|
Beatrice Cutler
Beatrice Cutler (1861–1942) was a matron who campaigned for State Registration of Nurses in the UK and was founding Secretary of the National Council of Nurses of the United Kingdom. Training Cutler was born 25 August 1861 in the Bloomsbury area of London. From 1885 to 1888 Cutler was a probationer nurse at St Bartholomew's Hospital, London where she successfully completed three years certified nurse training in 1888, becoming Staff Nurse there from May–November 1888. Cutler was trained by Ethel Gordon Fenwick the then Matron at St Bartholomew's, who was to be a great influence in her nursing career. Early career in Egypt In December 1888 Cutler relocated to Egypt for what she considered "the great adventure of her life" as Sister at Kasr-el-Aini Hospital, Cairo, until 1892. Between 1892 and 1898 she was Superintendent, Medical School for Girls Kasr-el-Aini Hospital, Cairo. The hospital had been founded in 1837, but with Britain's invasion of Egypt in 1882, there was th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Council Of Nurses Of The United Kingdom
The National Council of Nurses Great Britain and Ireland (NCN) was created in 1908 as a national representative body at the International Council of Nurses (ICN). It fulfilled this role until it amalgamated with the Royal College of Nursing in 1963. History Creation On 1 July 1899, Ethel Gordon Fenwick proposed that an International Council of Nurses (ICN), a federation of national nursing associations, should be created. She made her proposal at the annual conference of the Matron’s Council of Britain and Ireland. To represent the United Kingdom internationally, a national council was needed. As founder of the Royal British Nurses' Association in 1887, Fenwick lobbied nursing organisations such as the hospital nurses' leagues and the Association of Hospital Matrons to form a national council from as early as 1899. By 1904 Fenwick and Isla Stewart had managed to create the Provisional Committee of the National Council of Nurses of Great Britain and Ireland (NCN). Thi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I or the First World War (28 July 1914 – 11 November 1918), also known as the Great War, was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War I, Allies (or Entente) and the Central Powers. Fighting took place mainly in European theatre of World War I, Europe and the Middle Eastern theatre of World War I, Middle East, as well as in parts of African theatre of World War I, Africa and the Asian and Pacific theatre of World War I, Asia-Pacific, and in Europe was characterised by trench warfare; the widespread use of Artillery of World War I, artillery, machine guns, and Chemical weapons in World War I, chemical weapons (gas); and the introductions of Tanks in World War I, tanks and Aviation in World War I, aircraft. World War I was one of the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflicts in history, resulting in an estimated World War I casualties, 10 million military dead and more than 20 million wounded, plus some 10 million civilian de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1861 Births
This year saw significant progress in the Unification of Italy, the outbreak of the American Civil War, and the Emancipation reform of 1861, emancipation reform abolishing serfdom in the Russian Empire. Events January * January 1 ** Benito Juárez captures Mexico City. ** The first steam-powered carousel is recorded, in Bolton, England. * January 2 – Frederick William IV of Prussia, Friedrich Wilhelm IV of Prussia dies, and is succeeded by Wilhelm I of Germany, Wilhelm I. American Civil War: ** January 3 – Delaware votes not to secede from the United States, Union. ** January 9 – Mississippi in the American Civil War, Mississippi becomes the second state to secede from the Union. ** January 10 – Florida in the American Civil War, Florida secedes from the Union. ** January 11 – Alabama in the American Civil War, Alabama secedes from the Union. ** January 12 – Major Robert Anderson (Union officer), Robert Anderson sends dispatches to Was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Nurses
British may refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories and Crown Dependencies. * British national identity, the characteristics of British people and culture * British English, the English language as spoken and written in United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland and, more broadly, throughout the British Isles * Celtic Britons, an ancient ethno-linguistic group * Brittonic languages, a branch of the Insular Celtic language family (formerly called British) ** Common Brittonic, an ancient language Other uses *People or things associated with: ** Great Britain, an island ** British Isles, an island group ** United Kingdom, a sovereign state ** British Empire, a historical global colonial empire ** Kingdom of Great Britain (1707–1800) ** United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland (1801–1922) * British Raj, colonial India under the British Empire * British Hong Kong, colonial Ho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greater Paris University Hospitals
Greater Paris University Hospitals ( , AP-HP) is the university hospital trust operating in Paris and its surroundings. It is the largest hospital system in Europe and one of the largest in the world. It employs more than 90,000 people in 38 teaching hospitals and receives more than 10 million annual patient visits. AP-HP is organized in 6 hospital local trusts called "GHU", each associated to a university to offer integrative care to its population. It is affiliated with Paris Cité University (16 teaching hospitals), Sorbonne University (7 teaching hospitals), Saclay University (6 teaching hospitals), the University of Créteil (5 teaching hospitals), Sorbonne Paris North University (3 teaching hospitals) and their colleges of medicine, odontology, and pharmacy. As a teaching hospitals network, AP-HP trust is in charge of training healthcare professionals and doctors, and plays a prominent role in French healthcare research alongside Inserm. History Succeeding to the ''con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mons Star
The 1914 Star, colloquially known as the Mons Star, is a British First World War campaign medal for service in France or Belgium between 5 August and 22 November 1914. Institution The 1914 Star was authorised under Special Army Order no. 350 in November 1917 and by an Admiralty Fleet Order in January 1918, for award to officers and men of the British and Indian Expeditionary Forces who served in France or Belgium between 5 August and midnight of 22–23 November 1914. The former date is the day after Britain's declaration of war against the Central Powers, and the closing date marks the end of the First Battle of Ypres. Altogether 378,000 1914 Stars were awarded. Clasp A "5th AUG.–22nd NOV. 1914" clasp was instituted in 1919, as published in Army Order no. 361 of 16 October 1919. The clasp, together with two small silver roses, was awarded to those who had served under fire or who had operated within range of enemy mobile artillery in France or Belgium during the period betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
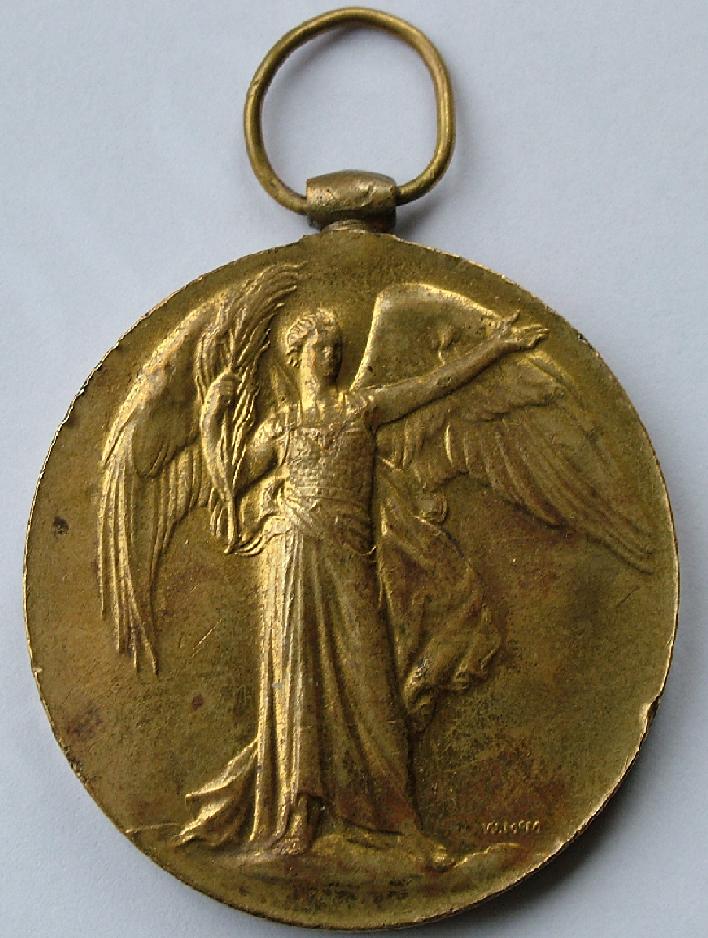
Victory Medal (United Kingdom)
The Victory Medal (also called the Inter-Allied Victory Medal) is a United Kingdom and British Empire First World War campaign medal. The award of a common allied campaign medal was recommended by an inter-allied committee in March 1919. Each allied nation would design a 'Victory Medal' for award to their own nationals, all issues having certain common features, including a winged figure of victory on the obverse and the same ribbon. Fourteen countries finally awarded the medal. Eligibility The Victory Medal (United Kingdom) was issued to all those who received the 1914 Star or the 1914–15 Star, and to most of those who were awarded the British War Medal. It was not awarded singly. To qualify, recipients need to have served in the armed forces of the United Kingdom or the British Empire, or with certain recognised voluntary organisations, and have entered any theatre of war between 5 August 1914 and 11 November 1918. While home service did not count, United Kingdom based me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British War Medal
The British War Medal is a campaign medal of the United Kingdom which was awarded to officers and men and women of British and Imperial forces for service in the First World War. Two versions of the medal were produced. About 6.5 million were struck in silver and 110,000 in bronze, the latter awarded to, among others, the Chinese, Maltese and Indian Labour Corps. Institution The British War Medal was instituted on 26 July 1919 for award to those who had rendered service between 5 August 1914, the day following the British declaration of war against the German Empire, and the armistice of 11 November 1918, both dates inclusive.The National Archives – British Army medal index cards 1914–1920 (Access date 24 June 2018) Consideration was given to the award of cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second World War
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surrey
Surrey () is a Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South East England. It is bordered by Greater London to the northeast, Kent to the east, East Sussex, East and West Sussex to the south, and Hampshire and Berkshire to the west. The largest settlement is Woking. The county has an area of and a population of 1,214,540. Much of the north of the county forms part of the Greater London Built-up Area, which includes the Suburb, suburbs within the M25 motorway as well as Woking (103,900), Guildford (77,057), and Leatherhead (32,522). The west of the county contains part of Farnborough/Aldershot built-up area, built-up area which includes Camberley, Farnham, and Frimley and which extends into Hampshire and Berkshire. The south of the county is rural, and its largest settlements are Horley (22,693) and Godalming (22,689). For Local government in England, local government purposes Surrey is a non-metropolitan county with eleven districts. The county historically includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limpsfield
Limpsfield is a village and civil parish in Surrey, England, at the foot of the North Downs close to Oxted railway station and the A25 road, A25.Online map distance reference tool Retrieved 27 April 2012 The composer Frederick Delius, orchestral conductor Sir Thomas Beecham and clarinettist Jack Brymer are buried in the village churchyard. The village contains 89 listed buildings. History The village lay within the Anglo-Saxons, Anglo-Saxon Tandridge (hundred), Tandridge hundred (county subdivision), hundred. Limpsfield appears in the Domesday Book of 1086 as ''Limenesfeld''. It was held by the Abbot of Battle Abbey, Sussex. Its Domesday assets were: 1 church, 1 Mill (grinding), mill worth 2s, 19 ploughs, 1 fishery, of meadow, woodland worth 150 hog (swine), hogs, 2 stone quarry, quarries, and 3 ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Nursing Council
General Nursing Councils for England & Wales, Scotland, and Ireland (then one country and part of the United Kingdom) were established by three country specific Nurses Registration Act 1919, Nurses Registration Acts 1919. Each General Nursing Council (GNC) was responsible for deciding the rules for: admission to the register; for the conditions of training of nurses; for qualifying examinations, for discipline, and the uniform of badge of nurses on the register. The composition of the first GNCs were to include: 2 appointees of the Privy Council (United Kingdom), Privy Council (with no associations to medicine or nursing), 2 appointees of the Board of Education (United Kingdom), Board of Education, 5 appointees of the Ministry of Health (United Kingdom), Ministry of Health and 16 nurses to be appointed by the Minister of Health (United Kingdom), Minister of Health. The Acts stated that the first Councils' term should be no longer than three years and the subsequent 16 nurses ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |