|
Beef Tapeworm
''Taenia saginata'' (synonym ''Taeniarhynchus saginatus''), commonly known as the beef tapeworm, is a zoonotic tapeworm belonging to the order Cyclophyllidea and genus ''Taenia''. It is an intestinal parasite in humans causing taeniasis (a type of helminthiasis) and cysticercosis in cattle. Cattle are the intermediate hosts, where larval development occurs, while humans are definitive hosts harbouring the adult worms. It is found globally and most prevalently where cattle are raised and beef is consumed. It is relatively common in Africa, Europe, Southeast Asia, South Asia, and Latin America. Humans are generally infected as a result of eating raw or undercooked beef which contains the infective larvae, called cysticerci. As hermaphrodites, each body segment called proglottid has complete sets of both male and female reproductive systems. Thus, reproduction is by self-fertilisation. From humans, embryonated eggs, called oncospheres, are released with faeces and are transmitted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann August Ephraim Goeze
Johann August Ephraim Goeze (; 28 May 1731 – 27 June 1793) was a German zoologist, born in Aschersleben. He is known for the discovery of tardigrades, also called water bears. He was the son of Johann Heinrich and Catherine Margarete (née Kirchhoff). He studied theology at University of Halle. He married Leopoldine Maria Keller in 1770, by whom he had four children. In 1751, he became a pastor in Aschersleben, in Quedlinburg, and later of in Quedlinburg in 1762, finally becoming first deacon of the seminary of Quedlinburg in 1787. He died in Quedlinburg. He did much work with aquatic invertebrates, particularly insects and worms. In 1784, Goeze perceived the similarities between the heads of tapeworms found in the human intestinal tract and the invaginated heads of '' Cysticercus cellulosae'' in pigs. In 1773, he was the first to describe tardigrades, naming them ''Kleiner Wasserbär'', meaning 'little water-bear'. Works *Goeze, J. A. E. 1776. Verzeichnisse der Namen von ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proglottid
Cestoda is a Class (biology), class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, commonly known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish-infecting parasites. All cestodes are parasitism, parasitic; many have complex Life history theory, life histories, including a stage in a Host (biology)#Definitive and secondary hosts, definitive (main) host in which the adults grow and reproduce, often for years, and one or two intermediate stages in which the larvae develop in other hosts. Typically the adults live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates, while the larvae often live in the bodies of other animals, either vertebrates or invertebrates. For example, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asymptomatic
Asymptomatic (or clinically silent) is an adjective categorising the medical conditions (i.e., injuries or diseases) that patients carry but without experiencing their symptoms, despite an explicit diagnosis (e.g., a positive medical test). Pre-symptomatic is the adjective categorising the time periods during which the medical conditions are asymptomatic. Subclinical and paucisymptomatic are other adjectives categorising either the asymptomatic infections (i.e., subclinical infections), or the psychosomatic illnesses and mental disorders expressing a subset of symptoms but not the entire set an explicit medical diagnosis requires. Examples An example of an asymptomatic disease is cytomegalovirus (CMV) which is a member of the herpes virus family. "It is estimated that 1% of all newborns are infected with CMV, but the majority of infections are asymptomatic." (Knox, 1983; Kumar et al. 1984) In some diseases, the proportion of asymptomatic cases can be important. For exam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysticercosis
Cysticercosis is a tissue infection caused by the young form of the pork tapeworm. People may have few or no symptoms for years. In some cases, particularly in Asia, solid lumps of between one and two centimeters may develop under the skin. After months or years, these lumps can become painful and swollen and then resolve. A specific form called neurocysticercosis, which affects the brain, can cause neurological symptoms. In developing countries, this is one of the most common causes of seizures. Cysticercosis is usually acquired by eating food or drinking water contaminated by tapeworms' eggs from human feces. Among foods egg-contaminated vegetables are a major source. The tapeworm eggs are present in the feces of a person infected with the adult worms, a condition known as taeniasis. Taeniasis, in the strict sense, is a different disease and is due to eating cysts in poorly cooked pork. People who live with someone with pork tapeworm have a greater risk of getting cysticerco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scolex
Cestoda is a class of parasitic worms in the flatworm phylum (Platyhelminthes). Most of the species—and the best-known—are those in the subclass Eucestoda; they are ribbon-like worms as adults, commonly known as tapeworms. Their bodies consist of many similar units known as proglottids—essentially packages of eggs which are regularly shed into the environment to infect other organisms. Species of the other subclass, Cestodaria, are mainly fish-infecting parasites. All cestodes are parasitic; many have complex life histories, including a stage in a definitive (main) host in which the adults grow and reproduce, often for years, and one or two intermediate stages in which the larvae develop in other hosts. Typically the adults live in the digestive tracts of vertebrates, while the larvae often live in the bodies of other animals, either vertebrates or invertebrates. For example, ''Diphyllobothrium'' has at least two intermediate hosts, a crustacean and then one or more fresh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', : uteri or uteruses) or womb () is the hollow organ, organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans, that accommodates the embryonic development, embryonic and prenatal development, fetal development of one or more Fertilized egg, fertilized eggs until birth. The uterus is a hormone-responsive sex organ that contains uterine gland, glands in its endometrium, lining that secrete uterine milk for embryonic nourishment. (The term ''uterus'' is also applied to analogous structures in some non-mammalian animals.) In humans, the lower end of the uterus is a narrow part known as the Uterine isthmus, isthmus that connects to the cervix, the anterior gateway leading to the vagina. The upper end, the body of the uterus, is connected to the fallopian tubes at the uterine horns; the rounded part, the fundus, is above the openings to the fallopian tubes. The connection of the uterine cavity with a fallopian tube is called the utero ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Testes
A testicle or testis ( testes) is the gonad in all male bilaterians, including humans, and is homologous to the ovary in females. Its primary functions are the production of sperm and the secretion of androgens, primarily testosterone. The release of testosterone is regulated by luteinizing hormone (LH) from the anterior pituitary gland. Sperm production is controlled by follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) from the anterior pituitary gland and by testosterone produced within the gonads. Structure Appearance Males have two testicles of similar size contained within the scrotum, which is an extension of the abdominal wall. Scrotal asymmetry, in which one testicle extends farther down into the scrotum than the other, is common. This is because of the differences in the vasculature's anatomy. For 85% of men, the right testis hangs lower than the left one. Measurement and volume The volume of the testicle can be estimated by palpating it and comparing it to ellipsoids (an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taenia Solium
''Taenia solium'', the pork tapeworm, belongs to the cyclophyllid cestode family Taeniidae. It is found throughout the world and is most common in countries where pork is eaten. It is a tapeworm that uses humans (''Homo sapiens'') as its definitive host and pigs and boars (family Suidae) as the Host (biology)#Types of hosts, intermediate or secondary hosts. It is transmitted to pigs through human feces that contain the parasite eggs and contaminate their fodder. Pigs ingest the morula, eggs, which develop into larvae, then into oncospheres, and ultimately into infective tapeworm cysts, called cysticerci. Humans acquire the cysts through consumption of uncooked or under-cooked pork and the cysts grow into adult worms in the small intestine. There are two forms of human infection. One is "primary hosting", called taeniasis, and is due to eating under-cooked pork that contains the cysts, resulting in adult worms in the intestines. This form generally is asymptomatic, without symptom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Taenia Asiatica
''Taenia asiatica'', commonly known as Asian taenia or Asian tapeworm, is a parasitic tapeworm of humans and pigs. It is one of the three species of '' Taenia'' infecting humans and causes taeniasis. Discovered only in 1980s from Taiwan and other East Asian countries as an unusual species, it is so notoriously similar to ''Taenia saginata'', the beef tapeworm, that it was for a time regarded as a slightly different strain. But anomaly arose as the tapeworm is not of cattle origin, but of pigs. Morphological details also showed significant variations, such as presence of rostellar hooks, shorter body, and fewer body segments. The scientific name designated was then Asian ''T. saginata''. But the taxonomic consensus turns out to be that it is a unique species. It was in 1993 that two Korean parasitologists, Keeseon S. Eom and Han Jong Rim, provided the biological bases for classifying it into a separate species. The use of mitochondrial genome sequence and molecular phylogeny in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cysticercus
Cysticercus (pl. cysticerci) is a scientific name given to the young tapeworms (larvae) belonging to the genus '' Taenia''. It is a small, sac-like vesicle resembling a bladder; hence, it is also known as bladder worm. It is filled with fluid, in which the main body of the larva, called scolex (which will eventually form the head of the tapeworm), resides. It normally develops from the eggs, which are ingested by the intermediate hosts, such as pigs and cattle. The tissue infection is called cysticercosis. Inside such hosts, they settle in the muscles. When humans eat raw or undercooked pork or beef that is contaminated with cysticerci, the larvae grow into adult worms inside the intestine. Under certain circumstances, specifically for the pork tapeworm, the eggs can be accidentally eaten by humans through contaminated foodstuffs. In such case, the eggs hatch inside the body, generally moving to muscles as well as inside the brain. Such brain infection can lead to a serious medical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
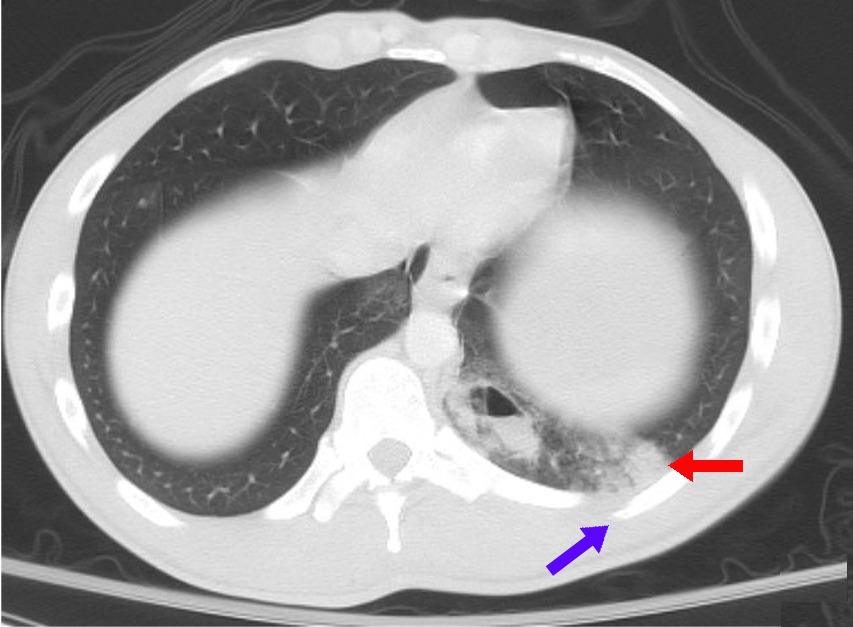
Lungs
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system in many animals, including humans. In mammals and most other tetrapods, two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart. Their function in the respiratory system is to extract oxygen from the atmosphere and transfer it into the bloodstream, and to release carbon dioxide from the bloodstream into the atmosphere, in a process of gas exchange. Respiration is driven by different muscular systems in different species. Mammals, reptiles and birds use their musculoskeletal systems to support and foster breathing. In early tetrapods, air was driven into the lungs by the pharyngeal muscles via buccal pumping, a mechanism still seen in amphibians. In humans, the primary muscle that drives breathing is the diaphragm. The lungs also provide airflow that makes vocalisation including speech possible. Humans have two lungs, a right lung and a left lung. They are situated within the thoracic cavity of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liver
The liver is a major metabolic organ (anatomy), organ exclusively found in vertebrates, which performs many essential biological Function (biology), functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of various proteins and various other Biochemistry, biochemicals necessary for digestion and growth. In humans, it is located in the quadrants and regions of abdomen, right upper quadrant of the abdomen, below the thoracic diaphragm, diaphragm and mostly shielded by the lower right rib cage. Its other metabolic roles include carbohydrate metabolism, the production of a number of hormones, conversion and storage of nutrients such as glucose and glycogen, and the decomposition of red blood cells. Anatomical and medical terminology often use the prefix List of medical roots, suffixes and prefixes#H, ''hepat-'' from ἡπατο-, from the Greek language, Greek word for liver, such as hepatology, and hepatitis The liver is also an accessory digestive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |