|
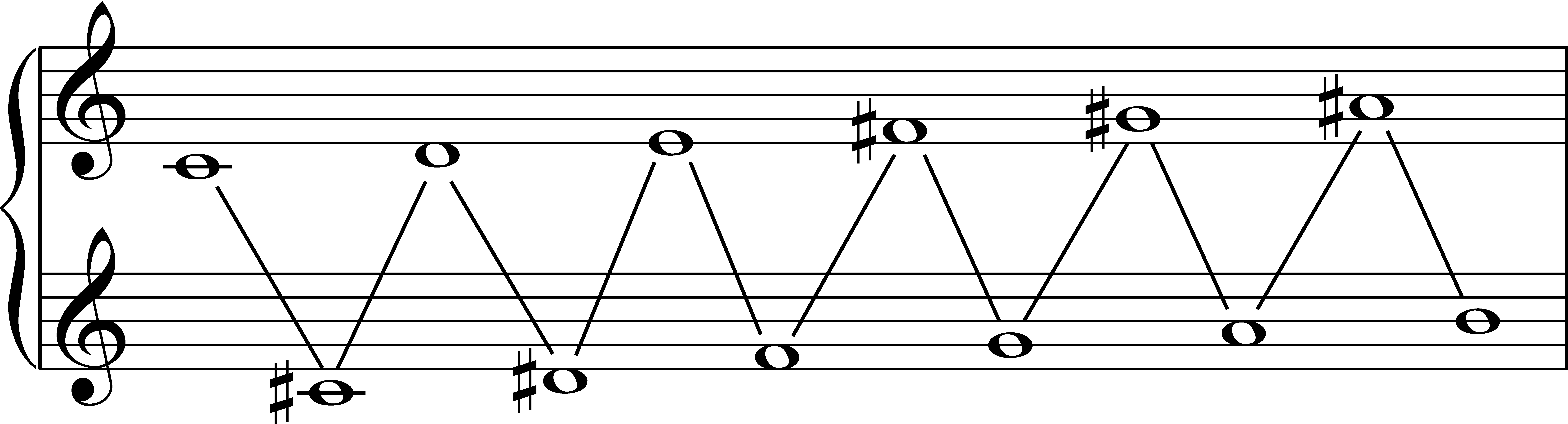
Bebop Dominant Scale
Bebop scale is a term referring to the practice of adding a note (typically a chromatic passing tone) to any common seven tone scale in order to make it an eight tone scale. Having eight notes enables the primary chord tones to continuously fall on the on-beats when the scale is played sequentially. This is unlike common seven note scales in which the chord tones do not all naturally fall on the on-beats due to an odd number of notes. These bebop scales are frequently used in jazz improvisation. Jazz educator David Baker nicknamed these scales the "bebop scales" because they were used often by jazz artists from the Bebop Era. These artists include Charlie Christian, Charlie Parker, Bud Powell, and Dizzy Gillespie, to name a few. In general, bebop scales consist of traditional scales with an added passing tone, and when the scale is played from any chord tone and placed on any on-beat, then all other chord tones will also continuously fall on on-beats. Chord tones on on-beats are ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptatonic Scale
A heptatonic scale is a musical scale (music), scale that has seven pitch (music), pitches, or musical tone, tones, per octave. Examples include: * the #Diatonic scale, diatonic scale; including the major scale and its modes (notably the natural minor scale, or Aeolian mode) * the #Melodic minor scale, melodic minor scale, like the Aeolian mode but with raised 6th and 7th ascending * the #Harmonic minor scale, harmonic minor scale, like the Aeolian mode but with raised 7th * the harmonic major scale, like the major scale but with lowered 6th Indian classical theory postulates seventy-two seven-tone scale types, collectively called ''#Melakarta, melakarta'' or ''#Thaat, thaat'', whereas others postulate twelve or ten (depending on the theorist) seven-tone scale types. Several heptatonic scales in Western culture, Western, Roman, Spanish, Hungarian, and Greek music can be analyzed as juxtapositions of Tetrachord#Romantic era, tetrachords.Dupré, Marcel (1962). ''Cours Complet d'Impr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sixth Chord
The term ''sixth chord'' refers to two different kinds of Chord (music), chord, one in classical music and the other in modern popular music. The original meaning of the term is a ''chord in first inversion'', in other words with its third (chord), third in the bass note, bass and its root (chord), root a Interval (music), sixth above it. This is how the term is still used in classical music today, and in this sense it is called also a chord of the sixth. In modern popular music, a sixth chord is any triad (music), triad with an added sixth above the root as a Factor (chord), chord factor. This was traditionally (and in classical music is still today) called an ''Added tone chord, added sixth chord'' or ''triad with added sixth'' since Jean-Philippe Rameau (''sixte ajoutée'') in the 18th century. It is not common to designate Inverted chord, chord inversions in popular music, so there is no need for a term designating the first inversion of a chord, and so the term ''sixth chord'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jazz Terminology
Jazz is a music genre that originated in the African-American communities of New Orleans, Louisiana, in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. Its roots are in blues, ragtime, European harmony, African rhythmic rituals, spirituals, hymns, marches, vaudeville song, and dance music. Since the 1920s Jazz Age, it has been recognized as a major form of musical expression in traditional and popular music. Jazz is characterized by swing and blue notes, complex chords, call and response vocals, polyrhythms and improvisation. As jazz spread around the world, it drew on national, regional, and local musical cultures, which gave rise to different styles. New Orleans jazz began in the early 1910s, combining earlier brass band marches, French quadrilles, biguine, ragtime and blues with collective polyphonic improvisation. However, jazz did not begin as a single musical tradition in New Orleans or elsewhere. In the 1930s, arranged dance-oriented swing big bands, Kansas City jazz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heptatonic Scales
A heptatonic scale is a musical scale that has seven pitches, or tones, per octave. Examples include: * the diatonic scale; including the major scale and its modes (notably the natural minor scale, or Aeolian mode) * the melodic minor scale, like the Aeolian mode but with raised 6th and 7th ascending * the harmonic minor scale, like the Aeolian mode but with raised 7th * the harmonic major scale, like the major scale but with lowered 6th Indian classical theory postulates seventy-two seven-tone scale types, collectively called '' melakarta'' or ''thaat'', whereas others postulate twelve or ten (depending on the theorist) seven-tone scale types. Several heptatonic scales in Western, Roman, Spanish, Hungarian, and Greek music can be analyzed as juxtapositions of tetrachords.Dupré, Marcel (1962). ''Cours Complet d'Improvisation a l'Orgue'', v.2, p. 35, trans. John Fenstermaker. Paris: Alphonse Leduc. ASIN: B0006CNH8E. All heptatonic scales have all intervals present in their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord-scale System
The chord-scale system is a method of matching, from a list of possible chord (music), chords, a list of possible scale (music), scales.Mervyn Cooke, David Horn (2003). ''Cambridge Companions to Music, The Cambridge Companion to Jazz'', p.266. . The system has been widely used since the 1970s. However, the majority of older players used the chord tone/chord arpeggio method. The system is an example of the difference between the treatment of consonance and dissonance, dissonance in jazz and classical harmony: "Classical treats all notes that don't belong to the chord ... as potential dissonances to be resolution (music), resolved. ... Non-classical harmony just tells you which note in the scale to [potentially] avoid-note, avoid ... meaning that all the others are okay". The chord-scale system may be compared with other common methods of improvisation, first, the older traditional chord tone/chord arpeggio method, and where one scale on one root note is used throughout all chords ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Whole Tone Scale
In music, a whole-tone scale is a scale (music), scale in which each Musical note, note is separated from its neighbors by the interval (music), interval of a whole tone. In twelve-tone equal temperament, there are only two Complement (music)#Aggregate complementation, complementary whole-tone scales, both six-note or ''Hexatonic scale, hexatonic'' scales. A single whole-tone scale can also be thought of as a "six-tone equal temperament". : : The whole-tone scale has no leading tone and because all tones are the same distance apart, "no single tone stands out, [and] the scale creates a blurred, indistinct effect". This effect is especially emphasised by the fact that triad (music), triads built on such scale tones are all augmented triads. Indeed, all six tones of a whole-tone scale can be played simply with two augmented triads whose roots are a major second apart. Since they are symmetric scale, symmetrical, whole-tone scales do not give a strong impression of the tonic ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mode Of Limited Transposition
Modes of limited transposition are musical modes or scales that fulfill specific criteria relating to their symmetry and the repetition of their interval groups. These scales may be transposed to all twelve notes of the chromatic scale, but at least two of these transpositions must result in the same pitch classes, thus their transpositions are "limited". They were compiled by the French composer Olivier Messiaen, and published in his book ''La technique de mon langage musical'' ("The Technique of my Musical Language"). Technical criteria There are two complementary ways to view the modes: considering their possible transpositions, and considering the different modes contained within them. Definition by chromatic transposition Transposing the diatonic major scale up in semitones results in a different set of notes being used each time. For example, C major consists of C, D, E, F, G, A, B, and the scale a semitone higher (D major) consists of D, E, F, G, A, B, C. By transposing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeolian Mode
The Aeolian mode is a musical mode or, in modern usage, a diatonic scale also called the natural minor scale. On the piano, using only the white keys, it is the scale that starts with A and continues to the next A only striking white keys. Its ascending interval form consists of a ''key note, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step, half step, whole step, whole step.'' That means that, in A aeolian (or A minor), a scale would be played beginning in A, move up a whole step (two piano keys) to B, move up a half step (one piano key) to C, then up a whole step to D, a whole step to E, a half step to F, a whole step to G, and a final whole step to a high A. : History The word ''Aeolian'', like the names for the other ancient Greek ''tonoi'' and ''harmoniai'', is an ethnic designation: in this case, for the inhabitants of Aeolis (), a coastal district of Anatolia. In the music theory of ancient Greece, it was an alternative name (used by some later writers, such as Cleoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Minor Scale
In Western classical music theory, the minor scale refers to three scale patterns – the natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode), the harmonic minor scale, and the melodic minor scale (ascending or descending). These scales contain all three notes of a minor triad: the root, a minor third (rather than the major third, as in a major triad or major scale), and a perfect fifth (rather than the diminished fifth, as in a diminished scale or half diminished scale). Minor scale is also used to refer to other scales with this property, such as the Dorian mode or the minor pentatonic scale (see other minor scales below). Natural minor scale Relationship to relative major A natural minor scale (or Aeolian mode) is a diatonic scale that is built by starting on the sixth degree of its relative major scale. For instance, the A natural minor scale can be built by starting on the 6th degree of the C major scale: : Because of this, the key of A minor is called the ''relativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roni Ben-Hur
Roni Ben-Hur () is an Israeli jazz guitarist who immigrated to the United States in 1985. His parents were Tunisian-Jewish from Tunisia. Biography Roni Bohobza grew up in Dimona, Israel. He is the youngest of seven children and one of two born after the family emigrated from Tunisia in 1955. His surname was legally changed to Ben-Hur via ritual at age 10. When he was eleven, he started playing guitar. He learned about jazz from a high school friend's record collection. In Israel he performed in clubs and at weddings and bar mitzvahs until he had enough money to move to the U.S. He arrived in New York City in 1985, spending time at Barry Harris's Jazz Cultural Theater. He took lessons from Harris, then became a member of his band. Ben-Hur's experience as an educator dates back to 1981 in Israel. In the U.S. he started jazz music programs at Professional Performing Arts School, the Coalition School for Social Change, and at the Lucy Moses School. At the request of Bette Midler, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harmonic Minor Scale
The harmonic minor scale (or Aeolian ♮7 scale) is a Scale (music), musical scale derived from the natural minor scale, with the minor seventh degree raised by one semitone to a major seventh, creating an augmented second between the sixth and seventh degrees. : Thus, a harmonic minor scale is represented by the following notation: : 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 A harmonic minor scale can be built by lowering the 3rd and 6th degrees of the parallel major scale by one semitone. Because of this construction, the 7th degree of the harmonic minor scale functions as a leading tone to the Tonic (music), tonic because it is a ''semitone'' lower than the tonic, rather than a ''whole tone'' lower than the tonic as it is in natural minor scales. The Interval (music), intervals between the notes of a harmonic minor scale follow the sequence below: : whole, half, whole, whole, half, augmented second, half While it evolved primarily as a basis for chords, the harmonic minor with its augment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Passing Note
A nonchord tone (NCT), nonharmonic tone, or embellishing tone is a note in a piece of music or song that is not part of the implied or expressed chord set out by the harmonic framework. In contrast, a chord tone is a note that is a part of the functional chord. Nonchord tones are most often discussed in the context of the common practice period of classical music, but the term can also be used in the analysis of other types of tonal music, such as Western popular music. Nonchord tones are often categorized as ''accented non-chord tones'' and ''unaccented non-chord tones'' depending on whether the dissonance occurs on an accented or unaccented beat (or part of a beat). Over time, some musical styles assimilated chord types outside of the common-practice style. In these chords, tones that might normally be considered nonchord tones are viewed as chord tones, such as the seventh of a minor seventh chord. For example, in 1940s-era bebop jazz, an F played with a C chord would be co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |