|
Beiyang Army
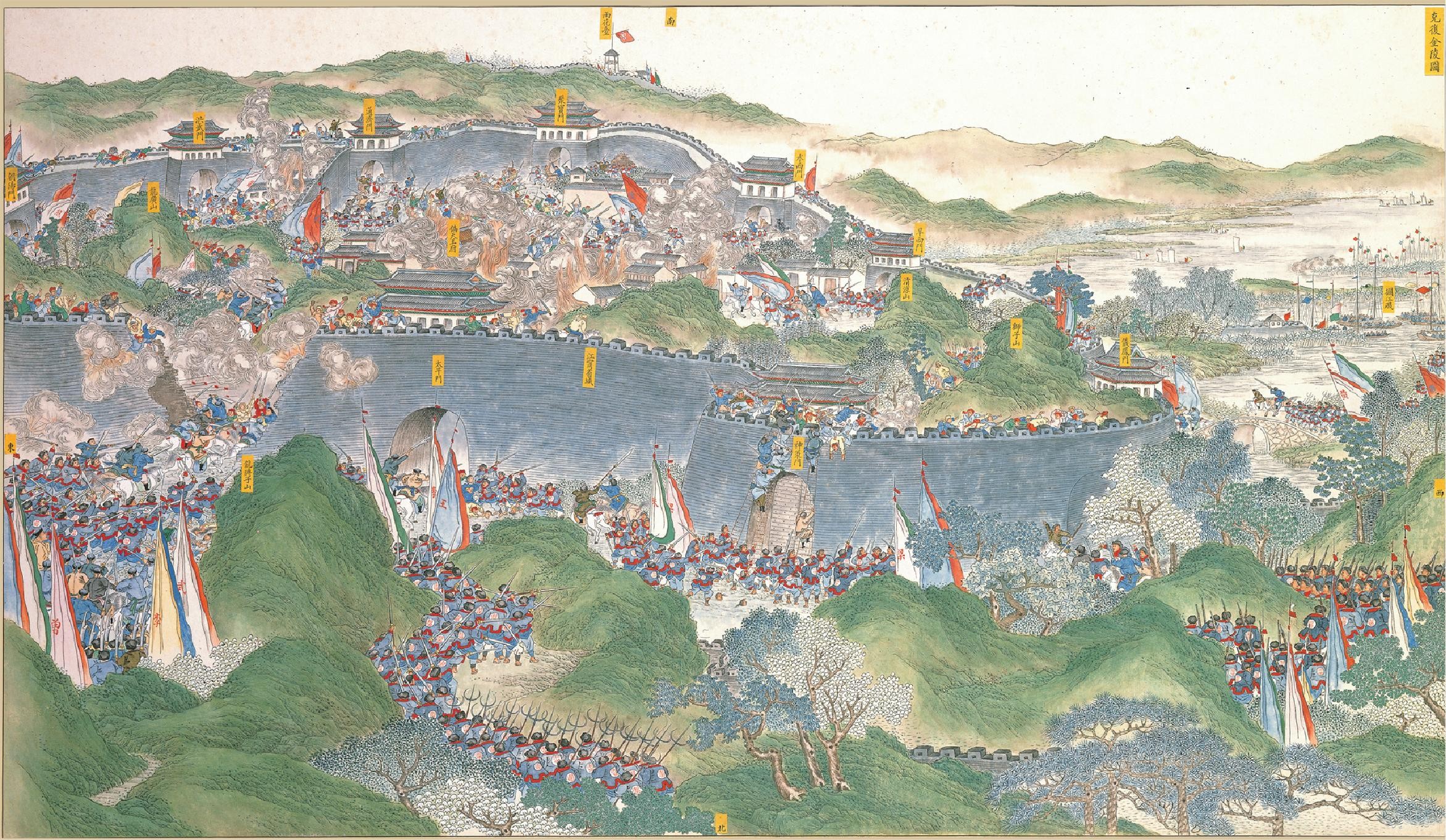
The Beiyang Army (), named after the Beiyang region, was a Western-style Imperial Chinese Army established by the Qing dynasty in the early 20th century. It was the centerpiece of a general reconstruction of the Qing military system in the wake of the Boxer Rebellion and the First Sino-Japanese War, becoming the dynasty's first regular army in terms of its training, equipment, and structure. The Beiyang Army played a major role in Chinese politics for at least three decades and arguably right up to 1949. It played an instrumental role in the 1911 Revolution against the Qing dynasty, and, by dividing into warlord factions known as the Beiyang clique (), ushered in a period of regional division. The Beiyang Army had its origins in the Newly Created Army established in late 1895 under Yuan Shikai's command, after China was defeated in the First Sino-Japanese War. Unlike its predecessors, it had a formal structure with infantry, cavalry, artillery, and logistical branches, and ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Five Races Under One Union
Five Races Under One Union was one of the major principles upon which the Republic of China was founded following the 1911 Revolution. Its central tenet was the harmonious existence under one nation of what were considered the five major ethnic groups in China: the Han, the Manchu, the Mongols, the Hui (Muslims), and the Tibetans. Description This principle emphasized harmony between what were considered the five major ethnic groups in China, as represented by the colored stripes of the Five-Colored Flag of the Republic: the Han (red); the Manchus (yellow); the Mongols (blue); the Hui or Muslims (white); and the Tibetans (black). The term "Hui" () here refers to all Muslims (回民, ''a.k.a.'' 穆斯林) in China as a whole regardless of ethnicity, including Chinese-speaking Muslims, Turkic-speaking Uyghurs, Kazakhs, Uzbeks, Kyrgyzs and Tatars, Mongolic-speaking Dongxiangs and Bonans, and Iranic-speaking Pamiris, ''etc.'' The term "Muslim Territory" (; ) was an older ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fengshan (general)
Fengshan (, 1860 25 October 1911) was a Qing dynasty general. A member of the Bordered White Banner, he passed the Imperial Examination with a focus on translation. After some time as a translator and secretary, as well as a stint in the police, he transferred to the military. Between 1900 and 1911, he held numerous positions, including division commander with the Beiyang Army as well as Tartar-General in Xi'an. Fengshan was assigned to Guangdong after the assassination of , but he was himself killed by the Chinese Assassination Corps upon arrival. His home in Beijing has been recognized as a cultural property. Early life and military career Fengshan was born in 1860, a member of the Liu clan. He took the courtesy name Yumen (, ) as an adult, and passed the Imperial Examination at the provincial level with a focus on translation. Part of the Bordered White Banner of the Eight Banners, he spent his early government career as a translator and secretary. Fengshan was later ele ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry, or infantryman are a type of soldier who specialize in ground combat, typically fighting dismounted. Historically the term was used to describe foot soldiers, i.e. those who march and fight on foot. In modern usage, the term broadly encompasses a wide variety of subspecialties, including light infantry, irregular infantry, heavy infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry, mechanized infantry, Airborne forces, airborne infantry, Air assault, air assault infantry, and Marines, naval infantry. Other subtypes of infantry, such as line infantry and mounted infantry, were once commonplace but fell out of favor in the 1800s with the invention of more accurate and powerful weapons. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French , from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warlord Era
The Warlord Era was the period in the history of the Republic of China between 1916 and 1928, when control of the country was divided between rival Warlord, military cliques of the Beiyang Army and other regional factions. It began after the death of Yuan Shikai, the President of the Republic of China, President of China after the Xinhai Revolution had overthrown the Qing dynasty and established the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China in 1912. Yuan's death on 6 June 1916 created a power vacuum which was filled by Warlord, military strongmen and widespread violence, chaos, and oppression. The Nationalist Kuomintang (KMT) government of Sun Yat-sen, based in Guangzhou, began to contest Yuan's Beiyang government based in Beijing for recognition as the legitimate government of China. The most powerful cliques were the Zhili clique led by Feng Guozhang, who controlled several northern provinces; the Anhui clique led by Duan Qirui, based in several southeastern provinces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Warlord
Warlords are individuals who exercise military, Economy, economic, and Politics, political control over a region, often one State collapse, without a strong central or national government, typically through informal control over Militia, local armed forces. Warlords have existed throughout much of history, albeit in a variety of different capacities within the political, economic, and social structure of State (polity), states or Anarchy, ungoverned territories. The term is often applied in the context of China around the end of the Qing dynasty, especially during the Warlord Era. The term may also be used for a General officer, supreme military leader. Historical origins and etymology The first appearance of the word "warlord" dates to 1856, when used by American philosopher and poet Ralph Waldo Emerson in a highly critical essay on the aristocracy in England, "Piracy and war gave place to trade, politics and letters; the war-lords'' to the law-lord; the privilege was kept, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regular Army
A regular army is the official army of a state or country (the official armed forces), contrasting with irregular forces, such as volunteer irregular militias, private armies, mercenaries, etc. A regular army usually has the following: * a standing army, the permanent force of the regular army that is maintained under arms during peacetime. * a military reserve force that can be mobilized when needed to expand the effectiveness of the regular army by complementing the standing army. A regular army may be: * a ''conscript army'', including professionals, volunteers and also conscripts (presence of enforced conscription, including recruits for the standing army and also a compulsory reserve). * a ''professional army'', with no conscripts (absence of compulsory service, and presence of a voluntary reserve), is not exactly the same as a standing army, as there are standing armies both in the conscript and the professional models. In the United Kingdom and the United States, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Sino-Japanese War
The First Sino-Japanese War (25 July 189417 April 1895), or the First China–Japan War, was a conflict between the Qing dynasty of China and the Empire of Japan primarily over influence in Joseon, Korea. In Chinese it is commonly known as the Jiawu War. After more than six months of unbroken successes by Japanese land and naval forces and the loss of the ports of Lüshunkou (Port Arthur) and Weihaiwei, the Qing government sued for peace in February 1895 and signed the Unequal treaties, unequal Treaty of Shimonoseki two months later, ending the war. In the late 19th century, Korea remained one of China's tributary states, while Japan viewed it as a target of imperial expansion. In June 1894, the Qing government, at the request of the Korean emperor Gojong of Korea, Gojong, sent 2,800 troops to aid in suppressing the Donghak Peasant Revolution. The Japanese considered this a violation of the 1885 Convention of Tientsin, and sent an expeditionary force of 8,000 troops, which la ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing, was a Manchu-led Dynasties of China, imperial dynasty of China and an early modern empire in East Asia. The last imperial dynasty in Chinese history, the Qing dynasty was preceded by the Ming dynasty and succeeded by the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China. At its height of power, the empire stretched from the Sea of Japan in the east to the Pamir Mountains in the west, and from the Mongolian Plateau in the north to the South China Sea in the south. Originally emerging from the Later Jin (1616–1636), Later Jin dynasty founded in 1616 and proclaimed in Shenyang in 1636, the dynasty seized control of the Ming capital Beijing and North China in 1644, traditionally considered the start of the dynasty's rule. The dynasty lasted until the Xinhai Revolution of October 1911 led to the abdication of the last emperor in February 1912. The multi-ethnic Qing dynasty Legacy of the Qing dynasty, assembled the territoria ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Of The Qing Dynasty
The Qing dynasty (1644–1912) was established by conquest and maintained by armed force. The founding emperors personally organized and led the armies, and the continued cultural and political legitimacy of the dynasty depended on their ability to defend the country from invasion and expand its territory. Military institutions, leadership, and finance were fundamental to the dynasty's initial success and ultimate decay. The early military system centered on the Eight Banners, a hybrid institution that also played social, economic, and political roles. The use of gunpowder during the High Qing can compete with the three gunpowder empires in western Asia. However, the military technology of the European Industrial Revolution made China's armament and military rapidly obsolete. By the middle of the 18th century, the military of the Qing dynasty numbered over 200,000 bannermen and 600,000 Green Standard troops. The Qing navy became the largest in East Asia, but its organizatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beiyang
The term Beiyang (; pinyin: Běiyáng; Wade-Giles: Peiyang) literally means Northern Ocean. Initially a purely geographic term, it originated toward the end of the Qing dynasty, and it referred to the coastal provinces of Zhili (Traditional Chinese:直隸, Simplified Chinese: 直隶, pinyin: Zhílì, today's Hebei), Shandong and Liaoning that bordered the Yellow Sea (itself a marginal sea of the Pacific Ocean) and surrounded the imperial capital of Beijing (then known as Peking). The term later acquired a political significance, denoting the imperial heartland. The position of Minister of Beiyang (北洋通商大臣) in the late Qing Dynasty was held by the Viceroy of Zhili, whose main responsibilities were trade relations and occasionally foreign affairs. See also *Beiyang Army *Beiyang Fleet *Beiyang Government The Beiyang government was the internationally recognized government of the Republic of China (1912–1949), Republic of China between 1912 and 1928, based in Beij ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cao Kun
General Cao Kun (; courtesy name: Zhongshan () (December 12, 1862 – May 15, 1938) was a Chinese warlord and politician, who served as the President of the Republic of China from 1923 to 1924, as well as the military leader of the Zhili clique in the Beiyang Army; he also served as a trustee of the Catholic University of Peking. Early life and rise to leadership Cao was born to a poor family in Tianjin. During the First Sino-Japanese War in 1894, he went with the army to fight in Joseon. After the war was over he joined Yuan Shikai to participate in the training of the New Army (known as the Beiyang Army). Admired by Yuan, Cao managed to rise very quickly. By the time of the 1911 Xinhai Revolution he commanded the Beiyang 3rd Division. He was made a general in the Beiyang Army and led the Zhili clique after the death of Feng Guozhang. During the 1918 election he was promised the vice-presidency by Duan Qirui but the office remained vacant after most of the National Assembl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |