Fortress in June 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belovezha Accords
The Belovezh Accords ( be, Белавежскае пагадненне, link=no, russian: Беловежские соглашения, link=no, uk, Біловезькі угоди, link=no) are accords forming the agreement declaring that the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR) had effectively ceased to exist and established the Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) in its place as a successor entity. The documentation was signed at the state dacha near Viskuli in Belovezhskaya Pushcha (Belarus) on 8 December 1991, by leaders of three of the four republics which had signed the 1922 Treaty on the Creation of the USSR: * Belarusian Parliament Chairman Stanislav Shushkevich and Prime Minister of Belarus Vyacheslav Kebich * Russian President Boris Yeltsin and First Deputy Prime Minister of the RSFSR/Russian Federation Gennady Burbulis * Ukrainian President Leonid Kravchuk and Ukrainian Prime Minister Vitold Fokin The original document could not be found as of 2013 (s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belarusian Orthodox Church
The Belarusian Orthodox Church (BOC; be, Беларуская праваслаўная царква, russian: Белорусская православная церковь) is the official name of the Belarusian Exarchate ( be, Беларускі экзархат, russian: Белорусский экзархат) of the Russian Orthodox Church in Belarus. It represents the union of Russian Orthodox eparchies in the territory of the Republic of Belarus and is the largest religious organization in the country, uniting the predominant majority of its Eastern Orthodox Christians. Bishop Beniamin Brikov III (Vitaly Ivanovich Tupieko) became the Patriarchal Exarch of the Belarusian Orthodox Church in 2020. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Democratic Party Of Belarus
The Liberal Democratic Party of Belarus ( be, Ліберальна-дэмакратычная партыя Беларусі, russian: Либерально-демократическая партия Беларуси, Liberal'no-demokraticheskaya partiya Belarusi), or ЛДПБ (LDPB), is a political party in Belarus. It was created in 1994 as the Belarusian successor of the Liberal Democratic Party of the Soviet Union. Despite claiming to be a "constructive and democratic opposition" the party ''de facto'' supports the current president, Alexander Lukashenko (much like the Liberal Democratic Party of Russia with Vladimir Putin). In the legislative elections, 13–17 October 2004, the party won 1 out of 110 seats. Its candidate in the presidential election of 2006, Sergei Gaidukevich, won 3.5% of the vote. Party leader Gaidukevich was a member of the House of Representatives from 2004 to 2008. He was later a member of the Council of the Republic from 2016 to 2019. Ideology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |