|
Beatrice (drug)
Beatrice, also known as 4-methyl-2,5-dimethoxy-''N''-methylamphetamine or as ''N''-methyl-DOM, MDOM, or MDO-D, is a lesser-known psychoactive drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and DOx families. It is a substituted methamphetamine and a homolog of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine (DOM). Beatrice was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. Use and effects In Shulgin's book ''PiHKAL'', the minimum dosage is listed as 30mg, and the duration is listed as 6 to 10hours. Beatrice produces a vague feeling of openness and receptiveness, and causes a stimulative effect. It also causes diarrhea. Pharmacology Beatrice shows affinity for serotonin receptors. Its affinities (Ki) were 415nM for the 5-HT2 receptor and 3,870nM for the 5-HT1 receptor. The affinity of Beatrice for the serotonin 5-HT2 receptor was about 4-fold lower than that of DOM. Functional activities were not reported. Analogues Analogues of Beatrice include ''N''-methyl-DOI (''N''-Me-DOI), ''N''-methyl-DOB, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psychoactive Drug
A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, mind-altering drug, consciousness-altering drug, psychoactive substance, or psychotropic substance is a chemical substance that alters psychological functioning by modulating central nervous system activity. Psychoactive and psychotropic drugs both affect the brain, with psychotropics sometimes referring to psychiatric drugs or high-abuse substances, while “drug” can have negative connotations. Designer drug, Novel psychoactive substances are designer drugs made to mimic illegal ones and bypass laws. Psychoactive drug use dates back to prehistory for medicinal and consciousness-altering purposes, with evidence of widespread cultural use. Many animals intentionally consume psychoactive substances, and some traditional legends suggest animals first introduced humans to their use. Psychoactive substances are used across cultures for purposes ranging from medicinal and therapeutic treatment of Mental disorder, mental disorders and pain, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
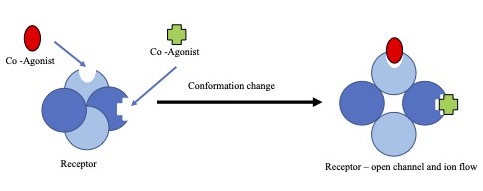
Functional Activity
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists can be activated by either ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOx (psychedelics)
4-Substituted-2,5-dimethoxyamphetamines (DO''x'') is a chemical class of substituted amphetamine derivatives featuring methoxy groups at the 2- and 5- positions of the phenyl ring, and a substituent such as alkyl or halogen at the 4- position of the phenyl ring. They are 4-substituted derivatives of 2,5-dimethoxyamphetamine (2,5-DMA, DOH) and are structurally related to the naturally occurring phenethylamine psychedelic mescaline. The most well-known DOx drugs are DOM, DOI, DOB, DOET, and DOC. DOI is widely used in scientific research. DOM has been used as a recreational drug, while DOET was an experimental pharmaceutical drug. Most compounds of this class are potent and long-lasting psychedelic drugs, and act as selective 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptor agonists. A few bulkier derivatives such as DOAM have similarly high affinity for 5-HT2 receptors but have reduced activational efficacy and do not produce psychedelic effects. DOI has been found to have ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Phenethylamine
Substituted phenethylamines (or simply phenethylamines) are a chemical class of organic compounds that are based upon the phenethylamine structure; the class is composed of all the derivative (chemistry), derivative compounds of phenethylamine which can be formed by replacing, or substitution reaction, substituting, one or more hydrogen atoms in the phenethylamine core structure with substituents. Phenylethylamines are also generally found to be central nervous system stimulants with many also being entactogens/empathogens, and hallucinogens. Structural classification The structural formula of any substituted phenethylamine contains a phenyl group, phenyl ring that is joined to an amino group, amino (NH) group via a two-carbon substituent, sidechain. Hence, any substituted phenethylamine can be classified according to the substitution of hydrogen atom, hydrogen (H) atoms on phenethylamine's phenyl ring, sidechain, or amino group with a moiety (chemistry), specific group of at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOET
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-ethylamphetamine (DOET) is a psychedelic drug of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and DOx families. It is closely related to DOM and is a synthetic analogue of the naturally occurring phenethylamine psychedelic mescaline. The drug acts as a selective agonist of the serotonin 5-HT2 receptors, including of the serotonin 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B, and 5-HT2C receptors. DOET was first discovered by Alexander Shulgin in the 1960s. It was clinically studied at low and sub-hallucinogenic doses for potential use as a pharmaceutical drug acting as a " psychic energizer" by Dow Chemical Company in the 1960s. However, its development was terminated after DOM emerged as a street drug and caused a public health crisis in San Francisco in 1967. Nonetheless, DOET's effects at low doses were extensively characterized in small clinical trials. The psychedelic effects of DOET at higher doses were subsequently described by Shulgin in his book PiHKAL in 1991. DOET is taken by mouth. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intrinsic Activity
Intrinsic activity (IA) and efficacy (Emax) refer to the relative ability of a drug- receptor complex to produce a maximum functional response. This must be distinguished from the affinity, which is a measure of the ability of the drug to bind to its molecular target, and the EC50, which is a measure of the potency of the drug and which is proportional to both efficacy and affinity. This use of the word "efficacy" was introduced by Stephenson (1956) to describe the way in which agonist An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an R ...s vary in the response they produce, even when they occupy the same number of receptors. High efficacy agonists can produce the maximal response of the receptor system while occupying a relatively low proportion of the receptors in that system. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DOI (drug)
2,5-Dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine (DOI) is a psychedelic drug of the amphetamine and 4-substituted-2,5-dimethoxyamphetamine (DOx) families. It is relatively little-used as a recreational drug but is frequently used in scientific research in the study of psychedelics and serotonin receptors. DOI acts as a potent serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonist, including of the serotonin 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors. The compound has a stereocenter, and ''R''-(−)-DOI is the more active stereoisomer. 125I">sup>125I''R''-(−)-DOI is used as a radioligand and indicator of the presence of serotonin 5-HT2A receptors in studies. DOI's effects have been compared to LSD, although there are differences that experienced users can distinguish. Besides the longer duration of DOI compared to LSD, the trip tends to be more energetic than an LSD trip, with more body load and a different subjective visual experience. The after effects include residual stimulation and difficulty sleeping, which, depen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-HT2A Receptor
The 5-HT2A receptor is a subtype of the 5-HT2 receptor, 5-HT2 receptor that belongs to the serotonin receptor family and functions as a GPCR, G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR). It is a cell surface receptor that activates multiple intracellular signalling cascades. Like all 5-HT2 receptors, the 5-HT2A receptor is coupled to the Gq protein, Gq/G11 signaling pathway. It is the primary excitatory receptor subtype among the serotonin-responsive GPCRs. The 5-HT2A receptor was initially noted for its central role as the primary target of serotonergic psychedelic drugs such as LSD and psilocybin mushrooms. It later regained research prominence when found to mediate, at least in part, the effects of many antipsychotic drugs, particularly atypical antipsychotic, atypical antipsychotics. Downregulation of post-synaptic 5-HT2A receptors is an adaptive response triggered by chronic administration of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and atypical antipsychotics. Elevated 5-HT2A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin (), also known as 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), is a monoamine neurotransmitter with a wide range of functions in both the central nervous system (CNS) and also peripheral tissues. It is involved in mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. In the CNS, serotonin regulates mood, appetite, and sleep. Most of the body's serotonin—about 90%—is synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract by enterochromaffin cells, where it regulates intestinal movements. It is also produced in smaller amounts in the brainstem's raphe nuclei, the skin's Merkel cells, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells, and taste receptor cells of the tongue. Once secreted, serotonin is taken up by platelets in the blood, which release it during clotting to promote vasoconstriction and platelet aggregation. Around 8% of the body's serotonin is stored in platelets, and 1–2% is found in the CNS. Serotonin acts as both a vasoconstrictor and vas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a Receptor (biochemistry), receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are Cell (biology), cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an Receptor antagonist, antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology The word originates from the Ancient Greek, Greek word (''agōnistēs''), "contestant; champion; rival" < (''agōn''), "contest, combat; exertion, struggle" < (''agō''), "I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive." Types of agonists Receptor (biochemistry), Receptors can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as hormones and neurotransmitters) or exogenous agonists (such as medication, drugs), resulting in a biological response. A physiological agonism an ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potency (pharmacology)
In pharmacology, potency or biological potency is a measure of a drug's biological activity expressed in terms of the dose required to produce a pharmacological effect of given intensity. A highly potent drug (e.g., fentanyl, clonazepam, risperidone, benperidol, bumetanide) evokes a given response at low concentrations, while a drug of lower potency (e.g. morphine, alprazolam, ziprasidone, haloperidol, furosemide) evokes the same response only at higher concentrations. Higher potency does not necessarily mean greater effectiveness nor more side effects nor less side effects. Types of potency The International Union of Basic and Clinical Pharmacology (IUPHAR) has stated that "potency is an imprecise term that should always be further defined", and lists of types of potency as follows: Miscellaneous Lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) is one of the most potent psychoactive drug A psychoactive drug, psychopharmaceutical, mind-altering drug, consciousness-altering drug, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IDNNA
IDNNA, also known as 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodo-''N,N''-dimethylamphetamine or as ''N'',''N''-dimethyl-DOI, is a lesser-known psychedelic drug and a substituted amphetamine. It is also the ''N,N''-dimethyl analog of DOI. IDNNA was first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin. In his book ''PiHKAL'', the minimum dosage is listed as 2.6 mg, and the duration unknown. IDNNA produces few to no effects. Very little data exists about the pharmacological properties, metabolism, and toxicity of IDNNA. Society and culture Legal status United Kingdom This substance is a Class A drug in the Drugs controlled by the UK Misuse of Drugs Act The Misuse of Drugs Act 1971 (c. 38) is an act of the Parliament of the United Kingdom. It represents action in line with treaty commitments under the Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs, the Convention on Psychotropic Substances, and the Un .... See also * Beatrice (''N''-methyl-DOM) * ''N''-Methyl-DOI * Methyl-DOB (''N''-methyl-DOB) * ''N''-Methyl-2C- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |