|
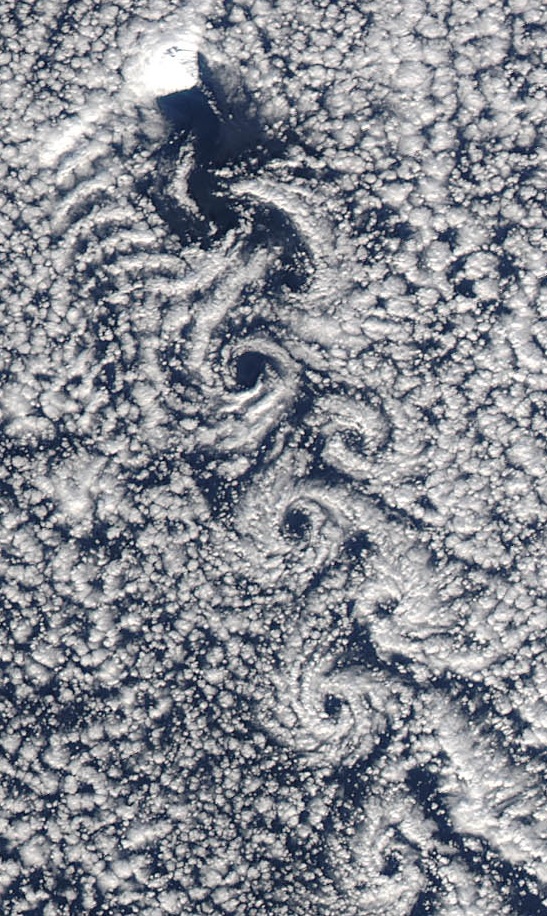
Beerenberg
Beerenberg is a stratovolcano dominating the northeastern end of the Norwegian island of Jan Mayen. It is high and is the world's northernmost subaerial active volcano and the List of volcanoes in Norway, only active volcano in Norway. The volcano is topped by a mostly ice-filled volcanic crater, crater about wide, with numerous peaks along its rim including the highest summit, Haakon VII Toppen, on its western side. Name Its name is Dutch language, Dutch for "Bear Mountain" and comes from the polar bears seen there by Dutch whalers in the early 17th century. Description The upper slopes of the volcano are largely ice-covered, with several major glaciers including five which reach the sea. The longest of the glaciers is the Weyprecht Glacier, which flows from the summit crater via a breach through the northwestern portion of the crater rim, and extends about down to the sea. Beerenberg is composed primarily of basaltic lava flows with minor amounts of tephra. Numerous c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jan Mayen
Jan Mayen () is a Norway, Norwegian volcanic island in the Arctic Ocean with no permanent population. It is long (southwest-northeast) and in area, partly covered by glaciers (an area of around the Beerenberg volcano). It has two parts: larger northeast Nord-Jan and smaller Sør-Jan, linked by a wide isthmus. It lies northeast of Iceland (495 km [305 mi] NE of Kolbeinsey), east of central Greenland, and northwest of Vesterålen, Norway. The island is mountainous, the highest summit being the Beerenberg volcano in the north. The isthmus is the location of the two largest lakes of the island, Sørlaguna (South Lagoon) and Nordlaguna (North Lagoon). A third lake is called Ullerenglaguna (Ullereng Lagoon). Jan Mayen was formed by the Jan Mayen hotspot and is defined by geologists as a Continental fragment, microcontinent. Although administered separately, in the ISO 3166-1 standard, Jan Mayen and Svalbard are collectively designated as ''Svalbard and Jan Mayen'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Weyprecht Glacier
Weyprecht Glacier () is a glacier in Jan Mayen. It is the longest glacier located in the Beerenberg area. The glacier is named after Austro-Hungarian Arctic explorer Karl Weyprecht. See also *List of glaciers in Norway *Svalbard and Jan Mayen Svalbard and Jan Mayen (, ISO 3166-1 alpha-2: SJ, ISO 3166-1 alpha-3: SJM, ISO 3166-1 numeric: 744) is a statistical designation defined by ISO 3166-1 for a collective grouping of two remote jurisdictions of Norway: Svalbard and Jan Mayen. While ... References External links Glacier retreat in Jan MayenGlaciers of Jan Mayen Glaciers of Jan Mayen {{JanMayen-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Volcanoes In Norway
This is a list of active and extinct (or non-active) volcanoes in Norway. References References {{ref list Norway Volcanoes A volcano is commonly defined as a vent or fissure in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often fo ... * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Mountains In Norway By Prominence
This is a list of the mountains of Norway, ordered by their topographic prominence. On the island Jan Mayen, a Norwegian administered island northeast of Iceland, the volcano Beerenberg has a height and prominence , and on the island Spitsbergen in Svalbard, the mountain Newtontoppen has height and prominence . For a list by height, see list of mountains in Norway by height. See also * List of mountains in Norway by height * List of mountains by prominence References * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Mountains in Norway by prominence Prominence In topography, prominence or relative height (also referred to as autonomous height, and shoulder drop in US English, and drop in British English) measures the height of a mountain or hill's summit relative to the lowest contour line encircling ... Norway, by prominence Mountains in Norway by prominence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
James Wordie
Sir James Mann Wordie CBE FRS FRSGS LLD (26 April 1889 – 16 January 1962) was a Scottish polar explorer and geologist. Friends knew him as Jock Wordie. He was President of the Royal Geographical Society from 1951 to 1954. Early life and education Wordie was born at Partick, Glasgow, the son of Jane Catherine ( Mann) and John Wordie, owner of Wordie & Co., a major carrier and carting contractor, with multiple premises throughout Glasgow. He had a sister, Helen. The family lived at 4 Buckingham Terrace in the Hillhead district. The house, which still stands, is a mid-terraced 19th-century three-storey and basement house facing Great Western Road. Wordie attended Glasgow Academy. He went on to study Sciences at the University of Glasgow, graduating with a BSc in Geology in 1910. He then studied at St John's College, Cambridge, graduating with an MA in 1912, after which he undertook research. His occupation brought him in contact with Frank Debenham and Raymond Priestle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Louis Mercanton
__NOTOC__ Paul-Louis Mercanton (11 May 1876 – 25 February 1963) was a Swiss glaciologist, meteorologist and Arctic explorer. Biography Mercanton was born in Lausanne on 11 May 1876, the son of Eugène Mercanton, a lawyer, and Félicie Marie Lavanchy. He graduated in electrical engineering from the University of Lausanne in 1899, and obtained a doctorate in physics from the same university in 1901. Mercanton was a professor of physics and electricity, then of meteorology and geophysics, at Lausanne from 1904 to 1938. He married Alice Marguerite Colomb in 1907. Mercanton directed Vaud's meteorological service from 1911 to 1941 and the Swiss Central Meteorological Station in Zurich from 1934 to 1941, and was editor and co-author of ''Variations périodiques des glaciers des Alpes suisses'' ("Periodic Variations of the Glaciers of the Swiss Alps") between 1907 and 1954. He also regularly wrote reports on other glaciers of Europe. Mercanton was a pioneer by publishing in 191 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ultra Prominent Peak
An ultra-prominent peak, or ultra for short, is a mountain summit with a topographic prominence of or more; it is also called a P1500. The prominence of a peak is the minimum height of climb to the summit on any route from a higher peak, or from sea level if there is no higher peak. There are approximately 1,500 such peaks on Earth. Some well-known peaks, such as the Matterhorn and Eiger, are not ultras because they are connected to higher mountains by high cols and thus do not achieve enough topographic prominence. The term "ultra" originated with earth scientist Steve Fry, from his studies of the prominence of peaks in Washington (state), Washington in the 1980s. His original term was "ultra major mountain", referring to peaks with at least of prominence. Distribution Currently, over 1,500 ultras have been identified above sea level: 654 in Asia, 357 in North America, 209 in South America, 119 in Europe (including 12 in the Caucasus), 84 in Africa, 54 in Oceania, and 39 in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fissure Vent
A fissure vent, also known as a volcanic fissure, eruption fissure or simply a fissure, is a linear volcanic vent through which lava erupts, usually without any explosive activity. The vent is often a few metres wide and may be many kilometres long. Fissure vents can cause large flood basalts which run first in lava channels and later in lava tubes. After some time, the eruption tends to become focused at one or more spatter cones. Volcanic cones and their craters that are aligned along a fissure form a crater row. Small fissure vents may not be easily discernible from the air, but the crater rows (see Laki) or the canyons (see Eldgjá) built up by some of them are. The dikes that feed fissures reach the surface from depths of a few kilometers and connect them to deeper magma reservoirs, often under volcanic centers. Fissures are usually found in or along rifts and rift zones, such as Iceland and the East African Rift. Fissure vents are often part of the structu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
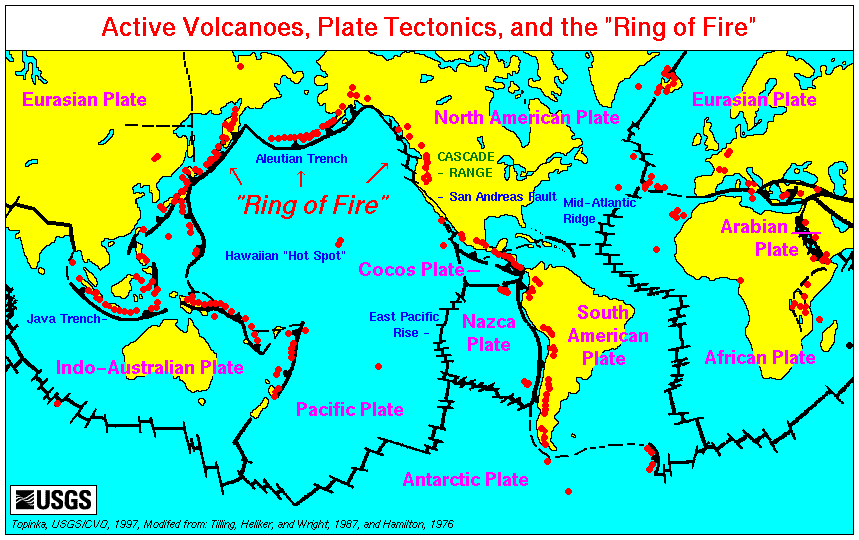
Active Volcanoes
An active volcano is a volcano that is currently erupting, or has the potential to erupt in the future. Conventionally it is applied to any that have erupted during the Holocene (the current geologic epoch that began approximately 11,700 years ago). A volcano that is not currently erupting but could erupt in the future is known as a dormant volcano. Volcanoes that will not erupt again are known as extinct volcanoes. Overview There are 1,350 potentially active volcanoes around the world, 500 of which have erupted in historical time. Many active volcanoes are located along the Pacific Rim, also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire. An estimated 500 million people live near active volcanoes. ''Historical time'' (or recorded history) is another timeframe for ''active''. The span of recorded history differs from region to region. In China and the Mediterranean, it reaches back nearly 3,000 years, but in the Pacific Northwest of the United States and Canada, it reaches back less tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ridge Volcanoes
A ridge is a long, narrow, elevated geomorphologic landform, structural feature, or a combination of both separated from the surrounding terrain by steep sides. The sides of a ridge slope away from a narrow top, the crest or ridgecrest, with the terrain dropping down on either side. The crest, if narrow, is also called a ridgeline. Limitations on the dimensions of a ridge are lacking. Its height above the surrounding terrain can vary from less than a meter to hundreds of meters. A ridge can be either depositional, erosional, tectonic, or a combination of these in origin and can consist of either bedrock, loose sediment, lava, or ice depending on its origin. A ridge can occur as either an isolated, independent feature or part of a larger geomorphological and/or structural feature. Frequently, a ridge can be further subdivided into smaller geomorphic or structural elements. Classification As in the case of landforms in general, there is a lack of any commonly agreed classi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Holocene Stratovolcanoes
The Holocene () is the current geological epoch, beginning approximately 11,700 years ago. It follows the Last Glacial Period, which concluded with the Holocene glacial retreat. The Holocene and the preceding Pleistocene together form the Quaternary period. The Holocene is an interglacial period within the ongoing glacial cycles of the Quaternary, and is equivalent to Marine Isotope Stage 1. The Holocene correlates with the last maximum axial tilt towards the Sun of the Earth's obliquity. The Holocene corresponds with the rapid proliferation, growth, and impacts of the human species worldwide, including all of its written history, technological revolutions, development of major civilizations, and overall significant transition towards urban living in the present. The human impact on modern-era Earth and its ecosystems may be considered of global significance for the future evolution of living species, including approximately synchronous lithospheric evidence, or more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mountains Of Norway
A mountain is an elevated portion of the Earth's crust, generally with steep sides that show significant exposed bedrock. Although definitions vary, a mountain may differ from a plateau in having a limited summit area, and is usually higher than a hill, typically rising at least above the surrounding land. A few mountains are isolated summits, but most occur in mountain ranges. Mountains are formed through tectonic forces, erosion, or volcanism, which act on time scales of up to tens of millions of years. Once mountain building ceases, mountains are slowly leveled through the action of weathering, through slumping and other forms of mass wasting, as well as through erosion by rivers and glaciers. High elevations on mountains produce colder climates than at sea level at similar latitude. These colder climates strongly affect the ecosystems of mountains: different elevations have different plants and animals. Because of the less hospitable terrain and climate, mountains te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |