|
Beclabuvir
Beclabuvir (also known by the research name BMS-791325; abbreviated BCV) is an antiviral drug for the treatment of hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection that has been studied in clinical trials. In February 2017, Bristol-Myers Squibb began sponsoring a post-marketing trial of beclabuvir, in combination with asunaprevir and daclatasvir, to study the combination's safety profile with regard to liver function. From February 2014 to November 2016, a phase II clinical trial was conducted on the combination of asunaprevir/daclatasvir/beclabuvir (beclabuvir is referred to as BMS-791325 in the trial) on patients infected with both HIV and HCV. Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis of six published six clinical trials showed high response rates in HCV genotype 1-infected patients treated with daclatasvir, asunaprevir, and beclabuvir irrespective of ribavirin use, prior interferon Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol-Myers Squibb
The Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, doing business as Bristol Myers Squibb (BMS), is an American multinational pharmaceutical company. Headquartered in Princeton, New Jersey, BMS is one of the world's largest pharmaceutical companies and consistently ranks on the ''Fortune'' 500 list of the largest U.S. corporations. For fiscal 2022, it had a total revenue of $46.2 billion. Bristol Myers Squibb manufactures prescription pharmaceuticals and biologics in several therapeutic areas, including cancer, HIV/AIDS, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, hepatitis, rheumatoid arthritis, and psychiatric disorders. BMS's primary research and development (R&D) sites are located in Lawrence, New Jersey (formerly Squibb, near Princeton), Summit, New Jersey, formerly HQ of Celgene, New Brunswick, New Jersey; Redwood City, California; and Seville in Spain, with other sites in Devens and Cambridge, Massachusetts; Braine-l'Alleud, Belgium; Tokyo, Japan; Hyderabad; Bangalore, India and Wirr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
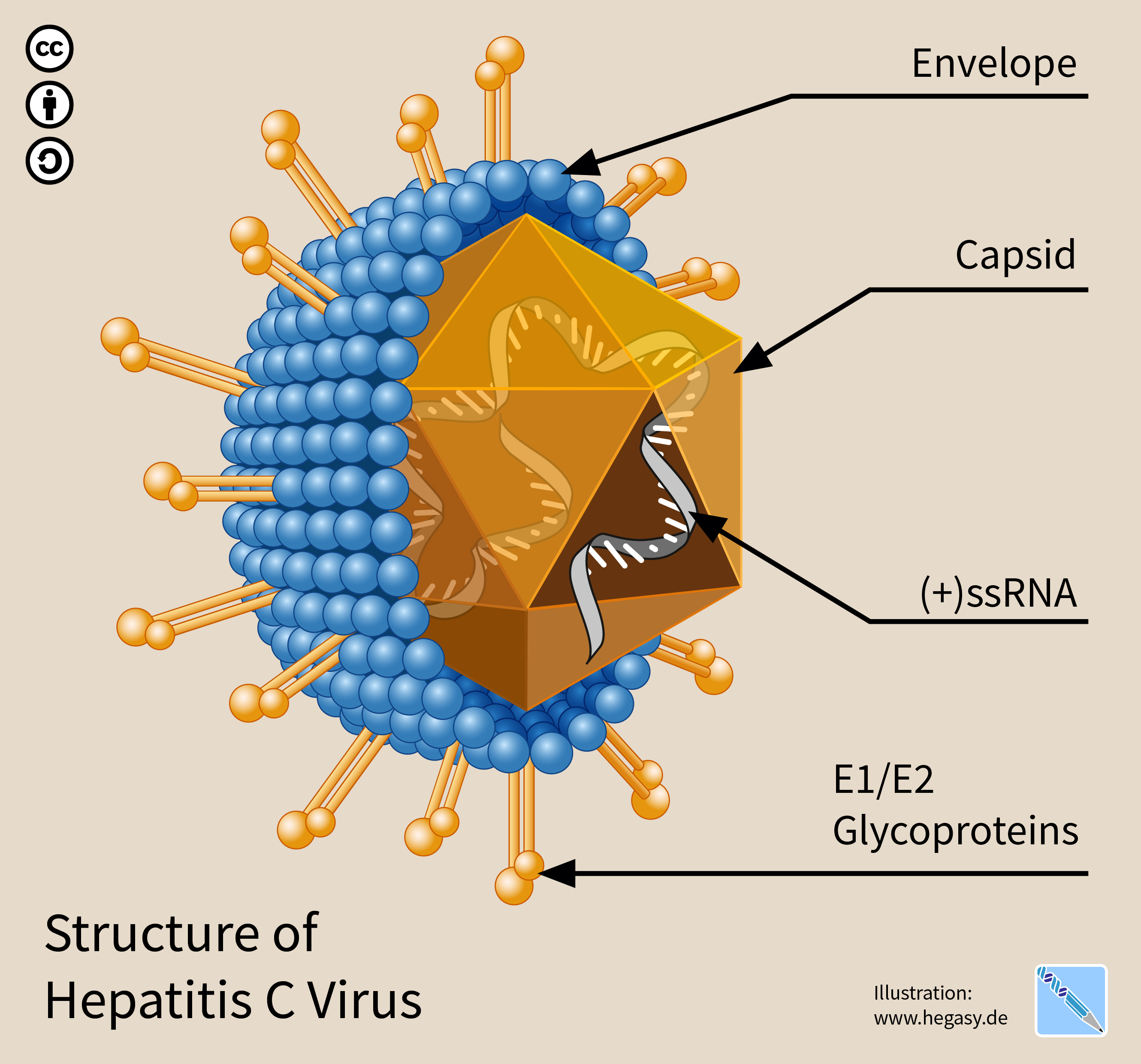
Hepatitis C Virus
The hepatitis C virus (HCV) is a small (55–65 nm in size), enveloped, positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus of the family ''Flaviviridae''. The hepatitis C virus is the cause of hepatitis C and some cancers such as liver cancer ( hepatocellular carcinoma, abbreviated HCC) and lymphomas in humans. Taxonomy The hepatitis C virus belongs to the genus '' Hepacivirus'', a member of the family ''Flaviviridae''. Before 2011, it was considered to be the only member of this genus. However a member of this genus has been discovered in dogs: canine hepacivirus. There is also at least one virus in this genus that infects horses. Several additional viruses in the genus have been described in bats and rodents. Structure The hepatitis C virus particle consists of a lipid membrane envelope that is 55 to 65 nm in diameter. Two viral envelope glycoproteins, E1 and E2, are embedded in the lipid envelope. They take part in viral attachment and entry into the cell. Within the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NS5B
Nonstructural protein 5B (NS5B) is a viral protein found in the hepatitis C virus (HCV). It is an RNA-dependent RNA polymerase, having the key function of replicating HCV's viral RNA by using the viral positive RNA strand as a template to catalyze the polymerization of ribonucleoside triphosphates (rNTP) during RNA replication. Several crystal structures of NS5B polymerase in several crystalline forms have been determined based on the same consensus sequence BK (HCV-BK, genotype 1). The structure can be represented by a right hand shape with fingers, palm, and thumb. The encircled active site, unique to NS5B, is contained within the palm structure of the protein. Recent studies on NS5B protein genotype 1b strain J4's (HC-J4) structure indicate a presence of an active site where possible control of nucleotide binding occurs and initiation of de-novo RNA synthesis. De-novo adds necessary primers for initiation of RNA replication. Drugs targeting NS5B Several drugs are either on the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiviral Drug
Antiviral drugs are a class of medication used for treating viral infections. Most antivirals target specific viruses, while a broad-spectrum antiviral is effective against a wide range of viruses. Antiviral drugs are a class of antimicrobials, a larger group which also includes antibiotic (also termed antibacterial), antifungal and antiparasitic drugs, or antiviral drugs based on monoclonal antibodies. Most antivirals are considered relatively harmless to the host, and therefore can be used to pharmacotherapy, treat infections. They should be distinguished from virucides, which are not medication but deactivate or destroy virus particles, either inside or outside the body. Natural virucides are produced by some plants such as eucalyptus and Australian tea trees. Medical uses Most of the antiviral drugs now available are designed to help deal with HIV, Herpesviridae, herpes viruses, the hepatitis B and Hepatitis C, C viruses, and Influenzavirus A, influenza A and Influenzavirus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are prospective biomedical or behavioral research studies on human subject research, human participants designed to answer specific questions about biomedical or behavioral interventions, including new treatments (such as novel vaccines, pharmaceutical drug, drugs, medical nutrition therapy, dietary choices, dietary supplements, and medical devices) and known interventions that warrant further study and comparison. Clinical trials generate data on dosage, safety and efficacy. They are conducted only after they have received institutional review board, health authority/ethics committee approval in the country where approval of the therapy is sought. These authorities are responsible for vetting the risk/benefit ratio of the trial—their approval does not mean the therapy is 'safe' or effective, only that the trial may be conducted. Depending on product type and development stage, investigators initially enroll volunteers or patients into small Pilot experiment, pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Asunaprevir
Asunaprevir (formerly BMS-650032, brand name in Japan and Russia Sunvepra) is an experimental drug candidate for the treatment of hepatitis C. It was undergoing development by Bristol-Myers Squibb and has completed Phase III clinical trials in 2013. Asunaprevir is an inhibitor of the hepatitis C virus enzyme serine protease NS3. Asunaprevir is being tested in combination with pegylated interferon and ribavirin, as well as in interferon-free regimens with other direct-acting antiviral agents including daclatasvir Daclatasvir, sold under the brand name Daklinza, is an antiviral medication used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C (HCV). The other medications used in combination include sofosbuvir, ribavirin, and Interferon#Drug formu .... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daclatasvir
Daclatasvir, sold under the brand name Daklinza, is an antiviral medication used in combination with other medications to treat hepatitis C (HCV). The other medications used in combination include sofosbuvir, ribavirin, and Interferon#Drug formulations, interferon, vary depending on the virus type and whether the person has cirrhosis. It is taken by mouth. Common side effects when used with sofusbivir and daclatasvir include headache, fatigue (medicine), feeling tired, and nausea. With daclatasvir, sofosbuvir, and ribavirin the most common side effects are headache, feeling tired, nausea, and hemolytic anemia, red blood cell breakdown. It should not be used with St. John's wort, rifampin, or carbamazepine. It works by inhibiting the HCV protein NS5A. Daclatasvir was approved for use in the European Union in 2014, and the United States and India in 2015. It is on the WHO Model List of Essential Medicines, World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines. The brand Dakli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase II Clinical Trial
The phases of clinical research are the stages in which scientists conduct experiments with a health intervention to obtain sufficient evidence for a process considered effective as a medical treatment. For drug development, the clinical phases start with testing for drug safety in a few human subjects, then expand to many study participants (potentially tens of thousands) to determine if the treatment is effective. Clinical research is conducted on drug candidates, vaccine candidates, new medical devices, and new diagnostic assays. Description Clinical trials testing potential medical products are commonly classified into four phases. The drug development process will normally proceed through all four phases over many years. When expressed specifically, a clinical trial phase is capitalized both in name and Roman numeral, such as "Phase I" clinical trial. If the drug successfully passes through Phases I, II, and III, it will usually be approved by the national regulatory auth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ribavirin
Ribavirin, also known as tribavirin, is an antiviral medication used to treat illness caused by respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) and hepatitis C virus (HCV) infections, as well as some viral hemorrhagic fevers. For HCV, it is used in combination with other medications, such as simeprevir, sofosbuvir, peginterferon alfa-2b or peginterferon alfa-2a. It can also be used for viral hemorrhagic fevers—specifically, for Lassa fever, Crimean–Congo hemorrhagic fever, and Hantavirus infections (with exceptions for Ebola or Marburg virus diseases). Ribavirin is usually taken orally (by mouth) or inhaled. Despite widespread usage, it has faced scrutiny in the 21st century because of lack of proven efficacy in treating viral infections for which it has been prescribed in the past. Its common side effects include fatigue, headache, nausea, fever, muscle pains, and an irritable mood. Serious side effects include red blood cell breakdown, liver problems, and allergic reacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interferon
Interferons (IFNs, ) are a group of signaling proteins made and released by host cells in response to the presence of several viruses. In a typical scenario, a virus-infected cell will release interferons causing nearby cells to heighten their anti-viral defenses. IFNs belong to the large class of proteins known as cytokines, molecules used for communication between cells to trigger the protective defenses of the immune system that help eradicate pathogens. Interferons are named for their ability to "interfere" with viral replication by protecting cells from virus infections. However, virus-encoded genetic elements have the ability to antagonize the IFN response, contributing to viral pathogenesis and viral diseases. IFNs also have various other functions: they activate immune cells, such as natural killer cells and macrophages, and they increase host defenses by up-regulating antigen presentation by virtue of increasing the expression of major histocompatibility compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Non-cirrhotic Portal Fibrosis
Non-cirrhotic portal fibrosis (NCPF) is a chronic liver disease and type of non-cirrhotic portal hypertension (NCPH). Presentation It is characterized by 'obliterative portovenopathy', which leads to various problems such as portal hypertension, massive splenomegaly, and variceal bleeding. It is estimated that about 85% of people with NCPF have repeated episodes of variceal bleeding. Diagnosis Hallmark of the disease is thrombosis/ sclerosis of branches of portal vein The portal vein or hepatic portal vein (HPV) is a blood vessel that carries blood from the gastrointestinal tract, gallbladder, pancreas and spleen to the liver. This blood contains nutrients and toxins extracted from digested contents. Approxima .... Vessels formed are often termed as mesangiosinusoids or periportal cavernoma. Treatment References External links {{Medical resources , ICD10 = , ICD9 = , ICDO = , OMIM = 617068 , DiseasesDB = , Med ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |